转:http://blog.csdn.net/cdnight/article/details/11650983
此坑待埋。
点击打开漫谈经典排序算法:一、从简单选择排序到堆排序的深度解析链接
堆排序(注:这篇文章说明了如何从一个数组构建一个最大堆,推荐看)
最大堆的插入/删除/调整/排序操作(图解+程序)(JAVA)
下面来说一说具体算法。
堆排序解释第一篇(描述不太清楚)
1.堆
堆实际上是一棵完全二叉树,其任何一非叶节点满足性质:
Key[i]<=key[2i+1]&&Key[i]<=key[2i+2]或者Key[i]>=Key[2i+1]&&key>=key[2i+2]
即任何一非叶节点的关键字不大于或者不小于其左右孩子节点的关键字。
堆分为大顶堆和小顶堆,满足Key[i]>=Key[2i+1]&&key>=key[2i+2]称为大顶堆,满足 Key[i]<=key[2i+1]&&Key[i]<=key[2i+2]称为小顶堆。由上述性质可知大顶堆的堆顶的关键字肯定是所有关键字中最大的,小顶堆的堆顶的关键字是所有关键字中最小的。
2.堆排序的思想
利用大顶堆(小顶堆)堆顶记录的是最大关键字(最小关键字)这一特性,使得每次从无序中选择最大记录(最小记录)变得简单。
其基本思想为(大顶堆):
1)将初始待排序关键字序列(R1,R2....Rn)构建成大顶堆,此堆为初始的无序区;
2)将堆顶元素R[1]与最后一个元素R[n]交换,此时得到新的无序区(R1,R2,......Rn-1)和新的有序区(Rn),且满足R[1,2...n-1]<=R[n];
3)由于交换后新的堆顶R[1]可能违反堆的性质,因此需要对当前无序区(R1,R2,......Rn-1)调整为新堆,然后再次将R[1]与无序区最后一个元素交换,得到新的无序区(R1,R2....Rn-2)和新的有序区(Rn-1,Rn)。不断重复此过程直到有序区的元素个数为n-1,则整个排序过程完成。
操作过程如下:
1)初始化堆:将R[1..n]构造为堆;
2)将当前无序区的堆顶元素R[1]同该区间的最后一个记录交换,然后将新的无序区调整为新的堆。
因此对于堆排序,最重要的两个操作就是构造初始堆和调整堆,其实构造初始堆事实上也是调整堆的过程,只不过构造初始堆是对所有的非叶节点都进行调整。
下面举例说明:
给定一个整形数组a[]={16,7,3,20,17,8},对其进行堆排序。
首先根据该数组元素构建一个完全二叉树,得到




20和16交换后导致16不满足堆的性质,因此需重新调整

这样就得到了初始堆。

此时3位于堆顶不满堆的性质,则需调整继续调整










0.待排序序列:
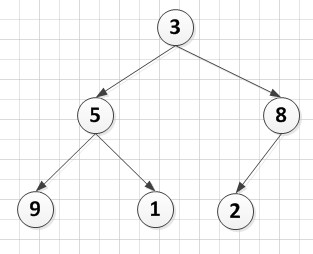 A[6]={3,5,8,9,1,2},
A[6]={3,5,8,9,1,2},
1.建堆后(建堆过程参见4.4):
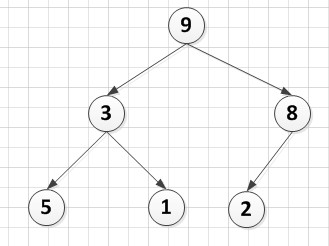 A[6]={9,3,8,5,1,2}
A[6]={9,3,8,5,1,2}
2.9和2交换,然后把9从堆中去掉后:
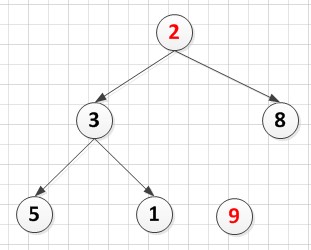 A[6]={2,3,8,5,1,9}
A[6]={2,3,8,5,1,9}
3.筛选法调整堆A[5]={2,3,8,5,1}后(调整过程参见4.3):
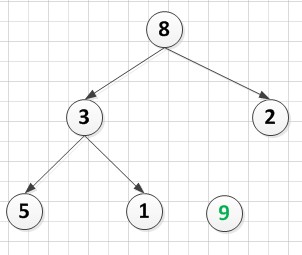 A[6]={8,3,2,5,1,9}
A[6]={8,3,2,5,1,9}
4.堆顶记录与最后一个记录互换,重复第二步,但是堆顶记录和最后一个记录的值变了
最大堆的插入/删除/调整/排序操作(图解+程序)(JAVA)
设有n个元素的序列{k1,k2,...,kn},当且仅当满足下列关系时,称之为堆。

堆的三种基本操作(以下以最大堆为例):
⑴最大堆的插入
由于需要维持完全二叉树的形态,需要先将要插入的结点x放在最底层的最右边,插入后满 足完全二叉树的特点;
然后把x依次向上调整到合适位置满足堆的性质,例如下图中插入80,先将80放在最后,然后两次上浮到合适位置.
