Spring Security
Spring Security是能够为J2EE项目提供综合性的安全访问控制解决方案的安全框架。它依赖于Servlet过滤器。这些过滤器拦截进入请求,并且在应用程序处理该请求之前进行某些安全处理。
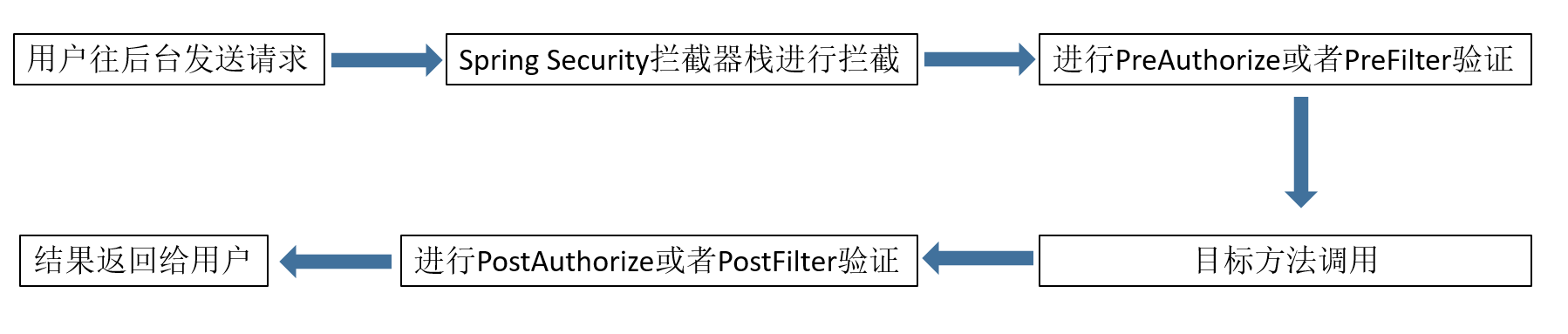
Spring Security对用户请求的拦截过程如下:
- 经过拦截器栈
- 在访问方法前进行Pre拦截
- 方法访问结束后进行Post拦截
其中拦截器栈的拦截主要用来防止恶意攻击、用户Session过期以及粗略的权限拦截。拦截器栈的图如下:
Pre和Post进行真正的权限拦截,它们以注解的形式添加在一个类或者一个方法前,它们主要有一下四种注解:
- @PreAuthorize 当前用户是否有权限调用该方法
- @PostAuthorize 当该方法被调用之后,还要执行哪些操作
- @PreFilter 在方法调用前过滤
- @PosFilter 当该方法被调用之后,会过滤掉不符合条件的返回值
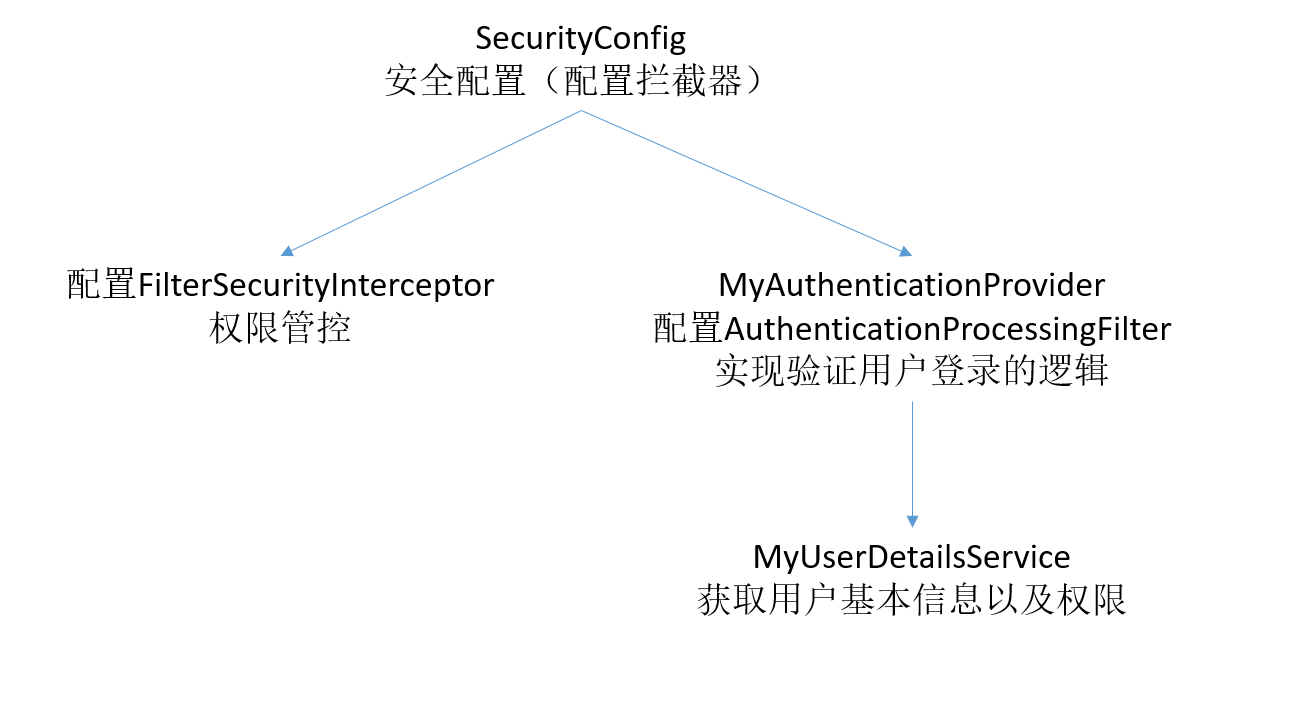
1. 在拦截器栈中,我们主要配置AuthenticationProcessingFilter和FilterSecurityInterceptor这两个过滤器。这几个类的关系如下图所示:
AuthenticationProcessingFilter主要是用来处理form登录请求,我们主要通过实现AuthenticationProvider和UserDetailsService这两个类来重写改过滤器的功能。
FilterSecurityInterceptor拦截器的配置通过继承WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter来配置,同时我们也把AuthenticationProcessingFilter过滤器配置进去。
首先我们来看SecurityConfig,它继承WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter,是配置拦截器的主入口,器代码如下:
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter{
@Autowired
private MyAuthenticationProvider authenticationProvider;//该类实现了用户登录的逻辑
@Autowired
private CustomAuthenticationSuccessHandler authenticationSuccessionHandler;//对用户成功登录后的处理
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth)
throws Exception {
auth.authenticationProvider(authenticationProvider);//配置用户登录过滤器
