目录
s统的内部细节 => 外观模式
外观模式基本介绍
概念
1) 外观模式(Facade),也叫“过程模式:外观模式为子系统中的一组接口提供一个一致的界面,此模式定义了一个高层接口,这个接口使得这一子系统更加容易使用
2) 外观模式通过定义一个一致的接口,用以屏蔽内部子系统的细节,使得调用端只需跟这个接口发生调用,而无需关心这个子系统的内部细节
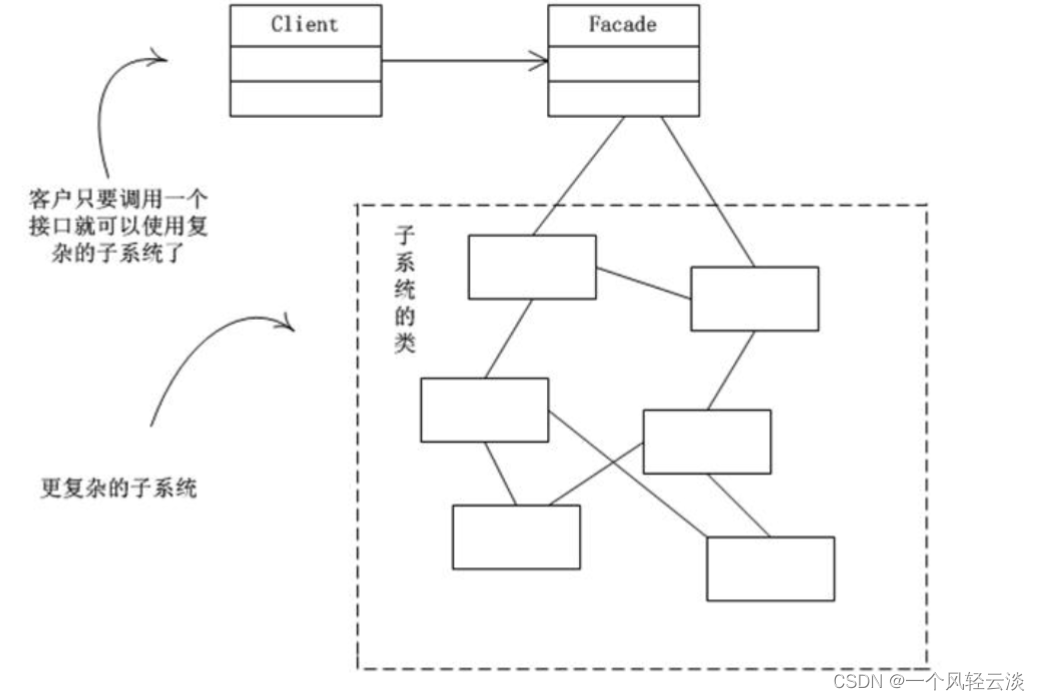
外观模式原理类图

分类外观模式的角色
1) 外观类(Facade): 为调用端提供统一的调用接口, 外观类知道哪些子系统负责处理请求,从而将调用端的请求代理给适当子系统对象
2) 调用者(Client): 外观接口的调用者
3) 子系统的集合:指模块或者子系统,处理 Facade 对象指派的任务,他是功能的实际提供者
外观模式解决影院管理
传统方式解决影院管理说明
1) 外观模式可以理解为转换一群接口,客户只要调用一个接口,而不用调用多个接口才能达到目的。比如:在 pc上安装软件的时候经常有一键安装选项(省去选择安装目录、安装的组件等等),还有就是手机的重启功能(把关机和启动合为一个操作)。
2) 外观模式就是解决多个复杂接口带来的使用困难,起到简化用户操作的作用
外观模式应用实例
1) 应用实例要求
2) 使用外观模式来完成家庭影院项目
3) 思路分析和图解(类图)

DVDPlayer
public class DVDPlayer {
//使用单例模式, 使用饿汉式
private static DVDPlayer instance = new DVDPlayer();
public static DVDPlayer getInstanc() {
return instance;
}
public void on() {
System.out.println(" dvd on ");
}
public void off() {
System.out.println(" dvd off ");
}
public void play() {
System.out.println(" dvd is playing ");
}
public void pause() {
System.out.println(" dvd pause ..");
}
}
Popcorn
public class Popcorn {
private static Popcorn instance = new Popcorn();
public static Popcorn getInstance() {
return instance;
}
public void on() {
System.out.println(" popcorn on ");
}
public void off() {
System.out.println(" popcorn ff ");
}
public void pop() {
System.out.println(" popcorn is poping ");
}
}
Projector
public class Projector {
private static Projector instance = new Projector();
public static Projector getInstance() {
return instance;
}
public void on() {
System.out.println(" Projector on ");
}
public void off() {
System.out.println(" Projector ff ");
}
public void focus() {
System.out.println(" Projector is Projector ");
}
}
Stereo
public class Stereo {
private static Stereo instance = new Stereo();
public static Stereo getInstance() {
return instance;
}
public void on() {
System.out.println(" Stereo on ");
}
public void off() {
System.out.println(" Screen off ");
}
public void up(){
System.out.println(" Screen up.. ");
}
}
TheaterLight
public class TheaterLight {