时间:O(logn)。 “结点上浮”

程序实现:
- //向最大堆中插入元素, heap:存放堆元素的数组
- public static void insert(List<Integer> heap, int value) {
- //在数组的尾部添加
- if(heap.size()==0)
- heap.add(0);//数组下标为0的位置不放元素
- heap.add(value);
- //开始上升操作
- // heapUp2(heap, heap.size() - 1);
- heapUp(heap, heap.size() - 1);
- }
- //上升,让插入的数和父节点的数值比较,当大于父节点的时候就和父节点的值相交换
- public static void heapUp(List<Integer> heap, int index) {
- //注意由于数值是从下标为1开始,当index = 1的时候,已经是根节点了
- if (index > 1) {
- //求出父亲的节点
- int parent = index / 2;
- //获取相应位置的数值
- int parentValue = (Integer) heap.get(parent);
- int indexValue = (Integer) heap.get(index);
- //如果父亲节点比index的数值小,就交换二者的数值
- if (parentValue < indexValue) {
- //交换数值
- swap(heap, parent, index);
- //递归调用
- heapUp(heap, parent);
- }
- }
- }
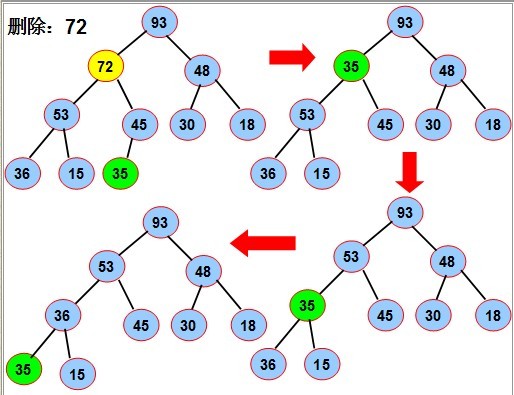
⑵删除
操作原理是:当删除节点的数值时,原来的位置就会出现一个孔,填充这个孔的方法就是,
把最后的叶子的值赋给该孔并下调到合适位置,最后把该叶子删除。
如图中要删除72,先用堆中最后一个元素来35替换72,再将35下沉到合适位置,最后将叶子节点删除。
“结点下沉”
- 程序:
- /**
- * 删除堆中位置是index处的节点
- * 操作原理是:当删除节点的数值时,原来的位置就会出现一个孔
- * 填充这个孔的方法就是,把最后的叶子的值赋给该孔,最后把该叶子删除
- * @param heap
- */
- public static void delete(List<Integer> heap,int index) {
- //把最后的一个叶子的数值赋值给index位置
- heap.set(index, heap.get(heap.size() - 1));
- //下沉操作
- //heapDown2(heap, index);
