Gated Recurrent Unit (GRU)
Outline
Background
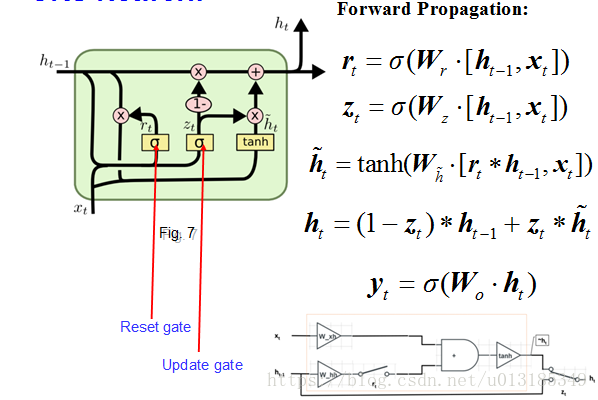
GRU Network
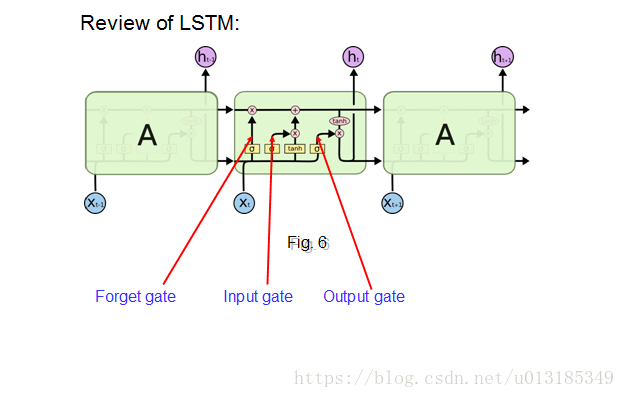
GRU vs. LSTM
Experiment
References
Background
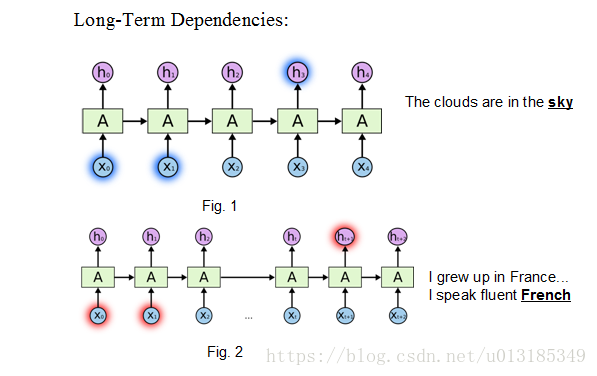
A gated recurrent unit (GRU) was proposed by Cho et al. [2014] to make each recurrent unit to adaptively capture dependencies of different time scales.
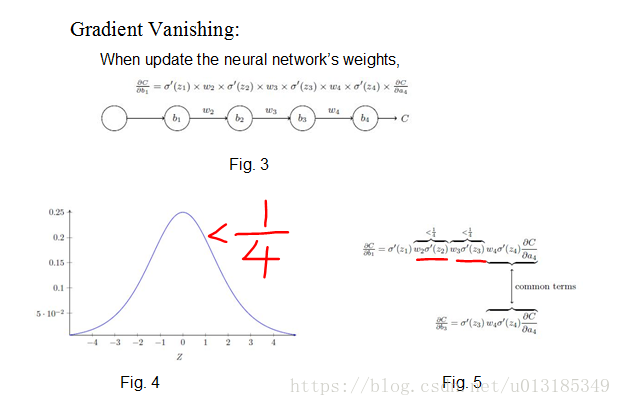
Solving problems existed in RNN: Gradient Vanishing.