private static TheaterLight instance = new TheaterLight();
public static TheaterLight getInstance() {
return instance;
}
public void on() {
System.out.println(" TheaterLight on ");
}
public void off() {
System.out.println(" TheaterLight off ");
}
public void dim() {
System.out.println(" TheaterLight dim.. ");
}
public void bright() {
System.out.println(" TheaterLight bright.. ");
}
}Screen
public class Screen {
private static Screen instance = new Screen();
public static Screen getInstance() {
return instance;
}
public void up() {
System.out.println(" Screen up ");
}
public void down() {
System.out.println(" Screen down ");
}
}HomeTheaterFacade
public class HomeTheaterFacade {
//定义各个子系统对象
private TheaterLight theaterLight;
private Popcorn popcorn;
private Stereo stereo;
private Projector projector;
private Screen screen;
private DVDPlayer dVDPlayer;
//构造器
public HomeTheaterFacade() {
super();
this.theaterLight = TheaterLight.getInstance();
this.popcorn = Popcorn.getInstance();
this.stereo = Stereo.getInstance();
this.projector = Projector.getInstance();
this.screen = Screen.getInstance();
this.dVDPlayer = DVDPlayer.getInstanc();
}
//操作分成 4 步
public void ready() {
popcorn.on();
popcorn.pop();
screen.down();
projector.on();
stereo.on();
dVDPlayer.on();
theaterLight.dim();
}
public void play() {
dVDPlayer.play();
}
public void pause() {
dVDPlayer.pause();
}
public void end() {
popcorn.off();
theaterLight.bright();
screen.up();
projector.off();
stereo.off();
dVDPlayer.off();
}
}Client
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HomeTheaterFacade homeTheaterFacade = new HomeTheaterFacade();
homeTheaterFacade.ready();
homeTheaterFacade.play();
homeTheaterFacade.end();
}
}外观模式的注意事项和细节
1) 外观模式对外屏蔽了子系统的细节,因此外观模式降低了客户端对子系统使用的复杂性
2) 外观模式对客户端与子系统的耦合关系 - 解耦,让子系统内部的模块更易维护和扩展
3) 通过合理的使用外观模式,可以帮我们更好的划分访问的层次
4) 当系统需要进行分层设计时,可以考虑使用 Facade 模式
5) 在维护一个遗留的大型系统时,可能这个系统已经变得非常难以维护和扩展,此时可以考虑为新系统开发一个Facade 类,来提供遗留系统的比较清晰简单的接口,让新系统与 Facade 类交互,提高复用性
6) 不能过多的或者不合理的使用外观模式,使用外观模式好,还是直接调用模块好。要以让系统有层次,利于维护为目的