一、解决了什么问题:
求得两个颜色之间颜色渐变的RGB。
二、公式:
Gradient = A + (B-A) / Step * N
编程时为了提高效率避免浮点运算,往往把除法放在最后面,这样公式就成了:Gradient = A + (B-A) * N / Step
注:Gradient表示第N步的R/G/B的值,A、B、Step表示从颜色A分Step步渐变为颜色B。
三、计算过程:
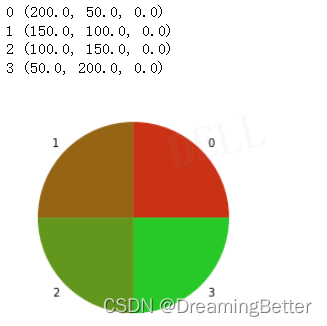
设Step=3,将RGB(200,50,0)颜色渐变为RGB(50,200,0),即:RGB(200,50,0)经过3次颜色渐变转为RGB(50,200,0)
第0次转换,即RGB(200,50,0)本身:
R0 = 200 + (50 - 200) / 3 * 0 = 200
G0 = 50 + (200 - 50) / 3 * 0 = 50
B0 = 0 + (0 - 0) / 3 * 0 = 0
RGB0 = (200, 50, 0)
第1次转换:
R1 = 200 + (50 - 200)/ 3 * 1 = 150
G1 = 50 + (200 - 50) / 3 * 1 = 100
B1 = 0 + (0 - 0) / 3 * 1 = 0
RGB1 = (150, 100, 0)
第2次转换:
R2 = 200 + (50 - 200)/ 3 * 2 = 100
G2 = 50 + (200 - 50) / 3 * 2 = 150
B2 = 0 + (0 - 0) / 3 * 2 = 0
RBG2 = (100, 150, 0)
第3次转换,即目标颜色RGB(50,200,0):
R3 = 200 + (50 - 200)/ 3 * 3 = 50
G3 = 50 + (200 - 50) / 3 * 3 = 200
B3 = 0 + (0 - 0) / 3 * 3 = 0
RBG3 = (50, 200, 0)
四、代码
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
step = 3 # 经过step步到达目标颜色
color_num = step + 1
one = np.ones(color_num)
from_rgb = (200,50,0) # 起始颜色
to_rbg = (50,200,0) # 目标颜色
colors = [((from_rgb[0] + (to_rbg[0]-from_rgb[0])/step*i),
(from_rgb[1] + (to_rbg[1]-from_rgb[1])/step*i),
(from_rgb[2] + (to_rbg[2]-from_rgb[2])/step*i))
for i in range(color_num)]
for index, color in enumerate(colors):
print(index, color)
colors = [((from_rgb[0] + (to_rbg[0]-from_rgb[0])/step*i) / 255,
(from_rgb[1] + (to_rbg[1]-from_rgb[1])/step*i) / 255,
(from_rgb[2] + (to_rbg[2]-from_rgb[2])/step*i) / 255)
for i in range(color_num)]
plt.pie(one, labels=range(color_num), colors=colors) # colors要求是0-1的浮点数
plt.show()
结果与颜色展示:
五、举一反三
下面对step、起始颜色、目标颜色进行修改,细分更多步骤的变化展示。
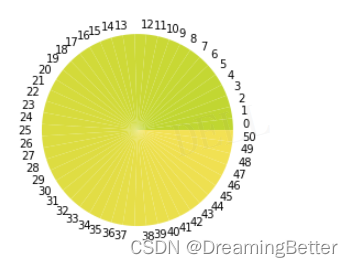
例1:
step = 50
from_rgb = (193, 214, 6)
to_rbg = (244, 225, 67)
例2:
step = 50
from_rgb = (244, 225, 67)
to_rbg = (227, 118, 0)