“Spring boot非常适合Web应用程序开发。您可以轻松创建自包含的HTTP应用。web服务器采用嵌入式Tomcat,或者Jetty等。大多数情况下Web应用程序将使用spring-bootstarter-web模块快速启动和运行。”
本例子通过显示用户列表展示如何使用spring boot和Thymeleaf开发web项目。
几点说明:
- Spring boot开发web项目,通常打成jar包,使用内置的web服务器 Tomcat、Jetty、undertow 来运行。
- 静态资源(css、js、图片等)默认放在resources/static下面。如果要修改默认存放目录,可以通过设置属性 spring.mvc.static-path-pattern来实现。
- 模板文件默认放在 templates目录下
- Spring boot支持使用模板来开发web应用,支持的模板类型包括
- FreeMarker
- Groovy
- Thymeleaf
- Mustache
Spring boot不建议使用jsp开发web。
本文使用Thymeleaf来作为模板引擎开发web项目。
Thymeleaf
Thymeleaf是一个Java模板引擎开发库,可以处理和生成HTML、XML、JavaScript、CSS和文本,在Web和非Web环境下都可以正常工作。
Thymeleaf可以跟Spring boot很好的集成。
Spring Boot+Thymeleaf开发web
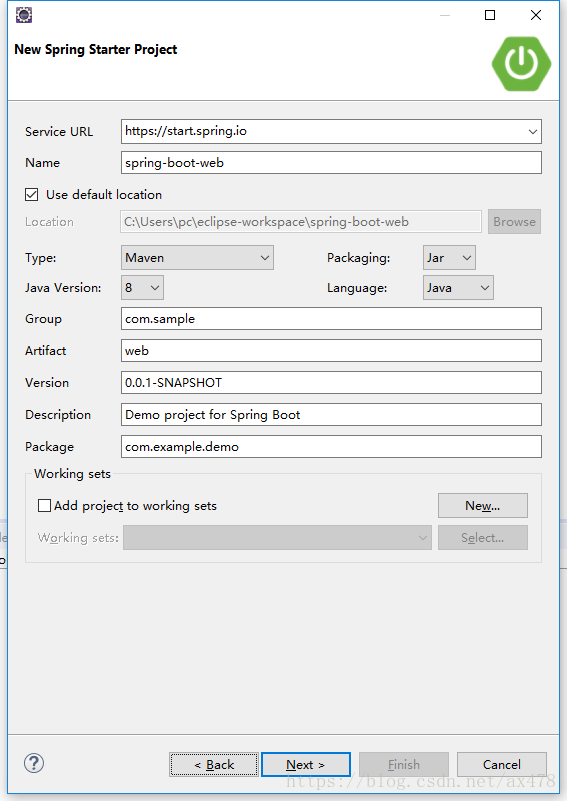
创建spring boot项目
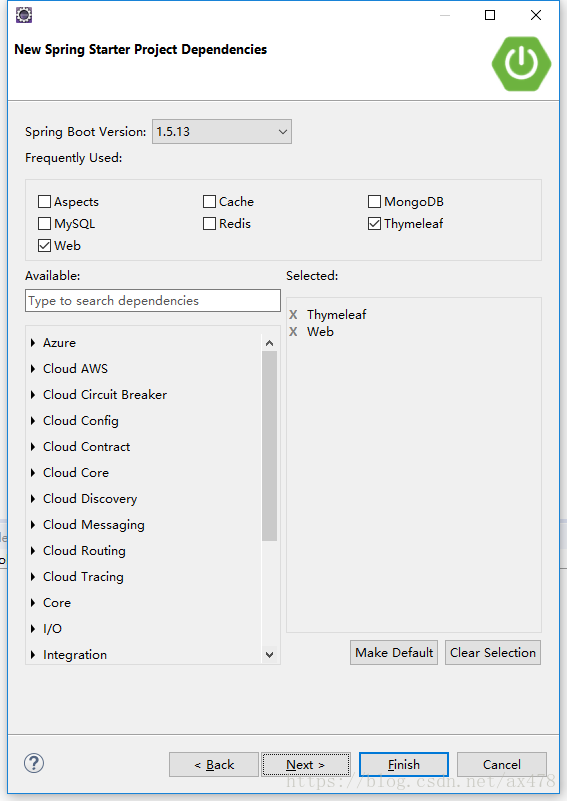
选择spring boot和依赖 ,注意需要的依赖包括web和Thymeleaf
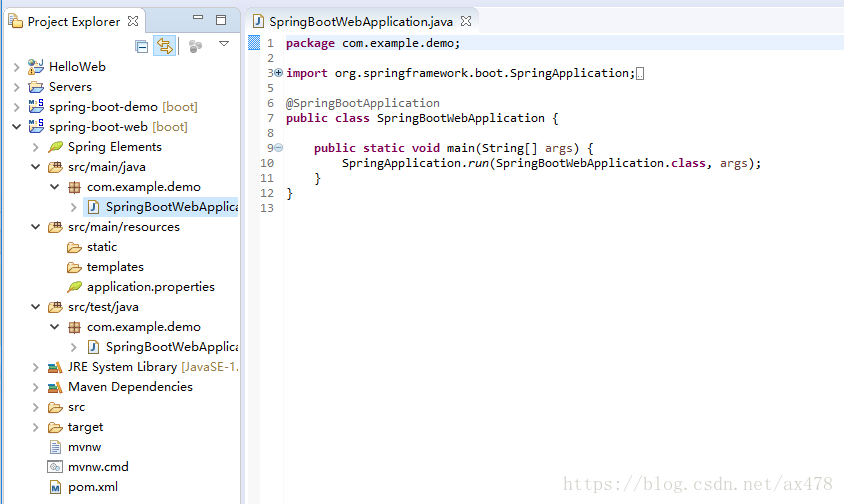
点击finish。创建的项目结构如下:
其中SpringBootWebApplication.java是自动生成的。是程序启动入口。
生成的POM.xml文件如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.sample</groupId>
<artifactId>web</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<name>spring-boot-web</name>
<description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>1.5.13.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>在com.example.demo.model中增加实体User
package com.example.demo.model;
public class User {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
private String address;
public User() {
}
public User(Integer id, String name, Integer age, String address) {
super();
