基本介绍
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor 是 Java 并发包中的一个可调度线程池,它继承自 ThreadPoolExecutor 类,并实现了 ScheduledExecutorService 接口。该线程池可以根据任务的执行时间进行调度执行,支持周期性任务和延迟执行任务。
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor
继层关系:
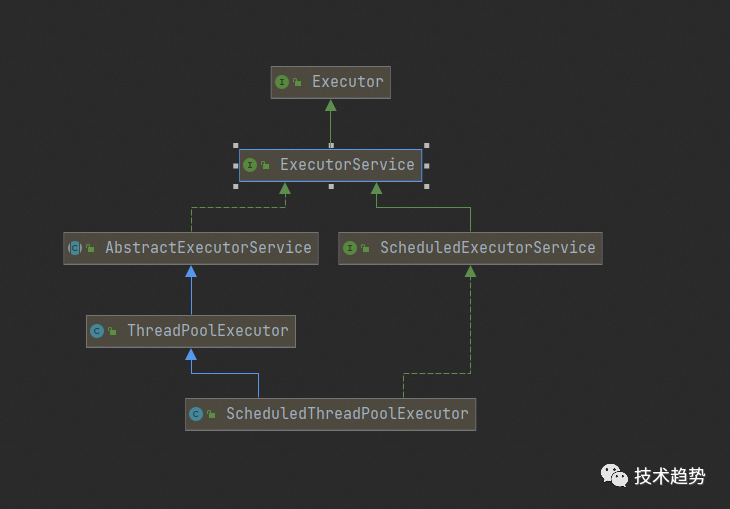
可以看出ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor继承于ThreadPoolExecutor与ScheduledExecutorService。
基本使用
package com.executor;
import java.util.concurrent.ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* @ClassName ScheduledThreadPoolExecutorStudy
* @Description 定时任务线程池
* @Author csh
* @Date 2023/4/7 9:52
*/
public class ScheduledThreadPoolExecutorStudy {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//corePoolSize指线程
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor executor = new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(1);
//延迟一秒执行
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
executor.schedule(new Task(i,"任务1:"),1, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
//周期性执行 每隔3秒(period) 延迟0秒(initialDelay) 定时任务
//period 用于间隔执行任务,
//1.执行时间小于period:执行完后再隔period时间再执行下一批;
//2.执行时间大于period:执行完后不会再隔period时间,而是直接执行。
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
executor.scheduleAtFixedRate(new Task(i,"任务2:"),0,3,TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
//周期性执行 每隔15秒(delay) 延迟0秒(initialDelay)
//initialDelay 首次启动延迟多久后执行
//delay 下次任务执行前的延迟时间
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
executor.scheduleWithFixedDelay(new Task(i,"任务3:"),3,1,TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
}
static class Task implements Runnable {
private int taskId;
private String taskName="默认!";
public Task(int taskId) {
this.taskId = taskId;
}
public Task(int taskId, String taskName) {
this.taskId = taskId;
this.taskName = taskName;
}
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(taskName + taskId + "开始执行,当前线程名为" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
try {
// 模拟任务执行的耗时
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(taskName + taskId + "执行完毕,当前线程名为" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}
}结果
任务2:0开始执行,当前线程名为pool-1-thread-1
任务2:0执行完毕,当前线程名为pool-1-thread-1
任务2:1开始执行,当前线程名为pool-1-thread-1
任务2:1执行完毕,当前线程名为pool-1-thread-1
任务2:2开始执行,当前线程名为pool-1-thread-1
任务2:2执行完毕,当前线程名为pool-1-thread-1
任务2:3开始执行,当前线程名为pool-1-thread-1
任务2:3执行完毕,当前线程名为pool-1-thread-1
任务2:4开始执行,当前线程名为pool-1-thread-1
任务2:4执行完毕,当前线程名为pool-1-thread-1
任务2:5开始执行,当前线程名为pool-1-thread-1
任务2:5执行完毕,当前线程名为pool-1-thread-1
任务2:6开始执行,当前线程名为pool-1-thread-1
任务2:6执行完毕,当前线程名为pool-1-thread-1
任务2:7开始执行,当前线程名为pool-1-thread-1
任务2:7执行完毕,当前线程名为pool-1-thread-1
任务2:8开始执行,当前线程名为pool-1-thread-1
任务2:8执行完毕,当前线程名为pool-1-thread-1
任务2:9开始执行,当前线程名为pool-1-thread-1
任务2:9执行完毕,当前线程名为pool-1-thread-1
任务1:0开始执行,当前线程名为pool-1-thread-1
任务1:0执行完毕,当前线程名为pool-1-thread-1
任务1:1开始执行,当前线程名为pool-1-thread-1
任务1:1执行完毕,当前线程名为pool-1-thread-1
任务1:2开始执行,当前线程名为pool-1-thread-1
任务1:2执行完毕,当前线程名为pool-1-thread-1