- heapDown(heap, index);
- //把最后一个位置的数字删除
- heap.remove(heap.size() - 1);
- }
- /**
- * 递归实现
- * 删除堆中一个数据的时候,根据堆的性质,应该把相应的位置下移,才能保持住堆性质不变
- * @param heap 保持堆元素的数组
- * @param index 被删除的那个节点的位置
- */
- public static void heapDown(List<Integer> heap, int index) {
- //因为第一个位置存储的是空值,不在考虑之内
- int n = heap.size() - 2;
- //记录最大的那个儿子节点的位置
- int child = -1;
- //2*index>n说明该节点没有左右儿子节点了,那么就返回
- if (2 * index > n) {
- return;
- } //如果左右儿子都存在
- else if (2 * index < n) {
- //定义左儿子节点
- child = 2 * index;
- //如果左儿子小于右儿子的数值,取右儿子的下标
- if ((Integer) heap.get(child) < (Integer) heap.get(child + 1)) {
- child++;
- }
- }//如果只有一个儿子(左儿子节点)
- else if (2 * index == n) {
- child = 2 * index;
- }
- if ((Integer) heap.get(child) > (Integer) heap.get(index)) {
- //交换堆中的child,和index位置的值
- swap(heap, child, index);
- //完成交换后递归调用,继续下降
- heapDown(heap, child);
- }
- }
⑶初始化
方法1:插入法:
从空堆开始,依次插入每一个结点,直到所有的结点全部插入到堆为止。
时间:O(n*log(n))
方法2:调整法:
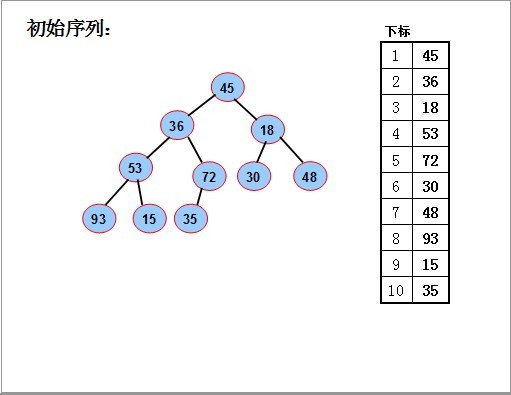
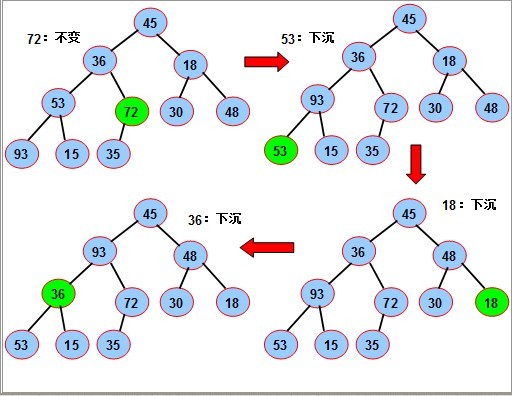
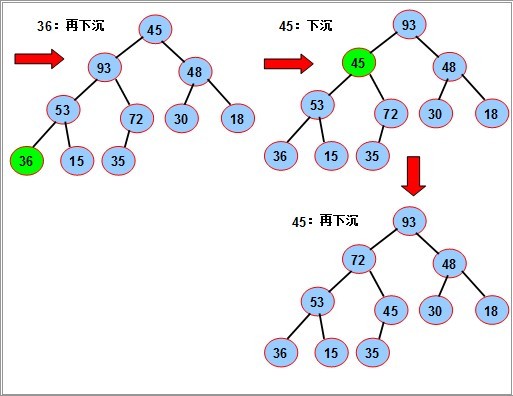
序列对应一个完全二叉树;从最后一个分支结点(n div 2)开始,到根(1)为止,依次对每个分支结点进行调整(下沉),
以便形成以每个分支结点为根的堆,当最后对树根结点进行调整后,整个树就变成了一个堆。
时间:O(n)
对如图的序列,要使其成为堆,我们从最后一个分支结点(10/2),其值为72开始,依次对每个分支节点53,18,36 45进行调整(下沉).
