概述
- 何为心跳?
心跳其实就是指在TCP长连接中,客户端和服务端之间发送心跳包来确认彼此存活。如果超过一段时间并未接收到心跳包,那么就会关闭TCP连接,释放资源。
- 心跳机制的作用?
因为网络环境的复杂性,客户端和服务端在保持TCP长连接的时候有可能因为断电、断网等意外情况导致客户端和服务端断开连接。而如果在这段时间内,客户端和服务端恰好没发生交互的话那么在短时间内很难感知到对方已经下线,白白浪费资源
所以,TCP就引入了心跳机制,通过客户端和服务端每间隔一段时间发送心跳包的方式来感知对方是否存活。一旦在规定的时间内并没有感知到对方的心跳,那么就可以做一些额外的操作,来避免资源的浪费。
- 实现方式
实现心跳机制通常有两种方式:
- 使用 TCP 协议层面的 keepalive 机制
- 在应用自定义实现心跳机制
我们在开发中一般还是会使用在应用层定义的心跳机制,因为TCP是传输层的协议,它只能感知连接是否可用,不能感知服务是否可用。当进程出现死锁或者阻塞的情况下,连接依然还是可用的,但是服务其实并不可用。
另外,keepalive机制默认关闭,需要自己手动打开,并且依赖于操作系统的实现,默认心跳时间是两小时,虽然可以修改,但是全局的配置,不具有灵活性。
Netty的心跳机制
基本介绍
Netty在应用层上自定义了心跳机制,其心跳机制依赖核心类IdleStateHandler实现,它可以对一个Channel进行读写事件的监听,当在规定的时间内没有数据交互就会触发相应的事件,我们可以在自定义的handler中重写userEventTriggered方法,对指定的事件做出对应的操作。
我们来看看Netty中的事件IdleStateEvent的源码:
public class IdleStateEvent {
public static final IdleStateEvent FIRST_READER_IDLE_STATE_EVENT;
public static final IdleStateEvent READER_IDLE_STATE_EVENT;
public static final IdleStateEvent FIRST_WRITER_IDLE_STATE_EVENT;
public static final IdleStateEvent WRITER_IDLE_STATE_EVENT;
public static final IdleStateEvent FIRST_ALL_IDLE_STATE_EVENT;
public static final IdleStateEvent ALL_IDLE_STATE_EVENT;
private final IdleState state;
private final boolean first;
protected IdleStateEvent(IdleState state, boolean first) {
this.state = (IdleState)ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(state, "state");
this.first = first;
}
static {
FIRST_READER_IDLE_STATE_EVENT = new IdleStateEvent.DefaultIdleStateEvent(IdleState.READER_IDLE, true);
READER_IDLE_STATE_EVENT = new IdleStateEvent.DefaultIdleStateEvent(IdleState.READER_IDLE, false);
FIRST_WRITER_IDLE_STATE_EVENT = new IdleStateEvent.DefaultIdleStateEvent(IdleState.WRITER_IDLE, true);
WRITER_IDLE_STATE_EVENT = new IdleStateEvent.DefaultIdleStateEvent(IdleState.WRITER_IDLE, false);
FIRST_ALL_IDLE_STATE_EVENT = new IdleStateEvent.DefaultIdleStateEvent(IdleState.ALL_IDLE, true);
ALL_IDLE_STATE_EVENT = new IdleStateEvent.DefaultIdleStateEvent(IdleState.ALL_IDLE, false);
}
private static final class DefaultIdleStateEvent extends IdleStateEvent {
private final String representation;
DefaultIdleStateEvent(IdleState state, boolean first) {
super(state, first);
this.representation = "IdleStateEvent(" + state + (first ? ", first" : "") + ')';
}
public String toString() {
return this.representation;
}
}
}
我们可以看到,在IdleStateEvent拥有两个成员属性和六个常量(分别对应六种不同的事件),两个常量分别是:
- first:判断该事件是否第一次触发,布尔值
- state:该属性是
IdleState类型的枚举类,定义事件的类型
下面我们来看看个枚举类:
public enum IdleState {
READER_IDLE,
WRITER_IDLE,
ALL_IDLE;
private IdleState() {
}
}
这个枚举类分别对应三种状态:
READER_IDLE:读超时WRITER_IDLE:写超时ALL_IDLE:超时(包扩写超时和读超时)
快速开始
事先准备
既然知道了基本的概念,那么我们就通过代码来快速体验一下Netty的心跳机制吧
要实现Netty中的心跳机制我们需要给Channel通道添加一个Netty官方提供的IdleStateHandler,并指定对应的参数:
/**
* Netty提供的IdleStateHandler,用于处理空闲状态,比如读写空闲、读写空闲、读写空闲三种状态。
*
* @param readerIdleTimeSeconds 读空闲时间,单位秒
* @param writerIdleTimeSeconds 写空闲时间,单位秒
* @param allIdleTimeSeconds 所有空闲时间,单位秒
*/
public IdleStateHandler(int readerIdleTimeSeconds, int writerIdleTimeSeconds, int allIdleTimeSeconds) {
this((long) readerIdleTimeSeconds, (long) writerIdleTimeSeconds, (long) allIdleTimeSeconds, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
我们提前指定TCP的协议:
+--------+-----+---------------+
| Length |Type | Content |
| 17 | 1 |"HELLO, WORLD" |
+--------+-----+---------------+
