秋招-数据结构-二叉树篇
介绍
- 基本信息
二叉树是n个有限元素的集合,该集合或者为空、或者由一个称为根(root)的元素及两个不相交的、被分别称为左子树和右子树的二叉树组成,是有序树。当集合为空时,称该二叉树为空二叉树。
- 优缺点
顺序存储可能会浪费空间,但是读取某个指定的节点的时候效率比较高,链式存储相对二叉树比较大的时候浪费空间较少,但是读取某个指定节点的时候效率偏低O(nlogn),整体考虑二叉树是从空间和时间上都较为平衡的一种结构。
题目思路
说过二叉树的递归分为「遍历」和「分解问题」两种思维模式,分别代表回溯算法和动态规划的底层思想。
例题
标准二叉树例题
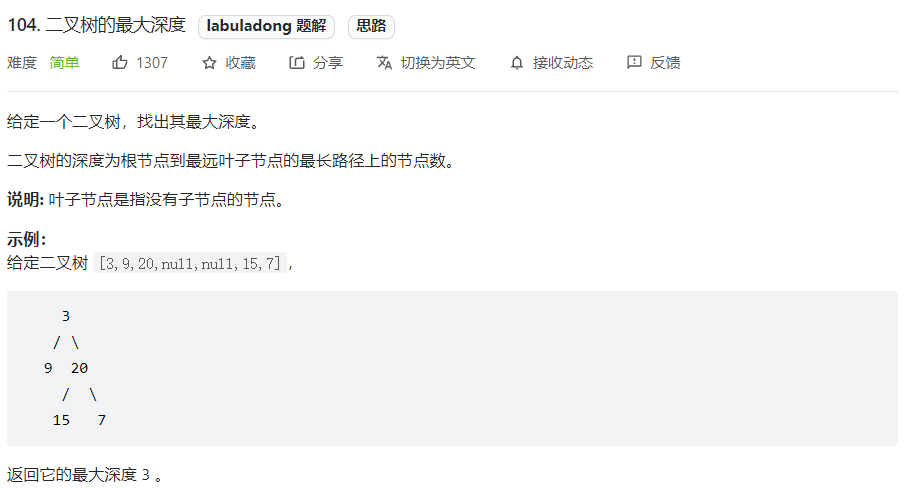
标准的遍历问题,使用递归遍历,获取深度,有以下两种思路:
- 动态规划
class Solution {
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root==null) return 0;
return findPath(root,0);
}
int findPath(TreeNode node, int dep) {
if (node==null){
return dep;
}
int leftDepth = findPath(node.left,dep+1);
int rightDepth = findPath(node.right,dep+1);
return Math.max(leftDepth, rightDepth);
}
}
- 遍历
class Solution {
int maxDep = 0;
int dep = 0;
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
traverse(root);
return maxDep;
}
void traverse(TreeNode root){
if (root == null) {
maxDep = Math.max(maxDep,dep);
return;
}
dep++;
traverse(root.left);
traverse(root.right);
dep--;
}
}
分解问题例题
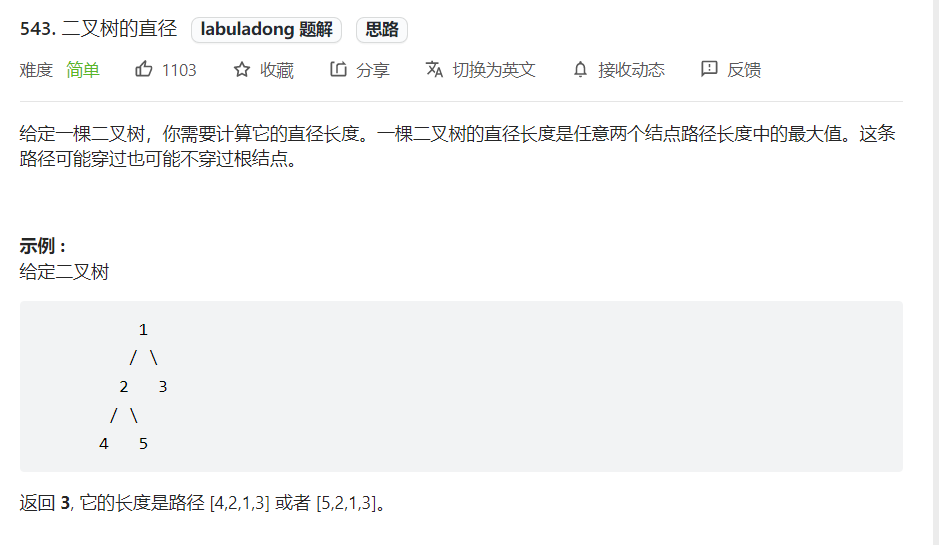
有两种思路:
自顶向下:遍历+计算当前遍历到的节点的长度,每向下到一个新的节点就要重新计算当前新节点的最大路径值。
自底向上:遍历+在向上return的时候将长度带回去,避免了重复计算深度,(实际上是后序遍历+分解问题的思路)以下为该思路解法:
class Solution {
int max = 0;