- 程序:
- /*根据树的性质建堆,树节点前一半一定是分支节点,即有孩子的,所以我们从这里开始调整出初始堆*/
- public static void adjust(List<Integer> heap){
- for (int i = heap.size() / 2; i > 0; i--)
- adjust(heap,i, heap.size()-1);
- System.out.println("=================================================");
- System.out.println("调整后的初始堆:");
- print(heap);
- }
- /**
- * 调整堆,使其满足堆得定义
- * @param i
- * @param n
- */
- public static void adjust(List<Integer> heap,int i, int n) {
- int child;
- for (; i <= n / 2; ) {
- child = i * 2;
- if(child+1<=n&&heap.get(child)<heap.get(child+1))
- child+=1;/*使child指向值较大的孩子*/
- if(heap.get(i)< heap.get(child)){
- swap(heap,i, child);
- /*交换后,以child为根的子树不一定满足堆定义,所以从child处开始调整*/
- i = child;
- } else break;
- }
- }
(4)最大堆排序
- //对一个最大堆heap排序
- public static void heapSort(List<Integer> heap) {
- for (int i = heap.size()-1; i > 0; i--) {
- /*把根节点跟最后一个元素交换位置,调整剩下的n-1个节点,即可排好序*/
- swap(heap,1, i);
- adjust(heap,1, i - 1);
- }
- }
(5)完整的代码
- import java.util.*;
- /**
- *实现的最大堆的插入和删除操作
- * @author Arthur
- */
- public class Heap {
- /**
- * 删除堆中位置是index处的值
- * 操作原理是:当删除节点的数值时,原来的位置就会出现一个孔
- * 填充这个孔的方法就是,把最后的叶子的值赋给该孔,最后把该叶子删除
- * @param heap 一个最大堆
- */
- public static void delete(List<Integer> heap,int index) {
- //把最后的一个叶子的数值赋值给index位置
- heap.set(index, heap.get(heap.size() - 1));
- //下沉操作
- //heapDown2(heap, index);
- heapDown(heap, index); //节点下沉
- //把最后一个位置的数字删除
- heap.remove(heap.size() - 1);
- }
- /**
- * 节点下沉递归实现
- * 删除一个堆中一个数据的时候,根据堆的性质,应该把相应的位置下移,才能保持住堆性质不变
- * @param heap 保持最大堆元素的数组
- * @param index 被删除的那个节点的位置
- */
- public static void heapDown(List<Integer> heap, int index) {
- //因为第一个位置存储的是空值,不在考虑之内
- int n = heap.size() - 2;
- //记录最大的那个儿子节点的位置
- int child = -1;
- //2*index>n说明该节点没有左右儿子节点了,那么就返回
- if (2 * index > n) {
- return;
- } //如果左右儿子都存在
- else if (2 * index < n) {
- //定义左儿子节点
- child = 2 * index;
- //如果左儿子小于右儿子的数值,取右儿子的下标
- if ((Integer) heap.get(child) < (Integer) heap.get(child + 1)) {
- child++;
- }
- }//如果只有一个儿子(左儿子节点)
- else if (2 * index == n) {
- child = 2 * index;
- }
- if ((Integer) heap.get(child) > (Integer) heap.get(index)) {
- //交换堆中的child,和index位置的值
- swap(heap, child, index);
- //完成交换后递归调用,继续下降
- heapDown(heap, child);
- }
- }
- //非递归实现
- public static void heapDown2(List<Integer> heap, int index) {
- int child = 0;//存储左儿子的位置
- int temp = (Integer) heap.get(index);
- int n = heap.size() - 2;
- //如果有儿子的话
- for (; 2 * index <= n; index = child) {
- //获取左儿子的位置
- child = 2 * index;
- //如果只有左儿子
- if (child == n) {
- child = 2 * index;
- } //如果右儿子比左儿子的数值大
- else if ((Integer) heap.get(child) < (Integer) heap.get(child + 1)) {
- child++;
- }
- //如果数值最大的儿子比temp的值大
- if ((Integer) heap.get(child) >temp) {
- //交换堆中的child,和index位置的值
- swap(heap, child, index);
- } else {
- break;
- }
- }
- }
- //打印链表
- public static void print(List<Integer> list) {
- for (int i = 1; i < list.size(); i++) {
- System.out.print(list.get(i) + " ");
- }
- System.out.println();
- }
- //把堆中的a,b位置的值互换
- public static void swap(List<Integer> heap, int a, int b) {
- //临时存储child位置的值
- int temp = (Integer) heap.get(a);
- //把index的值赋给child的位置
- heap.set(a, heap.get(b));
- //把原来的child位置的数值赋值给index位置
- heap.set(b, temp);
- }
- //向最大堆中插入元素
- public static void insert(List<Integer> heap, int value) {
- //在数组的尾部添加要插入的元素
- if(heap.size()==0)
- heap.add(0);//数组下标为0的位置不放元素
- heap.add(value);
- //开始上升操作
- // heapUp2(heap, heap.size() - 1);
- heapUp(heap, heap.size() - 1);
- }