任务1:3开始执行,当前线程名为pool-1-thread-1
任务1:3执行完毕,当前线程名为pool-1-thread-1
任务1:4开始执行,当前线程名为pool-1-thread-1
任务1:4执行完毕,当前线程名为pool-1-thread-1
任务1:5开始执行,当前线程名为pool-1-thread-1
任务1:5执行完毕,当前线程名为pool-1-thread-1
任务1:6开始执行,当前线程名为pool-1-thread-1
任务1:6执行完毕,当前线程名为pool-1-thread-1
任务1:7开始执行,当前线程名为pool-1-thread-1
任务1:7执行完毕,当前线程名为pool-1-thread-1
任务1:8开始执行,当前线程名为pool-1-thread-1
任务1:8执行完毕,当前线程名为pool-1-thread-1
任务1:9开始执行,当前线程名为pool-1-thread-1
任务1:9执行完毕,当前线程名为pool-1-thread-1
任务2:0开始执行,当前线程名为pool-1-thread-1
任务2:0执行完毕,当前线程名为pool-1-thread-1
任务2:1开始执行,当前线程名为pool-1-thread-1
任务2:1执行完毕,当前线程名为pool-1-thread-1
任务2:2开始执行,当前线程名为pool-1-thread-1
任务2:2执行完毕,当前线程名为pool-1-thread-1
任务2:3开始执行,当前线程名为pool-1-thread-1
任务2:3执行完毕,当前线程名为pool-1-thread-1
任务2:4开始执行,当前线程名为pool-1-thread-1
任务2:4执行完毕,当前线程名为pool-1-thread-1
任务2:5开始执行,当前线程名为pool-1-thread-1
任务2:5执行完毕,当前线程名为pool-1-thread-1
任务2:6开始执行,当前线程名为pool-1-thread-1
任务2:6执行完毕,当前线程名为pool-1-thread-1
任务2:7开始执行,当前线程名为pool-1-thread-1
任务2:7执行完毕,当前线程名为pool-1-thread-1
任务2:8开始执行,当前线程名为pool-1-thread-1
任务2:8执行完毕,当前线程名为pool-1-thread-1
任务2:9开始执行,当前线程名为pool-1-thread-1
任务2:9执行完毕,当前线程名为pool-1-thread-1
任务3:0开始执行,当前线程名为pool-1-thread-1
任务3:0执行完毕,当前线程名为pool-1-thread-1
任务3:1开始执行,当前线程名为pool-1-thread-1
任务3:1执行完毕,当前线程名为pool-1-thread-1
任务3:2开始执行,当前线程名为pool-1-thread-1
任务3:2执行完毕,当前线程名为pool-1-thread-1
任务3:3开始执行,当前线程名为pool-1-thread-1
任务3:3执行完毕,当前线程名为pool-1-thread-1
任务3:4开始执行,当前线程名为pool-1-thread-1
任务3:4执行完毕,当前线程名为pool-1-thread-1
任务3:5开始执行,当前线程名为pool-1-thread-1
任务3:5执行完毕,当前线程名为pool-1-thread-1
任务3:6开始执行,当前线程名为pool-1-thread-1
任务3:6执行完毕,当前线程名为pool-1-thread-1
任务3:7开始执行,当前线程名为pool-1-thread-1
任务3:7执行完毕,当前线程名为pool-1-thread-1
任务3:8开始执行,当前线程名为pool-1-thread-1
任务3:8执行完毕,当前线程名为pool-1-thread-1
任务3:9开始执行,当前线程名为pool-1-thread-1
任务3:9执行完毕,当前线程名为pool-1-thread-1
任务2:0开始执行,当前线程名为pool-1-thread-1
任务2:0执行完毕,当前线程名为pool-1-thread-1
任务2:1开始执行,当前线程名为pool-1-thread-1
任务2:1执行完毕,当前线程名为pool-1-thread-1源码学习
package java.util.concurrent;
import static java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicLong;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
import java.util.*;
//ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor 是一个可以定时或延迟执行任务的线程池,通过继承ThreadPoolExecutor和实现ScheduledExecutorService 的基础来实现功能。
public class ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor
extends ThreadPoolExecutor
implements ScheduledExecutorService {
/**
1 实现 ThreadPoolExecutor。使用自定义任务类型,ScheduledFutureTask 用于任务,即使是那些不需要调度的任务(即那些使用 ExecutorService 执行,而不是 ScheduledExecutorService 方法提交的任务),它们被视为延迟为零的延迟任务。
2. 使用自定义队列(DelayedWorkQueue),这是无限 DelayQueue 的变体。与 ThreadPoolExecutor 相比,缺乏容量约束以及 corePoolSize 和 maximumPoolSize 实际上相同的事实简化了一些执行机制(请参阅延迟执行)。
3. 支持可选的关机后运行参数,导致覆盖关机方法以删除和取消关机后不应运行的任务,以及任务(重新)提交与关机重叠时不同的重检逻辑。
4. 允许拦截和检测的任务修饰方法,这是必需的,因为子类无法以其他方式覆盖提交方法来获得此效果。不过,这些对池控制逻辑没有任何影响。
**/
/**
* 默认为false
用于shutDown周期性任务,若如为true则代码为周期性任务。(也用于判断是否关闭)
*/
private volatile boolean continueExistingPeriodicTasksAfterShutdown;
/**
*线程池停止后:取消不是周期任务则为false,返之为true(默认)
*/