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.address = address;
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ", age=" + age + ", address=" + address + "]";
}
}在com.example.demo.controller中增加UserController
package com.example.demo.controller;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import com.example.demo.model.User;
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
@RequestMapping("/{id}")
public String getUser(@PathVariable Integer id,Model model) {
model.addAttribute("user",new User(id,"张三",20,"中国广州"));
return "/user/detail";
}
@RequestMapping("/list")
public String listUser(Model model) {
List<User> userList = new ArrayList<User>();
for (int i = 0; i <10; i++) {
userList.add(new User(i,"张三"+i,20+i,"中国广州"));
}
model.addAttribute("users", userList);
return "/user/list";
}
}增加模版文件list.html,注意模版文件是放在tempplates目录下。本案例将文件放在/templates/user/下面。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>User List</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2>用户列表</h2>
<div>
<ul>
<li th:each="user:${users}">
<span th:text="${user.id}"></span>-
<span th:text="${user.name}"></span>-
<span th:text="${user.age}"></span>-
<span th:text="${user.address}"></span>
</li>
</ul>
</div>
</body>
</html>启动
以Spring Boot App方式启动SpringBootWebApplication.java
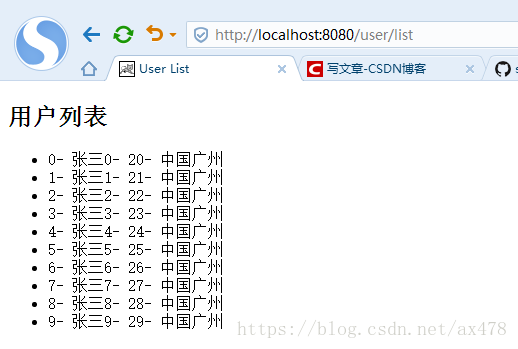
访问http://localhost:8080/user/list ,效果如下
总结
Spring boot开发web项目非常简单,对模版的支持也很到位。Thymeleaf模版引擎跟el表达式很相似,所以从jsp过渡到使用Thymeleaf 并不是太难的事。
本文案例代码下载地址