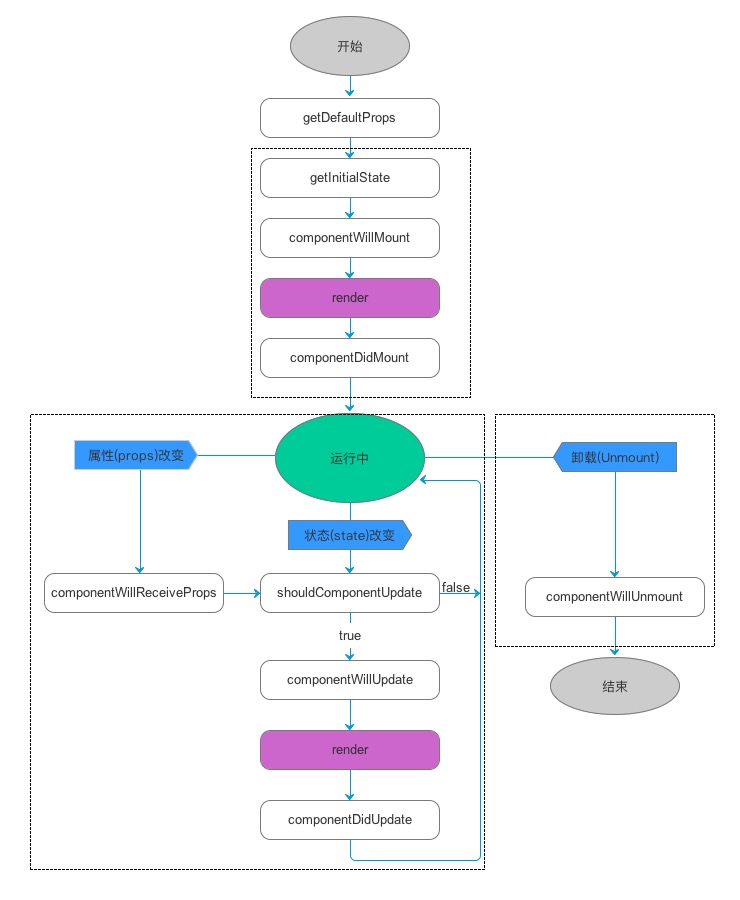
组件生命周期
众所周知,React Native是一个以组件为基本元素的开发框架,系统为我们提供了大量的现成的组件,我们也可以继承系统的Component和PurComponent自定义组件。既然是组件,那它就有自己的生命周期,通过不同的生命周期函数,我们可以干不同的事情。React Native将组件的生命周期分为如下几个阶段,总的概括起来有:挂载、存活和销毁几个阶段,涉及到的生命周期函数可以用下面的图来表示。
下面我们就这些生命周期函数给大家做一个总结。
getDefaultProps
getDefaultProps函数的定义如下:
object getDefaultProps()此方法在对象被创建之前执行,因此不能在方法内调用this.props,被创建的类会有缓存,映射的值会存在this.props。同时,需要注意的是getDefaultProps()返回的对象可以在实例中共享,但是不是复制。
getInitialState
getInitialState函数的定义如下:
object getInitialState()控件加载之前执行,返回值会被用于state的初始化值。
componentWillMount
componentWillMount函数的定义格式如下:
void componentWillMount()此方法在初始化render之前执行,如果在方法内调用setState(),则render()只执行一次。
render
render函数的定义格式如下:
ReactElement render()调用render()方法时,首先检查this.props和this.state返回一个子元素,子元素可以是DOM组件或者其他自定义复合控件的虚拟实现 。
如果不想渲染可以返回null或者false,这种场景下,React渲染一个<noscript>标签,当返回null或者false时,调用ReactDOM.findDOMNode(this)返回null 。
需要注意的是,render()是很纯粹的,之负责界面的渲染工作,如果需要与服务器进行交互,可以将网络请求放在componentDidMount()函数中。
componentDidMount
componentDidMount函数的定义格式如下:
void componentDidMount()在初始化render函数之后执行,且只执行一次,这个方法内可以访问任何组件,如果涉及到嵌套父子组件,则子组件的componentDidMount()方法在父组件之前执行,也就是说父组件的componentDidMount要等子组件的componentDidMount执行完成之后,父组件的componentDidMount才会执行。
shouldComponentUpdate
shouldComponentUpdate的函数定义格式如下:
boolean shouldComponentUpdate(
object nextProps, object nextState
)这个方法在初始化render()时是不会执行,只有当props或者state发生变化时才会执行,并且当发生变化后,shouldComponentUpdate函数在render之前执行,当新的props或者state不需要更新组件时,返回false。
默认情况下,shouldComponentUpdate方法返回true,如果shouldComponentUpdate方法返回false时,将不会执行render()方法,同时componentWillUpdate和componentDidUpdate方法也不会被调用。
componentWillUpdate
componentWillUpdate函数的定义格式如下:
void componentWillUpdate(
object nextProps, object nextState
)此方法在render方法之前执行,该方法执行的条件是当props和state发生变化时才会执行。
需要特别注意的是,在这个函数里面,你不能使用this.setState来修改状态,这样会修改状态机里面的对象的值。
componentDidUpdate
componentDidUpdate函数的格式如下:
void componentDidUpdate(