private volatile boolean executeExistingDelayedTasksAfterShutdown = true;
/**
* 是否将取消的任务移出队列,默认不移出
*/
private volatile boolean removeOnCancel = false;
/**
* 通过原子子来保证先进先出
*/
private static final AtomicLong sequencer = new AtomicLong();
/**
* 返回当前纳秒时间
*/
final long now() {
return System.nanoTime();
}
//定时任务的实现
private class ScheduledFutureTask<V>
extends FutureTask<V> implements RunnableScheduledFuture<V> {
/** 先进先出的序列号用于断开连接 */
private final long sequenceNumber;
/** 纳秒时间 */
private long time;
/**
* 重复任务的周期(以纳秒为单位)。
* 正值表示固定速率执行。
* 负值表示固定延迟执行。
值 0 表示非重复任务。
*/
private final long period;
/** 当前任务 */
RunnableScheduledFuture<V> outerTask = this;
/**
* 队列的索引
*/
int heapIndex;
/**
*构造方法
* ns 纳秒
* r r任务
* result 返回结果
*
*/
ScheduledFutureTask(Runnable r, V result, long ns) {
super(r, result);
this.time = ns;
this.period = 0;
this.sequenceNumber = sequencer.getAndIncrement();
}
/**
* 构造方法
*/
ScheduledFutureTask(Runnable r, V result, long ns, long period) {
super(r, result);
this.time = ns;
this.period = period;
this.sequenceNumber = sequencer.getAndIncrement();
}
/**
* 构造方法
*/
ScheduledFutureTask(Callable<V> callable, long ns) {
super(callable);
this.time = ns;
this.period = 0;
this.sequenceNumber = sequencer.getAndIncrement();
}
/** 获取延迟的纳秒时间**/
public long getDelay(TimeUnit unit) {
return unit.convert(time - now(), NANOSECONDS);
}
/**对比方法 传入的对象与当前的对象判断是否相同 ,相同返回0 不相同返回 **/
public int compareTo(Delayed other) {
//相同返回0
if (other == this) // compare zero if same object
return 0;
//判断是否ScheduledFutureTask类型
if (other instanceof ScheduledFutureTask) {
//转换成任务
ScheduledFutureTask<?> x = (ScheduledFutureTask<?>)other;
//获取减后时间
long diff = time - x.time;
//如果小于0 返回-1
if (diff < 0)
return -1;
//大于0返回 1
else if (diff > 0)
return 1;
//当前序号小于传进来参数序号 返回-1
else if (sequenceNumber < x.sequenceNumber)
return -1;
else
//都不是返回1
return 1;
}
//最后通过延迟时间计算返回
long diff = getDelay(NANOSECONDS) - other.getDelay(NANOSECONDS);
return (diff < 0) ? -1 : (diff > 0) ? 1 : 0;
}
/**
*判断是否延迟执行
*
* @return {@code true} if periodic
*/
public boolean isPeriodic() {
return period != 0;
}
/**
* 设置下次为定期任务运行的时间。
*/
private void setNextRunTime() {
long p = period;
if (p > 0)
time += p;
else
time = triggerTime(-p);
}
//取消任务
public boolean cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning) {
//取消任务
boolean cancelled = super.cancel(mayInterruptIfRunning);
//取消成功 且 删除标识为真 且 队列索引大于0则进行队列移除
if (cancelled && removeOnCancel && heapIndex >= 0)
remove(this);
return cancelled;
}
/**
*执行的方法
*/
public void run() {
//获取是否重复任务标识 true为是 false为否
boolean periodic = isPeriodic();
//判断线程池状态不支持执行任务,则取消
if (!canRunInCurrentRunState(periodic))
cancel(false);
//不需要重复执行,则直接调用run方法运行
else if (!periodic)
ScheduledFutureTask.super.run();
//重复执行 调用后置
else if (ScheduledFutureTask.super.runAndReset()) {
//计算下次触发时间
setNextRunTime();
//重新加入执行队列
reExecutePeriodic(outerTask);
}
}
}
/**
* periodic 是否重复周期
返回当然运行或关闭状态
*/
boolean canRunInCurrentRunState(boolean periodic) {
return isRunningOrShutdown(periodic ?
