下面是list中的自带的sort,因为list的迭代器是双向迭代器,所有不能使用STL算法中的sort(随机访问迭代器才能)
template <class _Tp, class _Alloc> template <class _StrictWeakOrdering>
void list<_Tp, _Alloc>::sort(_StrictWeakOrdering __comp)
{
// Do nothing if the list has length 0 or 1.
if (_M_node->_M_next != _M_node && _M_node->_M_next->_M_next != _M_node) {
list<_Tp, _Alloc> __carry;
list<_Tp, _Alloc> __counter[64];
int __fill = 0;
while (!empty()) {
__carry.splice(__carry.begin(), *this, begin());
int __i = 0;
while(__i < __fill && !__counter[__i].empty()) {
__counter[__i].merge(__carry, __comp);
__carry.swap(__counter[__i++]);
}
__carry.swap(__counter[__i]);
if (__i == __fill) ++__fill;
}
for (int __i = 1; __i < __fill; ++__i)
__counter[__i].merge(__counter[__i-1], __comp);
swap(__counter[__fill-1]);
}
}上面的该算法实际上使用了归并排序的思想,先归并前两个元素,接着归并后两个元素,然后归并前四个元素,然后是8个....,count[i]保存了归并排序的元素,最后将count[i]进行合并
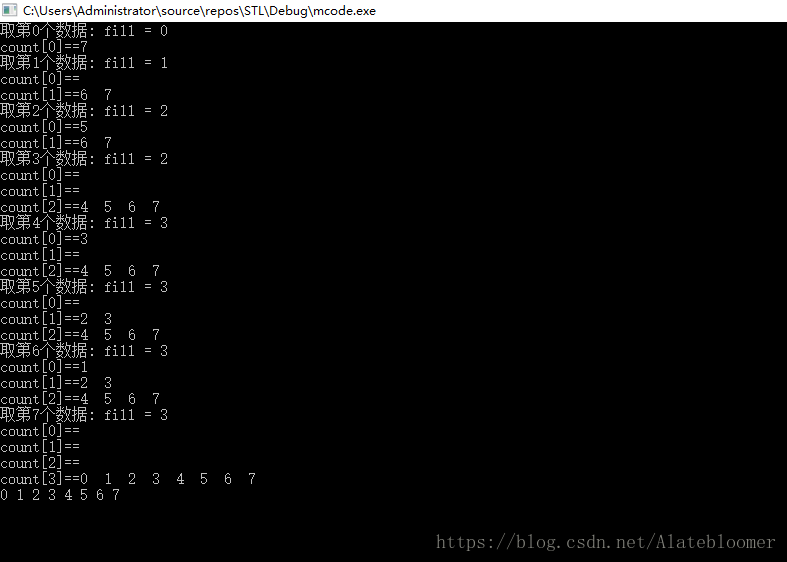
下面是该过程的一个测试,输出了归并的各个阶段的情况
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include<list>
using namespace std;
typedef list<int> IList;
void print(const IList& list)
{
IList::const_iterator ite = list.begin();
for (; ite != list.end(); ++ite)
{
cout << *ite << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
IList s;
s.push_back(7);
s.push_back(6);
s.push_back(5);
s.push_back(4);
s.push_back(3);
s.push_back(2);
s.push_back(1);
s.push_back(0);
IList carry;
IList counter[64];
int fill = 0;
int num = 0;
while (!s.empty())
{
cout << "取第" << num << "个数据: fill = " << fill << endl;
carry.splice(carry.begin(), s, s.begin());
int i = 0;
while (i < fill && !counter[i].empty())
{
counter[i].merge(carry);
carry.swap(counter[i++]);
}
carry.swap(counter[i]);
if (i == fill)
++fill;
//我自己加的计数
num++;
//打印每次完的结果
for (int i = 0; i < fill; ++i)
{
cout << "count["<<i<<"]==";
print(counter[i]);
}
}
for (int i = 1; i < fill; ++i)
counter[i].merge(counter[i - 1]);
s.swap(counter[fill - 1]);
for (auto& m : s)
cout << m << " ";
return 0;
}