}
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {//FilterSecurityInterceptor拦截器做配置
http.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/login").permitAll()
.requestMatchers(CorsUtils::isPreFlightRequest).permitAll()//处理跨域请求中的Preflight请求
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and().formLogin().permitAll()
.and().formLogin().successHandler(authenticationSuccessionHandler)//配置登录成功后的Handler
.and().formLogin().failureUrl("http://localhost:63342/yjsy-ui/build/login/login.html")//配置用户登录失败后的跳转页面
.and().csrf().disable();
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
在用户登录逻辑中,我们能够获取到用户通过表单提交过来的所有数据,然后进行逻辑验证,并通过UserDetailsService接口来获取用户权限。
2. Pre和Post的写法如下:
@PreAuthorize("hasMethodPrivilege('ExamDelete')")//类似这样
@RequestMapping(value = "/delete-exam", method = DELETE)
@ResponseBody
public Page<Exam> delete(@RequestParam int id,
@RequestParam(value = "page",defaultValue = PAGE_PAGE) Integer page,
@RequestParam(value = "size",defaultValue = PAGE_SIZE) Integer size) {
service.delete(id);
return this.getPage(page, size);
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
可以看到,在@PreAuthorize方法中,我们通过字符串的形式调用了hasMethodPrivilege方法,这个方法的参数是一个String类型的参数,我们也可用通过hasMethodPrivilege('#id')的形式传入前端传送过来的参数。然后Spring Security会通过反射来调用该方法。
那么这个方法我们应该写在哪里呢?