continueExistingPeriodicTasksAfterShutdown :
executeExistingDelayedTasksAfterShutdown);
}
/**
* 延迟或周期性任务的主要执行方法。如果池已关闭,则拒绝任务。
否则,将任务添加到队列并启动线程(如有必要)以运行它。
*
* @param task the task
*/
private void delayedExecute(RunnableScheduledFuture<?> task) {
//是否关闭
if (isShutdown())
//调用拒绝执行策略
reject(task);
else {
//不关闭情况下,将任务添加进了队列中
super.getQueue().add(task);
//再次判断是否关闭(有可能中间关了) 且
if (isShutdown() && 当前运行状态为已关闭
!canRunInCurrentRunState(task.isPeriodic()) &&
//从队列移除
remove(task))
//取消此次任务
task.cancel(false);
else
//预启动线程池中的工作线程
ensurePrestart();
}
}
/**
*重新执行指定的周期性任务,并将该任务插入到任务队列中。
*
* @param task the task
*/
void reExecutePeriodic(RunnableScheduledFuture<?> task) {
//判断是否允许执行的状态
if (canRunInCurrentRunState(true)) {
//加入队列
super.getQueue().add(task);
//再次判断如果为直就移除和取消任务
if (!canRunInCurrentRunState(true) && remove(task))
task.cancel(false);
else
//预启动线程池中的工作线程
ensurePrestart();
}
}
/**
* 取消并关闭线程池的方法
*/
@Override void onShutdown() {
//获取当前队列
BlockingQueue<Runnable> q = super.getQueue();
//获取延迟状态
boolean keepDelayed =
getExecuteExistingDelayedTasksAfterShutdownPolicy();
//获取周期任务状态
boolean keepPeriodic =
getContinueExistingPeriodicTasksAfterShutdownPolicy();
//不是延迟状态且不是周期任务
if (!keepDelayed && !keepPeriodic) {
//循环全部取消及清空
for (Object e : q.toArray())
if (e instanceof RunnableScheduledFuture<?>)
((RunnableScheduledFuture<?>) e).cancel(false);
q.clear();
}
else {
// Traverse snapshot to avoid iterator exceptions
//如果是周期的先获取列表
for (Object e : q.toArray()) {
//如果为RunnableScheduledFuture类型
if (e instanceof RunnableScheduledFuture) {
//转换
RunnableScheduledFuture<?> t =
(RunnableScheduledFuture<?>)e;
//全部删阴笑后取消当前任务
if ((t.isPeriodic() ? !keepPeriodic : !keepDelayed) ||
t.isCancelled()) { // also remove if already cancelled
if (q.remove(t))
t.cancel(false);
}
}
}
}
tryTerminate();
}
/**
* 修改或替换用于执行可运行对象的任务。(用于包装)
*/
protected <V> RunnableScheduledFuture<V> decorateTask(
Runnable runnable, RunnableScheduledFuture<V> task) {
return task;
}
//同上类似
protected <V> RunnableScheduledFuture<V> decorateTask(
Callable<V> callable, RunnableScheduledFuture<V> task) {
return task;
}
//构造方法 指定核心数
public ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize) {
super(corePoolSize, Integer.MAX_VALUE, 0, NANOSECONDS,
new DelayedWorkQueue());
}
//构造方法
//corePoolSize 核心数
//threadFactory 线程工厂
public ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
ThreadFactory threadFactory) {
super(corePoolSize, Integer.MAX_VALUE, 0, NANOSECONDS,
new DelayedWorkQueue(), threadFactory);
}
//构造方法
//corePoolSize 核心数
//handler 失败策略
public ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
RejectedExecutionHandler handler) {
super(corePoolSize, Integer.MAX_VALUE, 0, NANOSECONDS,
new DelayedWorkQueue(), handler);
}
//构造方法
//corePoolSize 核心数
//threadFactory 线程工厂
//handler 失败策略
public ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
ThreadFactory threadFactory,
RejectedExecutionHandler handler) {
super(corePoolSize, Integer.MAX_VALUE, 0, NANOSECONDS,
new DelayedWorkQueue(), threadFactory, handler);
}
/**
* 返回延迟操作的触发时间
*/
private long triggerTime(long delay, TimeUnit unit) {
//最小为0
return triggerTime(unit.toNanos((delay < 0) ? 0 : delay));
}
/**
* 计算时间 当前时间+延迟时间
*/
long triggerTime(long delay) {
return now() +
((delay < (Long.MAX_VALUE >> 1)) ? delay : overflowFree(delay));
}
/**
* 将队列中所有延迟的值限制在彼此的 Long.MAX_VALUE 范围内,以避免在比较中溢出。
*/
private long overflowFree(long delay) {
Delayed head = (Delayed) super.getQueue().peek();
if (head != null) {
long headDelay = head.getDelay(NANOSECONDS);
if (headDelay < 0 && (delay - headDelay < 0))
delay = Long.MAX_VALUE + headDelay;
}
return delay;
}
/**
* 定时执行方法
* command 执行任务
* delay 延迟时间
* unit 延迟时间单位
*/
public ScheduledFuture<?> schedule(Runnable command,
long delay,
TimeUnit unit) {
//为空进行异常 抛出
if (command == null || unit == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
