1 安装pycocotools
使用指令:conda/pip install pycocotools进行安装,如果安装不上,就看这个:
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_51116518/article/details/121207941
2 将YOLO的txt标签格式转换为json格式
这一步参考:YOLO的txt转json以及yolov5使用pycocotools评估
步骤
- 先将YOLO的txt文件生成需要使用的txt文件。
新的生成的txt文件格式:
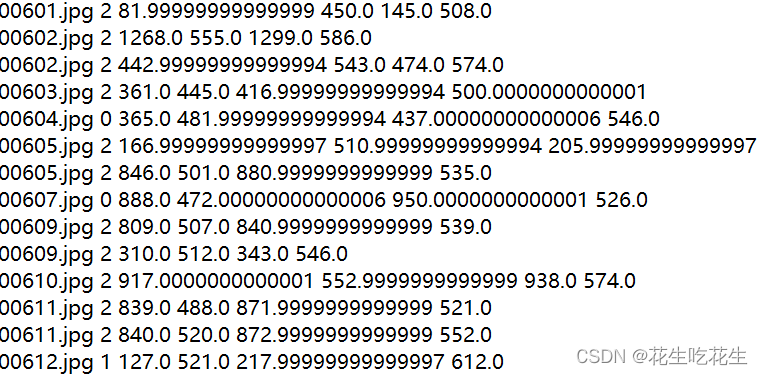
这个步骤的代码为:
import os
import cv2
'''
function:可将yolo格式的数据集转换为coco格式的(1), 生成annos.txt
需要准备:
labels:yolo格式的标签,是txt格式,名字为图片名
images:原始标签对应的图片,需要有序号
'''
# 原始标签路径E:\pyCharmProject\AI\papercode\datasets\GTSDB
originLabelsDir = '../labels/test'
# 转换后的文件保存路径
saveDir = '../labels/annos1.txt'
# 原始标签对应的图片路径
originImagesDir = '../images/test'
txtFileList = os.listdir(originLabelsDir)
with open(saveDir, 'w') as fw:
for txtFile in txtFileList:
with open(os.path.join(originLabelsDir, txtFile), 'r') as fr:
labelList = fr.readlines()
for label in labelList:
label = label.strip().split()
x = float(label[1])
y = float(label[2])
w = float(label[3])
h = float(label[4])
# convert x,y,w,h to x1,y1,x2,y2
imagePath = os.path.join(originImagesDir,
txtFile.replace('txt', 'jpg'))
print(imagePath)
image = cv2.imread(imagePath)
print(image.shape)
H, W, _ = image.shape
x1 = (x - w / 2) * W
y1 = (y - h / 2) * H
x2 = (x + w / 2) * W
y2 = (y + h / 2) * H
# 为了与coco标签方式对,标签序号从1开始计算
fw.write(txtFile.replace('txt', 'jpg') + ' {} {} {} {} {}\n'.format(int(label[0]), x1, y1, x2, y2))
print('{} done'.format(txtFile))
- 将txt转换为json格式。
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# @Time : 2022/9/5
# @Author : rickHan
# @Software: PyCharm
# @File : yolo2coco2.py
import json
import os
import cv2
#-------------------可用-----------------------------------
'''
function:可将yolo格式的数据集转换为coco格式的(2)
需要准备:
classes.txt:一行就是一个类,不需要数字,只要类名称
annos.txt:由上一个.py文件生成
images:与annos.txt对应的图片,需要有序号
生成.json文件,在annotations文件下
'''
# ------------用os提取images文件夹中的图片名称,并且将BBox都读进去------------
# 根路径,里面包含images(图片文件夹),annos.txt(bbox标注),classes.txt(类别标签),
# 以及annotations文件夹(如果没有则会自动创建,用于保存最后的json)
root_path = '../coco'
# 用于创建训练集或验证集
phase = 'val' # 需要修正,保存后的json文件名
# dataset用于保存所有数据的图片信息和标注信息
dataset = {'categories': [], 'annotations': [], 'images': []}
# 打开类别标签
with open(os.path.join(root_path, 'classes.txt')) as f:
classes = f.read().strip().split()
# 建立类别标签和数字id的对应关系
for i, cls in enumerate(classes, 1):
dataset['categories'].append({'id': i, 'name': cls, 'supercategory': 'mark'})
# 读取images文件夹的图片名称
indexes = os.listdir('../images/test')
# 统计处理图片的数量
global count
count = 0
# 读取Bbox信息
with open('../labels/annos1.txt') as tr:
annos = tr.readlines()
# ---------------接着将,以上数据转换为COCO所需要的格式---------------
for k, index in enumerate(indexes):
count += 1
# 用opencv读取图片,得到图像的宽和高
im = cv2.imread('../images/test/' + index)
