前言:之前学习hashmap,重点学习了hashmap的数据结构以及如何扩容,相关联的其实有ArrayList、LinkedList和HashTable这些,本文简单地学习一下ArrayList。
PS: 源码分析针对于Android O 的jdk,即jdk1.8
demo地址:jiatai的ArrayList demo
1. ArrayList简单介绍
就我印象,ArrayList在Java中扮演的角色对应于数据结果中的数组,或者说ArrayList是基于数组写出来的一个类,用于存储数据。
说一个小问题,如果我想在ArrayList里存12个数,是用无参的ArrayList好,还是有参的好,好在哪里?(有参的好,好在不用扩容)
2. ArrayList简单使用
简单的往Arraylist里面塞两个数字1和2:package com.example.demo_26_arraylist;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class MyClass {
public static void main(String[] args){
ArrayList arrayList = new ArrayList<Integer>();
System.out.println("the size is " + arrayList.size());
arrayList.add(1);
System.out.println("the size is " + arrayList.size());
arrayList.add(2);
System.out.println("the size is " + arrayList.size());
System.out.println(arrayList);
}
}
对应log:
the size is 0 the size is 1 the size is 2 [1, 2]
3. 简单使用所对应的内在
上面的使用主要涉及了四个方法
- 构造方法
- add()
- size()
- toString()
下面来简单地看下内在=-=
3.1 构造方法
构造方法有3个,这里先看下平常用的最多的无参构造方法。/**
* Constructs an empty list with an initial capacity of ten.
*/
public ArrayList() {
this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
无参构造方法是最简单的,也是我们比较常用的,内部其实就初始化了一下elementData这个成员变量,来看下elementData 和DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA是啥?
/**
* Shared empty array instance used for default sized empty instances. We
* distinguish this from EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA to know how much to inflate when
* first element is added.
*/
private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
/**
* The array buffer into which the elements of the ArrayList are stored.
* The capacity of the ArrayList is the length of this array buffer. Any
* empty ArrayList with elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA
* will be expanded to DEFAULT_CAPACITY when the first element is added.
*/
// Android-note: Also accessed from java.util.Collections
transient Object[] elementData; // non-private to simplify nested class access
DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA其实就是个空的数组。而elementData这里注释讲的很清楚,是用来存放数组成员的数组缓存,Arraylist的长度就是这个elementData的长度。并且任何空的数组,也就是用无参构造器初始的数组,在add第一个成员的时候会被扩展成DEFAULT_CAPACITY。
/**
* Default initial capacity.
*/
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;
也就是说空的数组第一次被add元素的时候会被扩展为容量为10的数组。
这里接着就看下add的源码。
3.2 add(E e)
/**
* Appends the specified element to the end of this list.
*
* @param e element to be appended to this list
* @return <tt>true</tt> (as specified by {@link Collection#add})
*/
public boolean add(E e) {
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
}
可以看到add分两个步骤
- 确保容量足够存储新来的成员
- 添加成员,并使size++
这里主要看下ensureCapacityInternal这个方法的后续:
private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) {
if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {
minCapacity = Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity);
}
ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity);
}
private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) {
modCount++;
// overflow-conscious code
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
grow(minCapacity);
}
这里可以看到
1.将minCapacity初始化为DEFAULT_CAPACITY,即10,这和之前看无参构造器注释一样的。
2.依据minCapacity的值调用grow方法进行扩容
/**
* The maximum size of array to allocate.
* Some VMs reserve some header words in an array.
* Attempts to allocate larger arrays may result in
* OutOfMemoryError: Requested array size exceeds VM limit
*/
private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8;
/**
* Increases the capacity to ensure that it can hold at least the
* number of elements specified by the minimum capacity argument.