//包装一下
RunnableScheduledFuture<?> t = decorateTask(command,
//定时任务包装
new ScheduledFutureTask<Void>(command, null,
//获取延迟执行时间
triggerTime(delay, unit)));
//延迟执行
delayedExecute(t);
//返回包装后的对象
return t;
}
/**
* 同上类似
*/
public <V> ScheduledFuture<V> schedule(Callable<V> callable,
long delay,
TimeUnit unit) {
if (callable == null || unit == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
RunnableScheduledFuture<V> t = decorateTask(callable,
new ScheduledFutureTask<V>(callable,
triggerTime(delay, unit)));
delayedExecute(t);
return t;
}
/**
* 周期性执行 每隔x秒(period) 延迟x秒(initialDelay) 定时任务
* //period 用于间隔执行任务,
* //1.执行时间小于period:执行完后再隔period时间再执行下一批;
* //2.执行时间大于period:执行完后不会再隔period时间,而是直接执行。
*/
public ScheduledFuture<?> scheduleAtFixedRate(Runnable command,
long initialDelay,
long period,
TimeUnit unit) {
//任务或单为空抛出空指针异常
if (command == null || unit == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
//如果延迟时间小于等于0则抛出异常
if (period <= 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
//创建任务
ScheduledFutureTask<Void> sft =
new ScheduledFutureTask<Void>(command,
null,
triggerTime(initialDelay, unit),
unit.toNanos(period));
//包装任务
RunnableScheduledFuture<Void> t = decorateTask(command, sft);
//初始化周期任务属性
sft.outerTask = t;
//执行任务
delayedExecute(t);
//返回封装后对象
return t;
}
/**
* 周期性执行 每隔x秒(delay) 延迟0秒(initialDelay)
//initialDelay 首次启动延迟多久后执行
//delay 下次任务执行前的延迟时间
*/
public ScheduledFuture<?> scheduleWithFixedDelay(Runnable command,
long initialDelay,
long delay,
TimeUnit unit) {
if (command == null || unit == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
if (delay <= 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
ScheduledFutureTask<Void> sft =
new ScheduledFutureTask<Void>(command,
null,
triggerTime(initialDelay, unit),
unit.toNanos(-delay));
RunnableScheduledFuture<Void> t = decorateTask(command, sft);
//初始化周期任务属性
sft.outerTask = t;
//执行任务
delayedExecute(t);
return t;
}
//无返回 零延迟执行任务
public void execute(Runnable command) {
schedule(command, 0, NANOSECONDS);
}
// Override AbstractExecutorService methods
//有返回 零延迟执行任务
public Future<?> submit(Runnable task) {
return schedule(task, 0, NANOSECONDS);
}
//带指定返回结果 的提交
public <T> Future<T> submit(Runnable task, T result) {
return schedule(Executors.callable(task, result), 0, NANOSECONDS);
}
//同上类似
public <T> Future<T> submit(Callable<T> task) {
return schedule(task, 0, NANOSECONDS);
}
/**
* 设置是否继续执行现有定期任务的策略。
*/
public void setContinueExistingPeriodicTasksAfterShutdownPolicy(boolean value) {
continueExistingPeriodicTasksAfterShutdown = value;
if (!value && isShutdown())
onShutdown();
}
/**
* 获取有关是否继续执行现有定期任务的策略
*/
public boolean getContinueExistingPeriodicTasksAfterShutdownPolicy() {
return continueExistingPeriodicTasksAfterShutdown;
}
/**
*设置是否执行现有延迟任务的策略,即使此执行程序已关闭。
在这种情况下,这些任务只会在 shutdownNow 时终止,或者在已关闭时将策略设置为 false 后终止。
默认情况下,此值为 true。
*/
public void setExecuteExistingDelayedTasksAfterShutdownPolicy(boolean value) {
executeExistingDelayedTasksAfterShutdown = value;
if (!value && isShutdown())
onShutdown();
}
/**
* 获取有关是否执行现有延迟任务的策略,即使此执行程序已关闭。
在这种情况下,这些任务只会在 shutdownNow 时终止,或者在已关闭时将策略设置为 false 后终止。
*/
public boolean getExecuteExistingDelayedTasksAfterShutdownPolicy() {
return executeExistingDelayedTasksAfterShutdown;
}
/**
* 设置在取消时是否应立即从工作队列中删除已取消任务的策略。
*/
public void setRemoveOnCancelPolicy(boolean value) {
removeOnCancel = value;
}
/**
* 获取有关在取消时是否应立即从工作队列中删除已取消任务的策略。
*/
public boolean getRemoveOnCancelPolicy() {
return removeOnCancel;
}
/**
* 关闭线程池方法(延迟)
*/
public void shutdown() {
super.shutdown();
}
/**
* 立即关闭线程池方法并返回任务列表
*/
public List<Runnable> shutdownNow() {
return super.shutdownNow();
}
/**
* 获取阻塞队列
*/
public BlockingQueue<Runnable> getQueue() {
return super.getQueue();
}
/**
*延迟队列 的实现
* 注意:DelayedWorkQueue 是基于堆结构的队列。底层使用的是数组