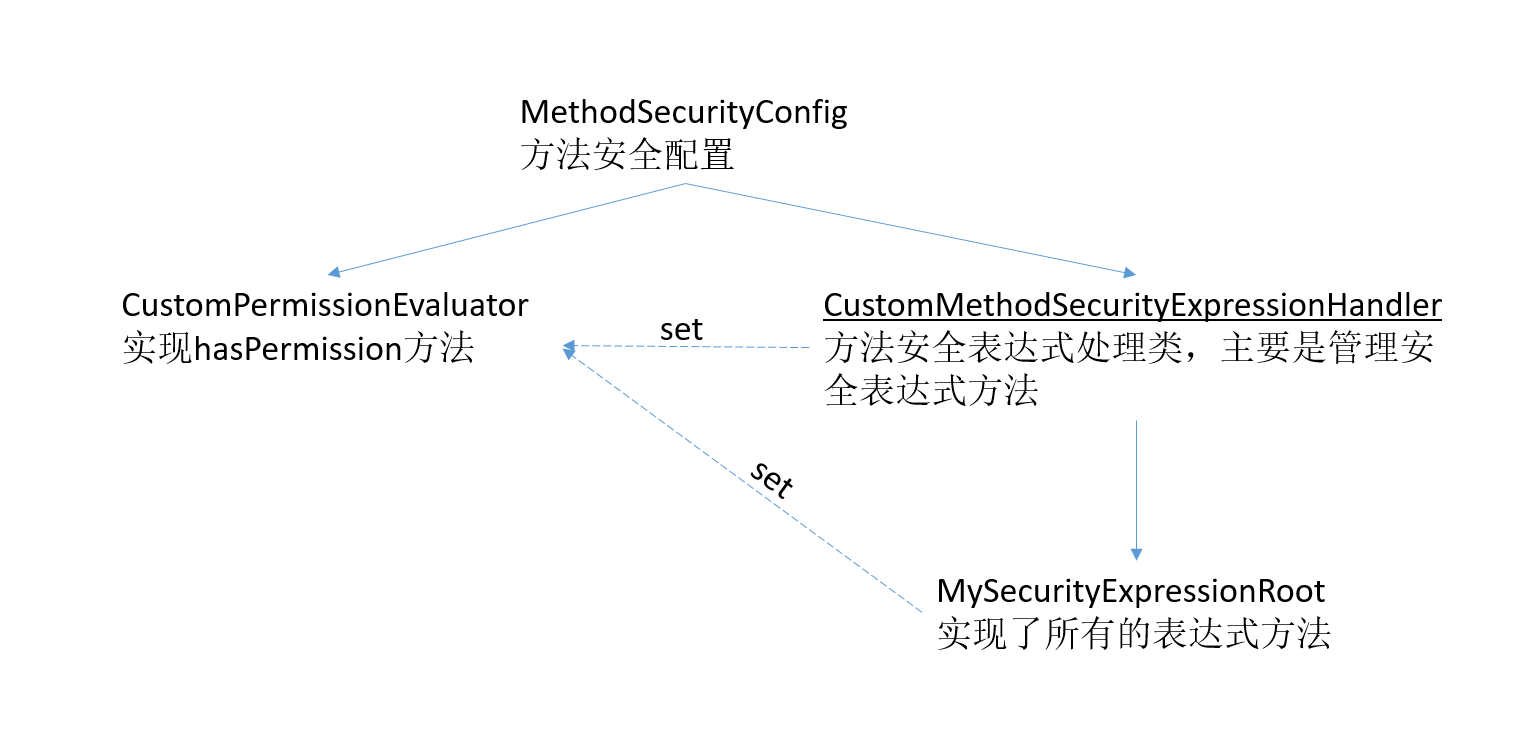
我们需要一个配置方法MethodSecurityConfig,这个方法继承自GlobalMethodSecurityConfiguration,在这里对表达式进行配置。
这几个类的关系如下图所示:
首先我们来看MethodSecurityConfig类:
@Configuration
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled = true)
public class MethodSecurityConfig extends GlobalMethodSecurityConfiguration{
@Autowired
private CustomPermissionEvaluator cpe;//用来重写hasPermission表达式
@Autowired
private CustomMethodSecurityExpressionHandler expressionHandler;//用来配置表达式
@Override
protected MethodSecurityExpressionHandler createExpressionHandler() {
expressionHandler.setPermissionEvaluator(cpe);
return expressionHandler;
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
CustomPermissionEvaluator类主要是用来重写hasPermiss方法,而真正的配置在CustomMethodSecurityExpressionHandler中。
下面我们来看CustomMethodSecurityExpressionHandler的代码:
@Service
public class CustomMethodSecurityExpressionHandler
extends DefaultMethodSecurityExpressionHandler {
private final AuthenticationTrustResolver trustResolver = new AuthenticationTrustResolverImpl();
@Autowired
private MySecurityExpressionRoot root;//我们要在这个类中写表达式
@Autowired
private CustomPermissionEvaluator cpe;//还是hasPermission的表达式
@Override
protected MethodSecurityExpressionOperations createSecurityExpressionRoot(
Authentication authentication, MethodInvocation invocation) {
root.setAuthentication(authentication);
root.setPermissionEvaluator(cpe);
root.setTrustResolver(this.trustResolver);
root.setRoleHierarchy(getRoleHierarchy());
return root;
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
下面看MySecurityExpressionRoot类:
@Component
public class MySecurityExpressionRoot
implements MethodSecurityExpressionOperations {
public final boolean permitAll = true;
public final boolean denyAll = false;
private String defaultRolePrefix = "ROLE_";
protected Authentication authentication;
private AuthenticationTrustResolver trustResolver;
private RoleHierarchy roleHierarchy;
private Set<String> roles;
private PermissionEvaluator permissionEvaluator;
private Object filterObject;
private Object returnObject;
public void setAuthentication(Authentication authentication) {
if (authentication == null) { throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Authentication object cannot be null"); }
this.authentication = authentication;
}
public boolean hasPagePrivilege(String privilege) {//这就是我们定义的方法,其他方法我们可以拷贝过来,在这里我们可以注入任何Component,具有很大的灵活性
for (GrantedAuthority authority : authentication.getAuthorities()) {
if (authority.getAuthority().equals(privilege)) return true;
}
return false;
}
@Override
public final boolean hasAuthority(String authority) {
throw new RuntimeException("method hasAuthority() not allowed");
}
@Override
public final boolean hasAnyAuthority(String... authorities) {
return hasAnyAuthorityName(null, authorities);
}
@Override
public final boolean hasRole(String role) {
return hasAnyRole(role);
}
@Override