*
* @param minCapacity the desired minimum capacity
*/
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
这边扩容不是说直接用 minCapacity 为ArrayList的大小就开始扩容了。
举个例子:现在数组长度为10,则新的扩容建议大小为10+10/2,即15,然后以15和minCapacity(11)继续比较,15比较大,所以当数组长度为10的数组新添一个元素后,长度会变为15。(第4节中有例子来验证)
对应于初始化就是minCapacity是10,而oldCapacity是0,没有可比较性,直接用minCapacity作为扩容后数组大小。
确定好扩容后数组大小后,用Arrays的copyOf方法将原数组元素复制到新的数组中。
/**
* Copies the specified array, truncating or padding with nulls (if necessary)
* so the copy has the specified length. For all indices that are
* valid in both the original array and the copy, the two arrays will
* contain identical values. For any indices that are valid in the
* copy but not the original, the copy will contain <tt>null</tt>.
* Such indices will exist if and only if the specified length
* is greater than that of the original array.
* The resulting array is of exactly the same class as the original array.
*
* @param <T> the class of the objects in the array
* @param original the array to be copied
* @param newLength the length of the copy to be returned
* @return a copy of the original array, truncated or padded with nulls
* to obtain the specified length
* @throws NegativeArraySizeException if <tt>newLength</tt> is negative
* @throws NullPointerException if <tt>original</tt> is null
* @since 1.6
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public static <T> T[] copyOf(T[] original, int newLength) {
return (T[]) copyOf(original, newLength, original.getClass());
}
3.3 size