*/
static class DelayedWorkQueue extends AbstractQueue<Runnable>
implements BlockingQueue<Runnable> {
/*
*DelayedWorkQueue 基于基于堆的数据结构,如 DelayQueue 和 PriorityQueue 中的数据结构,不同之处在于每个 ScheduledFutureTask 还将其索引记录到堆数组中。
这消除了在取消时查找任务的需要,大大加快了删除速度(从 O(n) 下降到 O(log n)),并减少了垃圾保留,否则在清除之前等待元素上升到顶部会发生这种情况。
但是由于队列也可能包含不是 ScheduledFutureTasks 的 RunnableScheduledFutures,因此我们不能保证有这样的索引可用,在这种情况下,我们回退到线性搜索。
(我们预计大多数任务不会被修饰,并且更快的情况将更加常见。所有堆操作都必须记录索引更改 - 主要是在 siftUp 和 siftDown 中。删除后,任务的堆索引设置为 -1。
*/
//队列的初始容量
private static final int INITIAL_CAPACITY = 16;
//队列
private RunnableScheduledFuture<?>[] queue =
new RunnableScheduledFuture<?>[INITIAL_CAPACITY];
//重入锁
private final ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
//队列当前长度
private int size = 0;
//指定用于等待队列头部任务的线程。
private Thread leader = null;
/**
* 当较新的任务在队列的头部可用时或需要更换leader,通过该条件发出信号
*/
private final Condition available = lock.newCondition();
/**
* 设置头部索引
*/
private void setIndex(RunnableScheduledFuture<?> f, int idx) {
if (f instanceof ScheduledFutureTask)
((ScheduledFutureTask)f).heapIndex = idx;
}
/**
* 右移 提供给删除时使用(从大到小)
*/
private void siftUp(int k, RunnableScheduledFuture<?> key) {
//循环获取
while (k > 0) {
//k-1向右移一位(无符号)
int parent = (k - 1) >>> 1;
//从队列中取一个线程
RunnableScheduledFuture<?> e = queue[parent];
//如果大于0跳出
if (key.compareTo(e) >= 0)
break;
//赋值
queue[k] = e;
setIndex(e, k);
k = parent;
}
//重新赋值
queue[k] = key;
setIndex(key, k);
}
/**
* 从队列中删除一个元素(从小到大)
*/
private void siftDown(int k, RunnableScheduledFuture<?> key) {
//当前右移动一位(无符号)
int half = size >>> 1;
//循环
while (k < half) {
//获取自增1 (k-1)再+1
int child = (k << 1) + 1;
//获取任务
RunnableScheduledFuture<?> c = queue[child];
//获取下一个位置
int right = child + 1;
//小于总数 且 对比一致
if (right < size && c.compareTo(queue[right]) > 0)
//获取元素
c = queue[child = right];
//如果相同
if (key.compareTo(c) <= 0)
//跳出
break;
//重新赋值
queue[k] = c;
setIndex(c, k);
k = child;
}
queue[k] = key;
setIndex(key, k);
}
/**
*调整堆数组的大小。
*/
private void grow() {
//获取队列长度
int oldCapacity = queue.length;
// 旧队列+旧队列右移一位 相当于 10+10/2= 15
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1); // grow 50%
//如果小于0 那么用最大值
if (newCapacity < 0) // overflow
newCapacity = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
//进行复制
queue = Arrays.copyOf(queue, newCapacity);
}
/**
*查询对象所在队列位置,如果找不到返回-1
*/
private int indexOf(Object x) {
//不为空
if (x != null) {
//为任务
if (x instanceof ScheduledFutureTask) {
int i = ((ScheduledFutureTask) x).heapIndex;
// Sanity check; x could conceivably be a
// ScheduledFutureTask from some other pool.
//循环判断
if (i >= 0 && i < size && queue[i] == x)
return i;
} else {
//不是任务循环列表查询
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
if (x.equals(queue[i]))
return i;
}
}
//找不到或传入对象为空返回-1
return -1;
}
//判断队列是否包含该任务 包含:true 不包含:false
public boolean contains(Object x) {
//上锁
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
return indexOf(x) != -1;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
//删除任务
public boolean remove(Object x) {
//上锁
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
//获取下标
int i = indexOf(x);
//小于0证明找不到
if (i < 0)
return false;
//总数-1
setIndex(queue[i], -1);
//重新获取数量
int s = --size;
RunnableScheduledFuture<?> replacement = queue[s];
//将队列置空
queue[s] = null;
if (s != i) {
//从队列中移出
siftDown(i, replacement);
if (queue[i] == replacement)
siftUp(i, replacement);
}
return true;
} finally {
//最后解锁
lock.unlock();
}
}
//获取队列总数 带锁
public int size() {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
return size;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
//判断当前队列是否为空 如果是则返回true
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size() == 0;
}
//获取最大容量
public int remainingCapacity() {
return Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
//获取第一个任务