object prevProps, object prevState
)此函数在组件更新结束之后执行,在初始化render时不执行。
componentWillReceiveProps
componentWillReceiveProps函数的定义格式如下:
void componentWillReceiveProps(
object nextProps
)此函数在props发生变化时执行,在实际使用过程中,你可以根据属性的变化,通过调用this.setState()来更新组件的状态,而旧的属性仍然可以通过this.props来获取。componentWillReceiveProps调用更新状态是安全的,并不会触发额外的render调用。例如:
componentWillReceiveProps: function(nextProps) {
this.setState({
likesIncreasing: nextProps.likeCount > this.props.likeCount
});
}componentWillUnmount
componentWillUnmount函数的格式如下:
void componentWillUnmount()当组件需要从界面上移除的时候,就会调用componentWillUnmount(),即组件的销毁阶段。
实例说明
为了说明和理解React Native组件的执行的顺序和流程,我们可以新建一个js页面,然后分别在函数的生命周期中打印函数。例如:
constructor(props){
super(props);
console.log("constructor")
}
componentWillMount(){
console.log("componentWillMount")
}
componentDidMount(){
console.log("componentDidMount")
}
shouldComponentUpdate(){
console.log("shouldComponentUpdate")
}
componentWillUpdate(){
console.log("componentWillUpdate")
}
componentDidUpdate(){
console.log("componentDidUpdate")
}
componentWillReceiveProps(){
console.log("componentWillReceiveProps")
}
componentWillUnmount(){
console.log("componentWillUnmount")
}然后我们使用远端调试就可以看到相应的执行顺序了。
父子组件传值
很多情况下我们会自定义一些组件,那么父子组件怎么传值呢?记住一句话,组件传值使用props,组件内部使用state状态机。做过Android和ios开发的同学都知道,我们自定义组件的时候,为了方便别人使用,我们都会提供自定义的属性,而React Native的自定义组件也可以使用上面的思路。例如:
import React, {Component} from 'react';
import {
StyleSheet,
Text,
View,
TouchableOpacity,
TextInput
} from 'react-native';
import PropTypes from 'prop-types';
export default class Counter extends Component {
// 构造函数
constructor(props) {
super(props);
// 初始状态
this.state = {
value: this.props.initValue || 1
};
}
// 默认属性
static defaultProps = {
initValue: 1
};
//绘制界面
render() {
}
// 样式文件
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
//样式文件
});
//自定义属性
Counter.propTypes = {
initValue: PropTypes.number,
style: PropTypes.object,
onUpdate: PropTypes.func
};