- //节点上浮,让插入的数和父节点的数值比较,当大于父节点的时候就和节点的值相交换
- public static void heapUp(List<Integer> heap, int index) {
- //注意由于数值是从小标为一开始,当index = 1的时候,已经是根节点了
- if (index > 1) {
- //保存父亲的节点
- int parent = index / 2;
- //获取相应位置的数值
- int parentValue = (Integer) heap.get(parent);
- int indexValue = (Integer) heap.get(index);
- //如果父亲节点比index的数值小,就交换二者的数值
- if (parentValue < indexValue) {
- //交换数值
- swap(heap, parent, index);
- //递归调用
- heapUp(heap, parent);
- }
- }
- }
- //非递归实现
- public static void heapUp2(List<Integer> heap, int index) {
- int parent = 0;
- for (; index > 1; index /= 2) {
- //获取index的父节点的下标
- parent = index / 2;
- //获得父节点的值
- int parentValue = (Integer) heap.get(parent);
- //获得index位置的值
- int indexValue = (Integer) heap.get(index);
- //如果小于就交换
- if (parentValue < indexValue) {
- swap(heap, parent, index);
- }
- }
- }
- /*根据树的性质建堆,树节点前一半一定是分支节点,即有孩子的,所以我们从这里开始调整出初始堆*/
- public static void adjust(List<Integer> heap){
- for (int i = heap.size() / 2; i > 0; i--)
- adjust(heap,i, heap.size()-1);
- System.out.println("=================================================");
- System.out.println("调整后的初始堆:");
- print(heap);
- }
- /**
- * 调整堆,使其满足堆得定义
- * @param i
- * @param n
- */
- public static void adjust(List<Integer> heap,int i, int n) {
- int child;
- for (; i <= n / 2; ) {
- child = i * 2;
- if(child+1<=n&&heap.get(child)<heap.get(child+1))
- child+=1;/*使child指向值较大的孩子*/
- if(heap.get(i)< heap.get(child)){
- swap(heap,i, child);
- /*交换后,以child为根的子树不一定满足堆定义,所以从child处开始调整*/
- i = child;
- } else break;
- }
- }
- //对一个最大堆heap排序
- public static void heapSort(List<Integer> heap) {
- for (int i = heap.size()-1; i > 0; i--) {
- /*把根节点跟最后一个元素交换位置,调整剩下的n-1个节点,即可排好序*/
- swap(heap,1, i);
- adjust(heap,1, i - 1);
- }
- }
- public static void main(String args[]) {
- List<Integer> array = new ArrayList<Integer>(Arrays.asList(null,
- 1, 2, 5, 10, 3, 7, 11, 15, 17, 20, 9, 15, 8, 16));
- adjust(array);//调整使array成为最大堆
- delete(array,8);//堆中删除下标是8的元素
- System.out.println("删除后");
- print(array);
- insert(array, 99);//堆中插入
- print(array);
- heapSort(array);//排序
- System.out.println("将堆排序后:");
- print(array);
- System.out.println("-------------------------");
- List<Integer> array1=new ArrayList<Integer>();
- insert(array1,0);
- insert(array1, 1);insert(array1, 2);insert(array1, 5);
- insert(array1, 10);insert(array1, 3);insert(array1, 7);
- insert(array1, 11);insert(array1, 15); insert(array1, 17);
- insert(array1, 20);insert(array1, 9);
- insert(array1, 15);insert(array1, 8);insert(array1, 16);
- print(array1);
- System.out.println("==============================");
- array=new ArrayList<Integer>(Arrays.asList(null,45,36,18,53,72,30,48,93,15,35));
- adjust(array);
- insert(array, 80);//堆中插入
- print(array);
- delete(array,2);//堆中删除80的元素
- print(array);
- delete(array,2);//堆中删除72的元素
- print(array);
- }
- }
程序运行:
D:\java>java Heap
=================================================
调整后的初始堆:
20 17 16 15 9 15 11 1 10 3 2 7 8 5
删除后
20 17 16 15 9 15 11 5 10 3 2 7 8
99 17 20 15 9 15 16 5 10 3 2 7 8 11
将堆排序后:
2 3 5 7 8 9 10 11 15 15 16 17 20 99
-------------------------
20 17 16 10 15 9 15 0 5 2 11 1 7 3 8
==============================
=================================================
调整后的初始堆:
93 72 48 53 45 30 18 36 15 35
93 80 48 53 72 30 18 36 15 35 45
93 72 48 53 45 30 18 36 15 35
93 53 48 36 45 30 18 35 15
好了,想必大家都明白了,下一篇文章将放出相关算法及结果。
https://blog.csdn.net/chen_lin111/article/details/50477642