注意区分size不是Arraylist的实际长度,而是其中包含的元素的数目,对应与上面的“当数组大小为10的时候,再添加一个元素会造成数组进行扩容为15”的例子,size是11,而不是15,elementData的数组长度才是15。 /**
* Returns the number of elements in this list.
*
* @return the number of elements in this list
*/
public int size() {
return size;
}
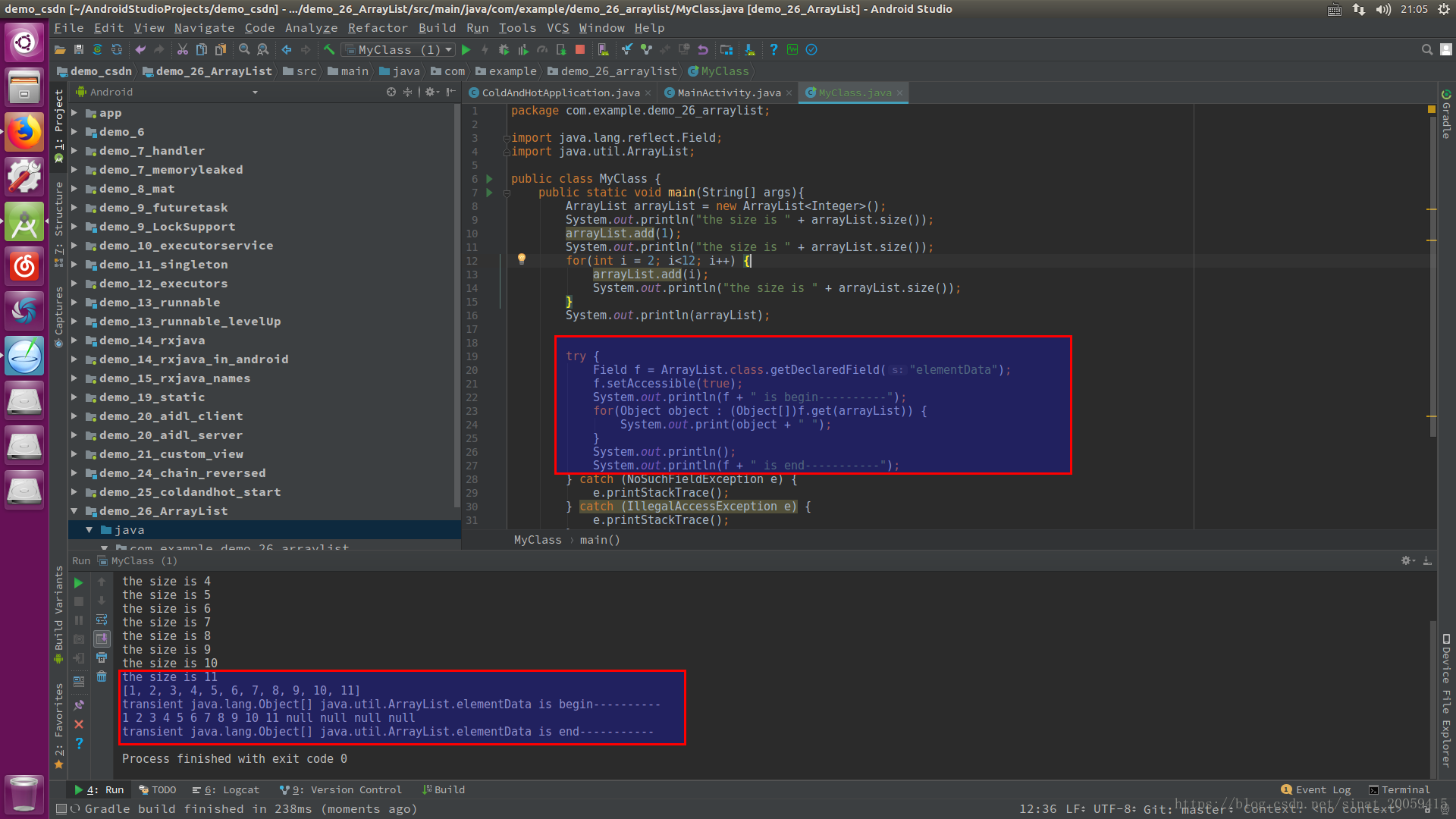
另外试了下arrayList是支持添加null元素的,并且size可以正常进行+1
3.4 toString
toString方法是继承的父类AbstractCollection的toString方法,将其所包含的元素都打印出来。 /**
* Returns a string representation of this collection. The string
* representation consists of a list of the collection's elements in the
* order they are returned by its iterator, enclosed in square brackets
* (<tt>"[]"</tt>). Adjacent elements are separated by the characters
* <tt>", "</tt> (comma and space). Elements are converted to strings as
* by {@link String#valueOf(Object)}.
*
* @return a string representation of this collection
*/
public String toString() {
Iterator<E> it = iterator();
if (! it.hasNext())
return "[]";
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append('[');
for (;;) {
E e = it.next();
sb.append(e == this ? "(this Collection)" : e);
if (! it.hasNext())
return sb.append(']').toString();
sb.append(',').append(' ');
}
}
3.5 指定位置插入add(int index, E element)
数组在指定位置插入元素效率比较低的,从下面源码可以看出,是将指定位置及后面的源码都往后挪一下,给指定元素挪一个位置出来让该元素落座。remove方法就是相反的操作=-=/**
* Inserts the specified element at the specified position in this
* list. Shifts the element currently at that position (if any) and
* any subsequent elements to the right (adds one to their indices).
