KNN实战Iris数据集
关于KNN的相关理论知识请查看:KNN
关于Iris数据集的相关信息可查看我的上一篇博客:感知机算法实战Iris数据集
接下来的实战我们将使用sklearn库
代码实战
首先,我们还是先导入数据集
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
iris = load_iris()
iris.data.shape(150, 4)
sklearn的datasets都有详细的数据集信息,我们可以把这些信息打印出来查看
print(iris.DESCR)Iris Plants Database
Notes
Data Set Characteristics:
:Number of Instances: 150 (50 in each of three classes)
:Number of Attributes: 4 numeric, predictive attributes and the class
:Attribute Information:
- sepal length in cm
- sepal width in cm
- petal length in cm
- petal width in cm
- class:
- Iris-Setosa
- Iris-Versicolour
- Iris-Virginica
:Summary Statistics:============== ==== ==== ======= ===== ==================== Min Max Mean SD Class Correlation ============== ==== ==== ======= ===== ==================== sepal length: 4.3 7.9 5.84 0.83 0.7826 sepal width: 2.0 4.4 3.05 0.43 -0.4194 petal length: 1.0 6.9 3.76 1.76 0.9490 (high!) petal width: 0.1 2.5 1.20 0.76 0.9565 (high!) ============== ==== ==== ======= ===== ==================== :Missing Attribute Values: None :Class Distribution: 33.3% for each of 3 classes. :Creator: R.A. Fisher :Donor: Michael Marshall (MARSHALL%[email protected]) :Date: July, 1988This is a copy of UCI ML iris datasets.
http://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/datasets/IrisThe famous Iris database, first used by Sir R.A Fisher
This is perhaps the best known database to be found in the
pattern recognition literature. Fisher’s paper is a classic in the field and
is referenced frequently to this day. (See Duda & Hart, for example.) The
data set contains 3 classes of 50 instances each, where each class refers to a
type of iris plant. One class is linearly separable from the other 2; the
latter are NOT linearly separable from each other.References
- Fisher,R.A. “The use of multiple measurements in taxonomic problems”
Annual Eugenics, 7, Part II, 179-188 (1936); also in “Contributions to
Mathematical Statistics” (John Wiley, NY, 1950).- Duda,R.O., & Hart,P.E. (1973) Pattern Classification and Scene Analysis.
(Q327.D83) John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 0-471-22361-1. See page 218.- Dasarathy, B.V. (1980) “Nosing Around the Neighborhood: A New System
Structure and Classification Rule for Recognition in Partially Exposed
Environments”. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine
Intelligence, Vol. PAMI-2, No. 1, 67-71.- Gates, G.W. (1972) “The Reduced Nearest Neighbor Rule”. IEEE Transactions
on Information Theory, May 1972, 431-433.- See also: 1988 MLC Proceedings, 54-64. Cheeseman et al”s AUTOCLASS II
conceptual clustering system finds 3 classes in the data.- Many, many more …
按照一般机器学习的套路,我们将整个数据分成训练集和测试集,75%的训练集和25%的测试集
from sklearn.cross_validation import train_test_split
X_train,X_test,Y_train,Y_test = train_test_split(iris.data,iris.target,test_size=0.25,random_state=33)下一步,我们将数据进行标准化处理,然后导入KNN模型,进行训练(这些都是套路)
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
ss = StandardScaler()
X_train = ss.fit_transform(X_train)
X_test = ss.fit_transform(X_test)
knc = KNeighborsClassifier()
knc.fit(X_train,Y_train)
y_predict = knc.predict(X_test)最后,我们来检验一下模型的好坏
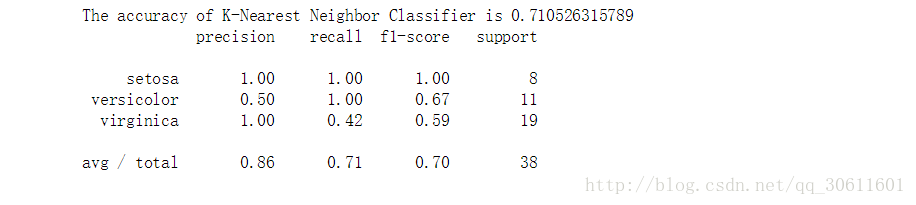
print('The accuracy of K-Nearest Neighbor Classifier is',knc.score(X_test,Y_test))
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report
print(classification_report(Y_test,y_predict,target_names=iris.target_names))代码参考:《Python机器学习及实践:从零开始通往Kaggle竞赛之路》