Example:
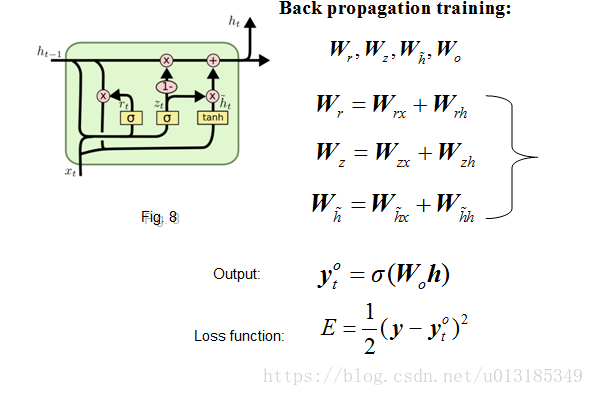
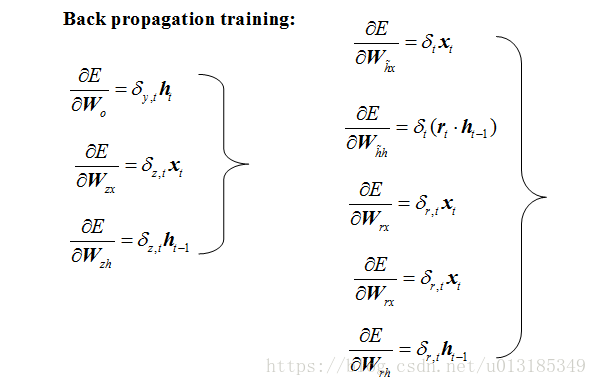
GRU Network
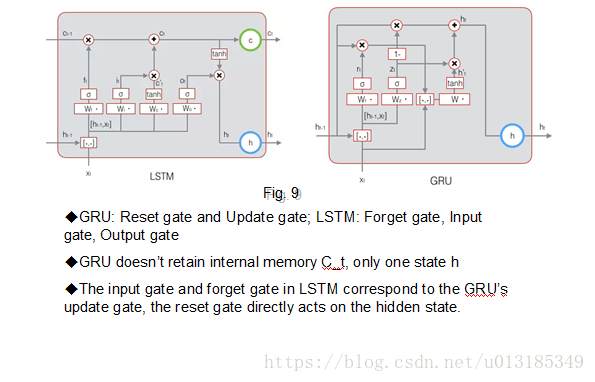
GRU vs. LSTM
Code Example:
import tensorflow as tf
x = tf.constant([[1]], dtype = tf.float32)
…
state0_lstm = lstm_cell.zero_state(1,dtype=tf.float32)
output,state = lstm_cell(x,state0_lstm)
state0_gru = gru_cell.zero_state(1,dtype=tf.float32)
output2,state2 = gru_cell(x,state0_gru)
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init)
print(sess.run(output))
print(sess.run(state))
print(sess.run(output2))
print(sess.run(state2))
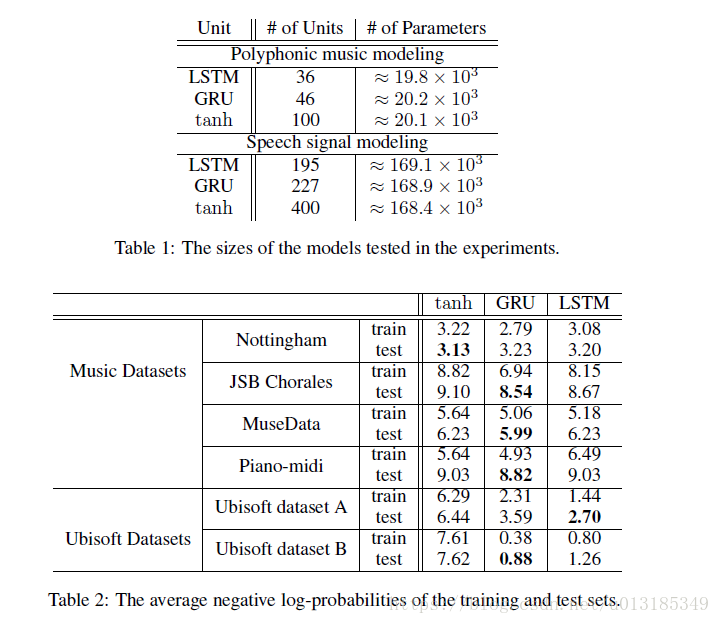
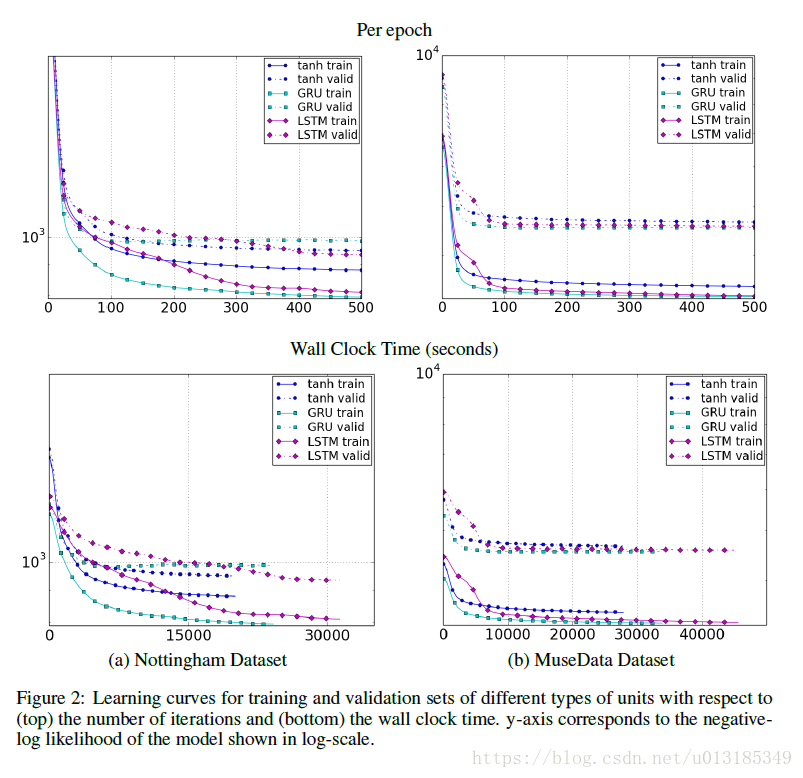
Experiment
References
1. Empirical Evaluation of Gated Recurrent Neural Networks on Sequence Modeling
2. Learned-norm pooling for deep feedforward and recurrent neural networks
3. Long short-term memory