height, width, _ = im.shape
print(index)
# 添加图像的信息到dataset中
dataset['images'].append({'file_name': index.replace("\\", "/"),
'id': int(index[:5]), # 提取文件名 里的数字标号 必须是int类型,不能是str
'width': width,
'height': height})
for ii, anno in enumerate(annos):
parts = anno.strip().split()
# 如果图像的名称和标记的名称对上,则添加标记
if parts[0] == index:
# 类别
cls_id = parts[1]
# x_min
x1 = float(parts[2])
# y_min
y1 = float(parts[3])
# x_max
x2 = float(parts[4])
# y_max
y2 = float(parts[5])
width = max(0, x2 - x1)
height = max(0, y2 - y1)
dataset['annotations'].append({
'area': width * height,
'bbox': [x1, y1, width, height],
'category_id': int(cls_id),
'id': ii,
'image_id': int(index[0:5]), # 提取文件名里的数字标号 必须是int类型,不能是str
'iscrowd': 0,
# mask, 矩形是从左上角点按顺时针的四个顶点
'segmentation': [[x1, y1, x2, y1, x2, y2, x1, y2]]
})
print('{} images handled'.format(count))
# 保存结果的文件夹
folder = os.path.join(root_path, './valid/annotations')
if not os.path.exists(folder):
os.makedirs(folder)
json_name = os.path.join(root_path, './valid/annotations/{}.json'.format(phase))
with open(json_name, 'w') as f:
json.dump(dataset, f, ensure_ascii=False, indent=1)
- 测试:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# @Time : 2022/9/5
# @Author : rickHan
# @Software: PyCharm
# @File : drawtest.py
import os
from pycocotools.coco import COCO
from PIL import Image, ImageDraw
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
'''
function:绘制标注的数据集和对应图片的位置是否正确
绘制前三张,如果yoyo转换标注的json数据集没有问题,则也能在图上画出框
'''
json_path = '../coco/valid/annotations/val.json'
# json_path = r'predictions.json'
img_path = '../images/test' #json对应的图片
# load coco data
coco = COCO(annotation_file=json_path)
# get all image index info
ids = list(sorted(coco.imgs.keys()))
print("number of images: {}".format(len(ids)))
# get all coco class labels
coco_classes = dict([(v["id"], v["name"]) for k, v in coco.cats.items()])
# 遍历前三张图像
for img_id in ids[:3]:
# 获取对应图像id的所有annotations idx信息
ann_ids = coco.getAnnIds(imgIds=img_id)
# 根据annotations idx信息获取所有标注信息
targets = coco.loadAnns(ann_ids)
# get image file name
path = coco.loadImgs(img_id)[0]['file_name']
# read image
img = Image.open(os.path.join(img_path, path)).convert('RGB')
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(img)
# draw box to image
for target in targets:
x, y, w, h = target["bbox"]
x1, y1, x2, y2 = x, y, int(x + w), int(y + h)
draw.rectangle((x1, y1, x2, y2))
draw.text((x1, y1), coco_classes[target["category_id"]])
# show image
plt.imshow(img)
plt.show()
没有报错就OK了。
4. 将生成的.json文件改名为instances_val2017.json,然后放到数据集目录文件中的annptations文件夹中,没有需要自己创建。
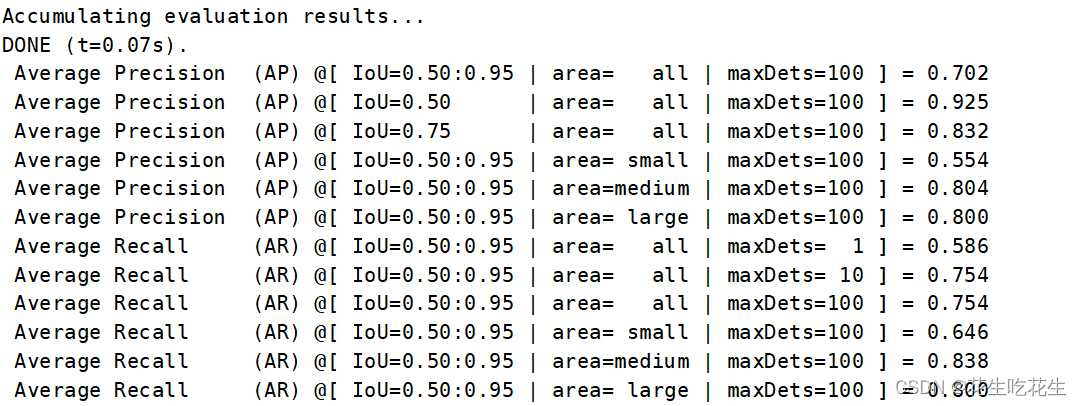
3.运行程序
终端输入:
python val.py --save-json即可。
大功告成!