public final boolean hasAnyRole(String... roles) {
return hasAnyAuthorityName(defaultRolePrefix, roles);
}
private boolean hasAnyAuthorityName(String prefix, String... roles) {
final Set<String> roleSet = getAuthoritySet();
for (final String role : roles) {
final String defaultedRole = getRoleWithDefaultPrefix(prefix, role);
if (roleSet.contains(defaultedRole)) { return true; }
}
return false;
}
@Override
public final Authentication getAuthentication() {
return authentication;
}
@Override
public final boolean permitAll() {
return true;
}
@Override
public final boolean denyAll() {
return false;
}
@Override
public final boolean isAnonymous() {
return trustResolver.isAnonymous(authentication);
}
@Override
public final boolean isAuthenticated() {
return !isAnonymous();
}
@Override
public final boolean isRememberMe() {
return trustResolver.isRememberMe(authentication);
}
@Override
public final boolean isFullyAuthenticated() {
return !trustResolver.isAnonymous(authentication)
&& !trustResolver.isRememberMe(authentication);
}
public Object getPrincipal() {
return authentication.getPrincipal();
}
public void setTrustResolver(AuthenticationTrustResolver trustResolver) {
this.trustResolver = trustResolver;
}
public void setRoleHierarchy(RoleHierarchy roleHierarchy) {
this.roleHierarchy = roleHierarchy;
}
private Set<String> getAuthoritySet() {
if (roles == null) {
roles = new HashSet<String>();
Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> userAuthorities = authentication
.getAuthorities();
if (roleHierarchy != null) {
userAuthorities = roleHierarchy
.getReachableGrantedAuthorities(userAuthorities);
}
roles = AuthorityUtils.authorityListToSet(userAuthorities);
}
return roles;
}
@Override
public boolean hasPermission(Object target, Object permission) {
return permissionEvaluator.hasPermission(authentication, target,
permission);
}
@Override
public boolean hasPermission(Object targetId, String targetType,
Object permission) {
return permissionEvaluator.hasPermission(authentication,
(Serializable) targetId, targetType, permission);
}
public void setPermissionEvaluator(
PermissionEvaluator permissionEvaluator) {
this.permissionEvaluator = permissionEvaluator;
}
private static String getRoleWithDefaultPrefix(String defaultRolePrefix,
String role) {
if (role == null) { return role; }
if ((defaultRolePrefix == null)
|| (defaultRolePrefix.length() == 0)) { return role; }
if (role.startsWith(defaultRolePrefix)) { return role; }
return defaultRolePrefix + role;
}
@Override
public Object getFilterObject() {
return this.filterObject;
}
@Override
public Object getReturnObject() {
return this.returnObject;
}
@Override
public Object getThis() {
return this;
}
@Override
public void setFilterObject(Object obj) {
this.filterObject = obj;
}
@Override
public void setReturnObject(Object obj) {
this.returnObject = obj;
}
}转自:https://blog.csdn.net/dalangzhonghangxing/article/details/53024640