*
* @param index index at which the specified element is to be inserted
* @param element element to be inserted
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public void add(int index, E element) {
if (index > size || index < 0)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1,
size - index);
elementData[index] = element;
size++;
}
4. 扩容
扩容其实在3.2节中有提及,如果不考虑边界情况,即初始化为10和数目大于整数最大值的时候,扩容其实就是将数组大小变为n+n/2,然后调用Arrays.copyOf方法将之前的数组成员复制到新数组中去并返回新数组。
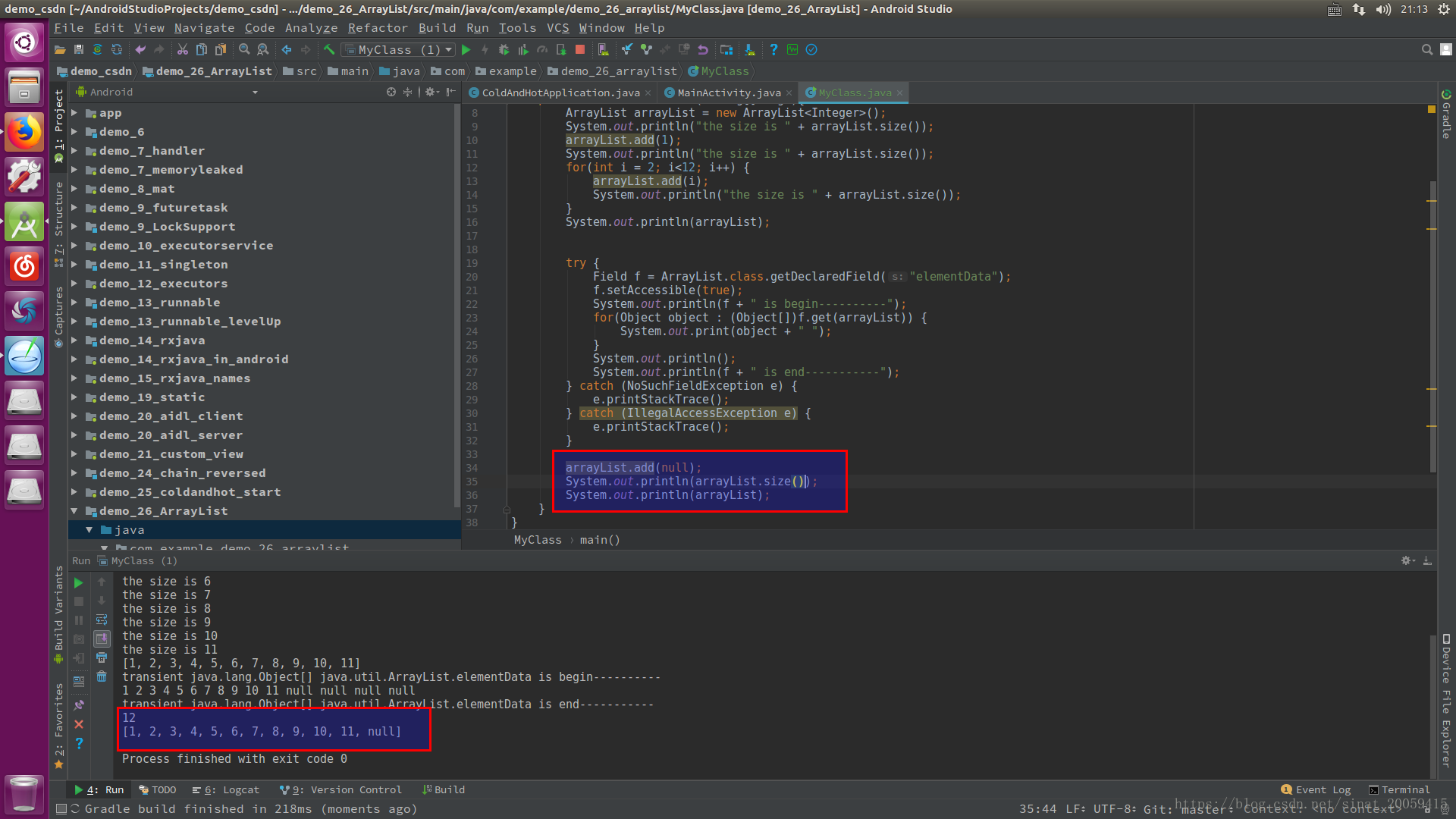
写了个简单的例子来验证上面说的ArrayList的扩容原理和之前举的例子:
当数组大小为10的时候,再添加一个元素会造成数组进行扩容为15,其中4个空档会用null占据。
5. 总结
ArrayList本质可以看成是一个固定大小的数组,然后一直往里面塞成员,不够塞了就扩容一下,继续赛。这里想起来之前阿里编码规范里有说,如果确定了ArrayList大小,则指定大小,不然比如10到11会造成一次数组扩容,影响效率。