public RunnableScheduledFuture<?> peek() {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
return queue[0];
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
//将一个工作项插入到延迟工作队列中。工作项会按照其延迟时间进行排序,并被放置在适当的位置上。如果工作项已经过期,则会立即被取出并执行。
public boolean offer(Runnable x) {
if (x == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
RunnableScheduledFuture<?> e = (RunnableScheduledFuture<?>)x;
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
int i = size;
if (i >= queue.length)
grow();
//总数+1
size = i + 1;
//如果为第一个进行赋值
if (i == 0) {
queue[0] = e;
setIndex(e, 0);
} else {
//添加任务到队列中
siftUp(i, e);
}
//第0个相等
if (queue[0] == e) {
//leader置空 重新分配
leader = null;
available.signal();
}
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
return true;
}
//添加任务方法
public void put(Runnable e) {
offer(e);
}
//有返回添加方法
public boolean add(Runnable e) {
return offer(e);
}
//带过期时间有返回添加方法
public boolean offer(Runnable e, long timeout, TimeUnit unit) {
return offer(e);
}
/**
*将第一个元素替换为最后一个元素并筛选它。
*/
private RunnableScheduledFuture<?> finishPoll(RunnableScheduledFuture<?> f) {
int s = --size;
RunnableScheduledFuture<?> x = queue[s];
queue[s] = null;
if (s != 0)
siftDown(0, x);
setIndex(f, -1);
return f;
}
//从延迟工作队列中取出并返回一个可以执行的工作项。如果队列为空,则返回 null。
public RunnableScheduledFuture<?> poll() {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
RunnableScheduledFuture<?> first = queue[0];
if (first == null || first.getDelay(NANOSECONDS) > 0)
return null;
else
return finishPoll(first);
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
//从延迟工作队列中取出并返回一个可以执行的工作项,如果队列为空,则当前线程会被阻塞直到队列中有可用的工作项。
public RunnableScheduledFuture<?> take() throws InterruptedException {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
//带中断锁
lock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
//循环
for (;;) {
//获取第一个
RunnableScheduledFuture<?> first = queue[0];
//为空则进入等待
if (first == null)
available.await();
else {
//不为空获取延迟时间
long delay = first.getDelay(NANOSECONDS);
//不延迟则直接返回
if (delay <= 0)
return finishPoll(first);
//将引用置用
first = null; // don't retain ref while waiting
//leader为空则等待
if (leader != null)
available.await();
else {
//获取当前线程并将当前线程赋给leader
Thread thisThread = Thread.currentThread();
leader = thisThread;
try {
//等待延迟时间
available.awaitNanos(delay);
} finally {
//如果leader与当前线程一致则将leader置空
if (leader == thisThread)
leader = null;
}
}
}
}
} finally {
//如果leader为空且队列有值进行重置leader
if (leader == null && queue[0] != null)
available.signal();
//解锁
lock.unlock();
}
}
//带过期时间从延迟工作队列中取出并返回一个可以执行的工作项。如果队列为空,则返回 null。
public RunnableScheduledFuture<?> poll(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException {
long nanos = unit.toNanos(timeout);
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
for (;;) {
RunnableScheduledFuture<?> first = queue[0];
if (first == null) {
if (nanos <= 0)
return null;
else
nanos = available.awaitNanos(nanos);
} else {
long delay = first.getDelay(NANOSECONDS);
if (delay <= 0)
return finishPoll(first);
if (nanos <= 0)
return null;
first = null; // don't retain ref while waiting
if (nanos < delay || leader != null)
nanos = available.awaitNanos(nanos);
else {
Thread thisThread = Thread.currentThread();
leader = thisThread;
try {
long timeLeft = available.awaitNanos(delay);
nanos -= delay - timeLeft;
} finally {
if (leader == thisThread)
leader = null;
}
}
}
}
} finally {
if (leader == null && queue[0] != null)
available.signal();
lock.unlock();
}
}
//清空队列的方法
public void clear() {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
RunnableScheduledFuture<?> t = queue[i];
if (t != null) {
queue[i] = null;
setIndex(t, -1);
}
}
size = 0;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
/**
* 获取队列第一个元素
*/
private RunnableScheduledFuture<?> peekExpired() {
// assert lock.isHeldByCurrentThread();
RunnableScheduledFuture<?> first = queue[0];
