目录
GGally
GGally通过添加几个函数来扩展ggplot2,以降低geom与转换数据组合的复杂性。其中一些功能包括配对图矩阵,散点图矩阵,平行坐标图,生存图,以及绘制网络的几个函数。
ggmatrix: ggplot2矩阵
用法
ggmatrix()参数
plots:将要列入矩阵的图形列表
nrow, ncol:行数和列数
xAxisLabels, yAxisLabels:# x标签和y标签。设置NULL为不显示
title, xlab, ylab:标题,x标签和y标签。设置NULL为不显示
byrow:布尔值,用于确定图应该按行还是按列排序
showStrips:布尔值来确定是否应显示每个图块。NULL将仅默认为顶部和右侧地块。
showAxisPlotLabels, showXAxisPlotLabels, showYAxisPlotLabels:布尔值,用于确定绘图轴标签是否打印在绘图矩阵的X(底部)或Y(左侧)部分。
plotList <- list()
for (i in 1:6) {
plotList[[i]] <- ggally_text(paste("Plot #", i, sep = ""))
}
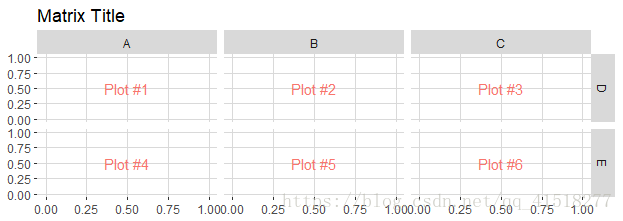
pm <- ggmatrix(
plotList, #将要列入矩阵的图形列表
nrow = 2, ncol = 3, # 行数和列数
xAxisLabels = c("A", "B", "C"), #x标题。设置NULL为不显示
yAxisLabels = c("D", "E"),
by
title = "Matrix Title"
)
pm
pm <- pm + theme_bw() #可以添加ggplot2主题
p2 <- pm[1,2] #也可以提取子集使用
p3 <- pm[1,3]ggpairs:ggplot2广义配对图
选定列映射
data(tips, package = "reshape")
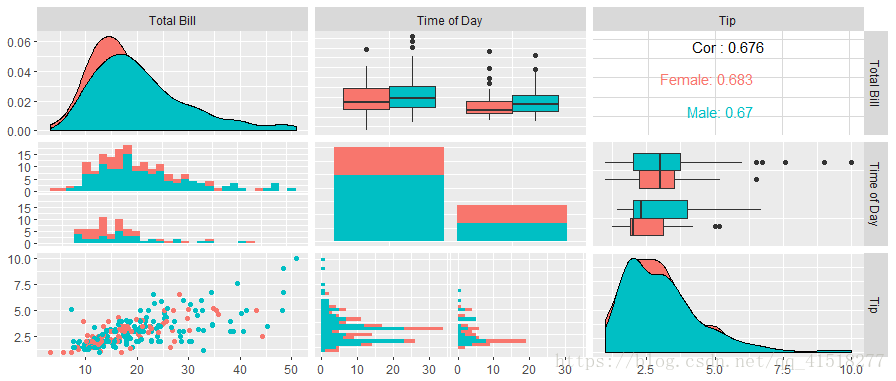
pm <- ggpairs(tips, mapping = aes(color = sex),
columns = c("total_bill", "time", "tip"),columnLabels = c("Total Bill", "Time of Day", "Tip"))
pm矩阵部分
成对矩阵有三个主要部分:lower,upper,和diag。lower和upper包含三个类型:continuous,combo,和discrete。diag只包含continuous或者discrete。
- continuous:X和Y都是连续变量
- combo:一个是离散的,而另一个是连续的
- discrete:X和Y都是离散变量
要对每个部分进行调整,需要提供一个信息列表。该列表可以由以下元素组成:
- continuous:
- 表示ggally_NAME函数尾部的字符串或自定义函数
- 当前有效的
upper$continuous和lower$continuous字符串:’points’,’smooth’,’density’,’cor’,’blank’ - 当前有效的
diag$continuous字符串:’densityDiag’,’barDiag’,’blankDiag’
- combo:
表示ggally_NAME函数尾部的字符串或自定义函数。(不适用于diag列表)
当前有效的upper$combo和lower$combo字符串:’box’,’dot’,’facethist’,’facetdensity’,’denstrip’,’blank’ - discrete:
- 表示ggally_NAME函数尾部的字符串或自定义函数
- 当前有效的
upper$discrete和lower$discrete字符串:’ratio’,’facetbar’,’blank’ - 当前有效的
diag$discrete字符串:’barDiag’,’blankDiag’
- mapping:如果提供了映射,则只会覆盖该部分的映射
library(ggplot2)
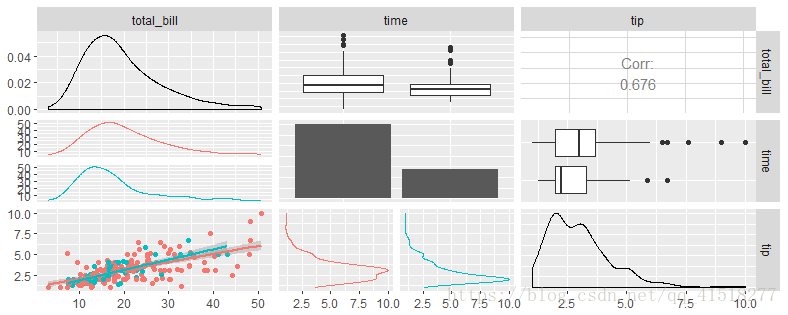
pm <- ggpairs(
tips, columns = c("total_bill", "time", "tip"),
lower = list(
continuous = "smooth",
combo = "facetdensity",
mapping = aes(color = time)
)
)
pm自定义函数
这些ggally_NAME函数不提供所有图形选项。一个自定义函数可以代替供给字符串到continuous,combo或discrete内的元件upper,lower或diag。
自定义函数应该遵循:只要返回一个ggplot2对象即可
custom_function <- function(data, mapping, ...){
# produce ggplot2 object here
}my_bin <- function(data, mapping, ..., low = "#132B43", high = "#56B1F7") {
ggplot(data = data, mapping = mapping) +
geom_bin2d(...) +
scale_fill_gradient(low = low, high = high)
}
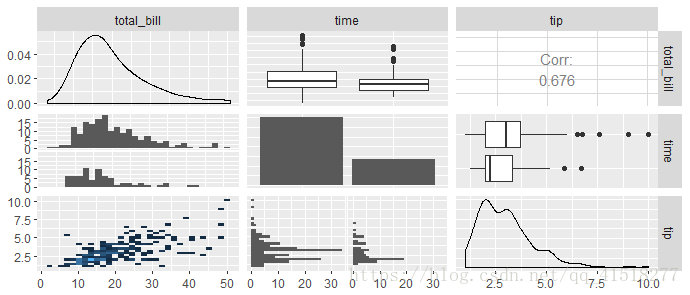
pm <- ggpairs(
tips, columns = c("total_bill", "time", "tip"),
lower = list(
continuous = my_bin
)
)
pm函数包装
上面的例子使用每个子图的默认参数。要更改默认的参数binwidth设置,我们将使用wrap函数。wrap第一个参数是一个字符串或一个自定义函数。提供给wrap的其余参数将在运行时提供给函数。
pm <- ggpairs(
tips, columns = c("total_bill", "time", "tip"),
lower = list(
combo = wrap("facethist", binwidth = 1),
continuous = wrap(my_bin, binwidth = c(5, 0.5), high = "red")
)
)
pm取矩阵子集和添加主题
p <- pm[3,1] # 取子集
p <- p + aes(color = time)
p + theme_bw() #添加主题ggscatmat:纯粹定量变量的传统散点图矩阵
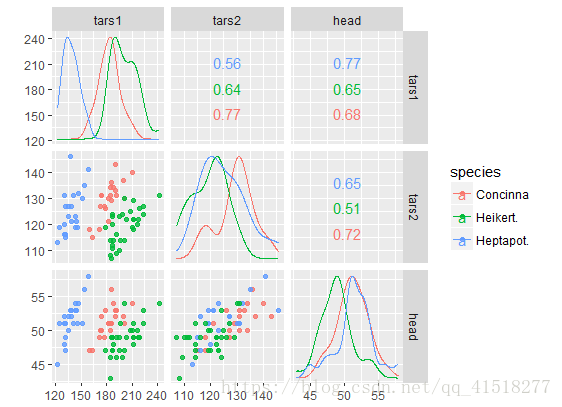
ggscatmat(data, columns = 1:ncol(data), color = NULL, alpha = 1, corMethod = "pearson")比ggpairs更快,因为需要做出更少的选择。它创建了一个矩阵,其中包含对角线下的散点图,对角线的密度图以及对角线上的相关系数。
data(flea)
ggscatmat(flea, columns = 2:4, color="species", alpha=0.8)其余函数待更新