public int diameterOfBinaryTree(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null) return 0;
distance(root);
return max-1;
}
int distance(TreeNode root){
if(root==null) return 0;
int lenL = distance(root.left);
int lenR = distance(root.right);
max = Math.max(max,lenL+lenR+1);
return Math.max(lenL,lenR)+1;
}
}
后序遍历例题
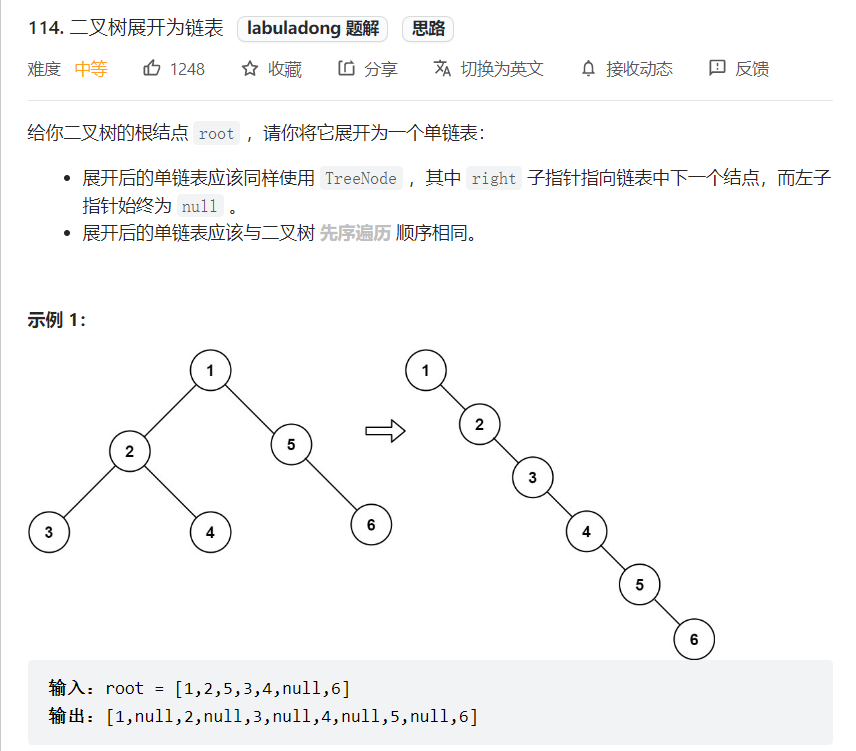
后序遍历代表,最后处理结果——将左节点改为现右节点,将原右节点放到现右节点末尾。
class Solution {
public void flatten(TreeNode root) {
ana(root);
}
void ana(TreeNode root){
if(root==null) return;
ana(root.left);
ana(root.right);
if(root.left!=null&&root.right==null){
root.right = root.left;
root.left = null;
}
if(root.left!=null&&root.right!=null){
TreeNode teR = root.right;
root.right = root.left;
root.left = null;
TreeNode te = root.right;
while(te.right!=null){
te = te.right;
}
te.right = teR;
}
}
}
前序遍历例题
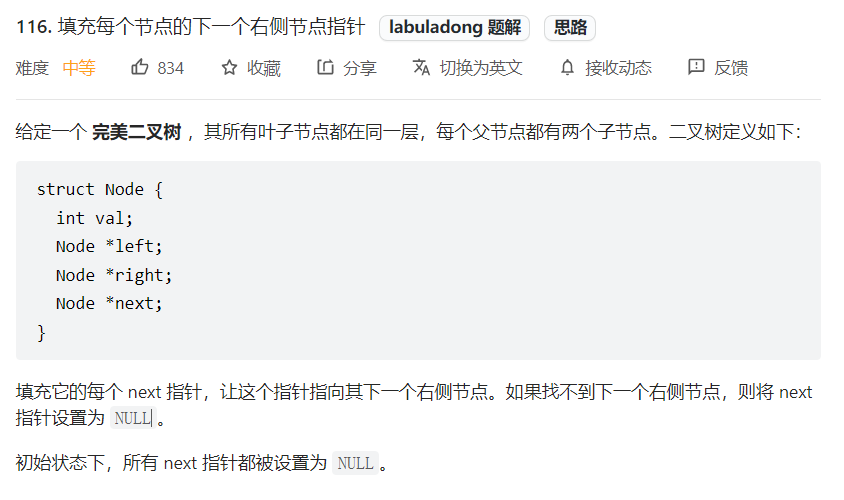
前序遍历代表,优先将计算做完再遍历
class Solution {
public Node connect(Node root) {
ana(root);
return root;
}
void ana(Node root){
if(root == null) return;
if(root.left!=null)
root.left.next = root.right;
if(root.right!=null&&root.next!=null)
root.right.next = root.next.left;
ana(root.left);
ana(root.right);
}
}