return (first == null || first.getDelay(NANOSECONDS) > 0) ?
null : first;
}
//将队列中数据放到c中,并返回数量;(关闭时使用到)
public int drainTo(Collection<? super Runnable> c) {
if (c == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
if (c == this)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
RunnableScheduledFuture<?> first;
int n = 0;
while ((first = peekExpired()) != null) {
c.add(first); // In this order, in case add() throws.
finishPoll(first);
++n;
}
return n;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
//同上类似
public int drainTo(Collection<? super Runnable> c, int maxElements) {
if (c == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
if (c == this)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
if (maxElements <= 0)
return 0;
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
RunnableScheduledFuture<?> first;
int n = 0;
while (n < maxElements && (first = peekExpired()) != null) {
c.add(first); // In this order, in case add() throws.
finishPoll(first);
++n;
}
return n;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
//将队列转成数组
public Object[] toArray() {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
return Arrays.copyOf(queue, size, Object[].class);
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
//传入a数组将结果放进a返回
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
if (a.length < size)
return (T[]) Arrays.copyOf(queue, size, a.getClass());
System.arraycopy(queue, 0, a, 0, size);
if (a.length > size)
a[size] = null;
return a;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
//迭代方法
public Iterator<Runnable> iterator() {
return new Itr(Arrays.copyOf(queue, size));
}
//迭代器的实现 包含增 查 删 改
private class Itr implements Iterator<Runnable> {
final RunnableScheduledFuture<?>[] array;
int cursor = 0; // index of next element to return
int lastRet = -1; // index of last element, or -1 if no such
Itr(RunnableScheduledFuture<?>[] array) {
this.array = array;
}
public boolean hasNext() {
return cursor < array.length;
}
public Runnable next() {
if (cursor >= array.length)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
lastRet = cursor;
return array[cursor++];
}
public void remove() {
if (lastRet < 0)
throw new IllegalStateException();
DelayedWorkQueue.this.remove(array[lastRet]);
lastRet = -1;
}
}
}
}关于DelayedWorkQueue队列介绍
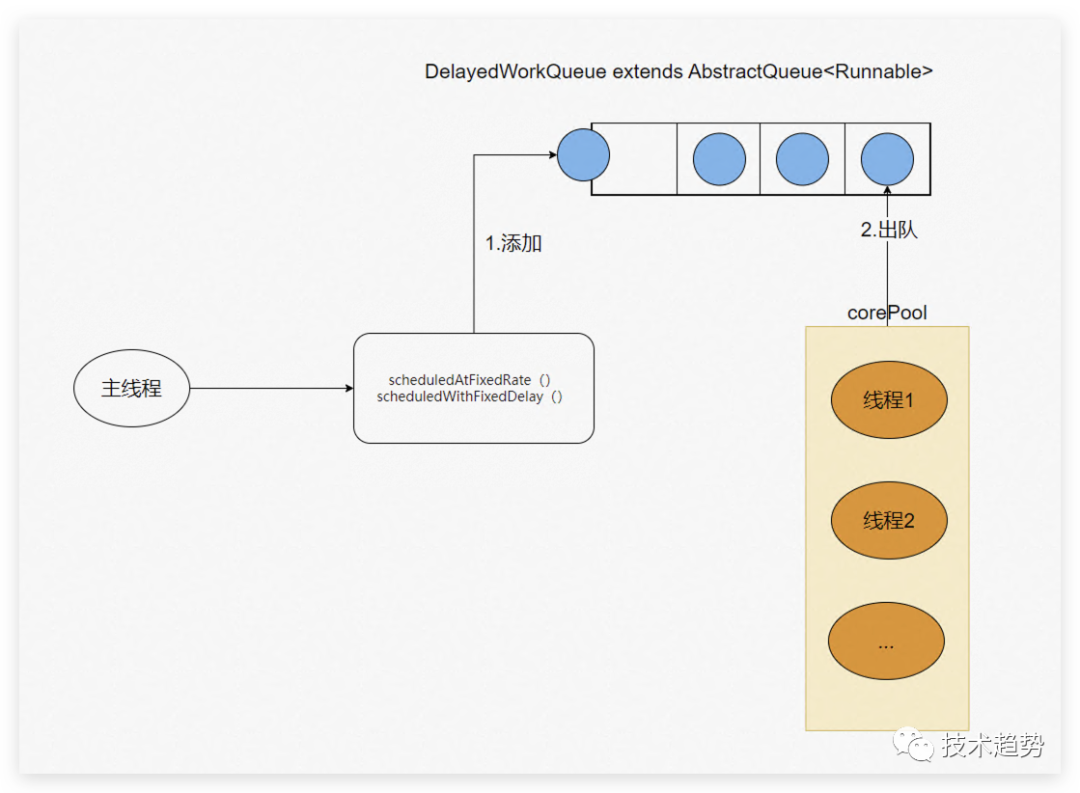

DelayedWorkQueue是一个基于最小堆结构的优先队列,主要用于实现延迟任务调度,它可以让我们在指定的时间之后执行一个任务。通过实现Delayed接口,我们可以将需要延迟执行的任务放入这个队列中,并且队列会根据任务的延迟时间进行排序,从而保证按照规定的时间顺序执行任务。DelayedWorkQueue实现于BlockingQueue所以是一个阻塞队列,是一个无界队列。
使用DelayedWorkQueue可以很方便地实现诸如如下需求的场景:
在指定时间之后执行某个任务,比如凌晨3点执行特定任务;
实现任务的延迟执行,比如任务完成后需要等待30秒才能执行下一步操作;
对于需要进行定时调度的任务,比如每10分钟执行一次清理工作。
使用DelayedWorkQueue可以帮助我们避免使用Thread.sleep()等阻塞操作,提高代码效率和可维护性。同时,由于DelayedWorkQueue是基于Java并发包中的线程安全队列实现的,因此也能够保证多线程程序的正确性。
DelayedWorkQueue的特性主要体现在以下两个方面:
支持延迟执行。DelayedWorkQueue允许指定执行任务的延迟时间,从而实现异步任务调度的功能。
支持优先级调度。DelayedWorkQueue通常支持优先级调度,可以根据任务的优先级来决定处理任务的顺序,从而保证高优先级任务能够尽早得到执行。
什么是最小堆?
最小堆是一种完全二叉树,其中每个节点都比它的子节点小。也就是说,最小堆的根节点是所有节点中最小的节点。因此,最小堆通常被用来实现优先级队列。
最小堆是一种经典的数据结构,在算法和数据结构中有广泛的应用。构建最小堆的过程通常是通过“下沉”操作来完成的。从末尾节点的父节点的这棵树开始调整,根据小根堆的性质,越小的数据往上移动,注意,被调整的节点还有子节点的情况,需要递归进行调整。
最小堆和最大堆类似,但是一个是贪心思想,一个是动态规划的思想,可以用于解决一些算法问题,如堆排序、求Top K等问题。
参考:
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/299756305
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/341418979
最后
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor中的轮训或者说是延迟实现,可以很好的解决定时去执行的任务,并且通过线程池能够很有效的去管理资源的分配。当然ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor实现了自已优先队列DelayedWorkQueue是一个基于最小堆结构的优先队列,保证每次出队时取出的任务是队列中下次执行时间最小的任务。像很多开源的xxjob或者一些开源框架都有大量的引用,通过该工具类可以支持很多业务场景,当然在使用该线程池要特别注意策略这块的配置,避免因为不知道或者使用默认导致各种场景未考虑到。
参考:
https://www.cs.usfca.edu/~galles/visualization/Heap.html
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_40685275/article/details/99836268