- Length:协议包总长度
- Type:协议包的类型
- Content:内容
编写核心类
经过上面的准备,我们使用模板模式,定义一个抽象通用的SimpleChannelInboundHandler类,客户端和服务端通过继承这个类来实现自己具体的逻辑,相关的实现逻辑我已经在代码中注明
- 通用模板
package cuit.pymjl.handler;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.SimpleChannelInboundHandler;
import io.netty.handler.timeout.IdleStateEvent;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
/**
* @author Pymjl
* @version 1.0
* @date 2022/6/23 18:27
**/
public abstract class AbstractCustomHeartbeatHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<ByteBuf> {
/**
* 数据类型:PING(心跳包)
*/
public static final byte PING_MSG = (byte) 1;
/**
* 数据类型:PONG(心跳包)
*/
public static final byte PONG_MSG = (byte) 2;
/**
* 数据类型:自定义内容
*/
public static final byte CUSTOM_MSG = (byte) 3;
/**
* 名称
*/
protected String name;
/**
* 触发事件的次数
*/
protected AtomicInteger heartbeatCount;
public AbstractCustomHeartbeatHandler(String name) {
this.name = name;
this.heartbeatCount = new AtomicInteger(0);
}
/**
* 当有数据到达时,触发该方法,定义处理数据的模板方法
*
* @param context 上下文
* @param byteBuf 字节缓冲区
* @throws Exception 异常
*/
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext context, ByteBuf byteBuf) throws Exception {
if (byteBuf.getByte(4) == PING_MSG) {
//服务端接到ping才发送pong
sendPongMsg(context);
} else if (byteBuf.getByte(4) == PONG_MSG) {
System.out.println(name + " get pong msg from " + context.channel().remoteAddress());
} else {
handleData(context, byteBuf);
}
}
/**
* 处理数据的方法,由子类实现
*
* @param context 上下文
* @param byteBuf 字节缓冲区
*/
protected abstract void handleData(ChannelHandlerContext context, ByteBuf byteBuf);
/**
* 当触发事件后,会根据不同的事件类型,调用不同的方法
*
* @param ctx ctx channel handler context
* @param evt evt idle state event
* @throws Exception 异常
*/
@Override
public void userEventTriggered(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object evt) throws Exception {
// IdleStateHandler 所产生的 IdleStateEvent 的处理逻辑.
if (evt instanceof IdleStateEvent) {
IdleStateEvent e = (IdleStateEvent) evt;
switch (e.state()) {
// 当读空闲时,说明没有收到客户端数据,服务端关闭连接
case READER_IDLE:
handleReaderIdle(ctx);
break;
// 写空闲
case WRITER_IDLE:
handleWriterIdle(ctx);
break;
// 读写空闲,客户端发送心跳包,发送了五个心跳包后,停止发送,触发服务端的读事件,关闭连接
case ALL_IDLE:
handleAllIdle(ctx);
break;
default:
break;
}
}
}
protected void handleReaderIdle(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) {
System.err.println("---READER_IDLE---");
}
protected void handleWriterIdle(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) {
System.err.println("---WRITER_IDLE---");
}
protected void handleAllIdle(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) {
System.err.println("---ALL_IDLE---");
}
/**
* 发送pong心跳包,由服务端发送
*
* @param context 上下文
*/
private void sendPongMsg(ChannelHandlerContext context) {
ByteBuf buf = context.alloc().buffer(5);
buf.writeInt(5);
buf.writeByte(PONG_MSG);
context.channel().writeAndFlush(buf);
System.out.println(name + " sent pong msg to " + context.channel().remoteAddress() +
", count: " + heartbeatCount.incrementAndGet());
}
/**
* 发送ping心跳包,由客户端发送
*
* @param context 上下文
*/
protected void sendPingMsg(ChannelHandlerContext context) {
ByteBuf buf = context.alloc().buffer(5);
buf.writeInt(5);
buf.writeByte(PING_MSG);
context.writeAndFlush(buf);
System.out.println(name + " sent ping msg to " + context.channel().remoteAddress()
+ ", count: " + heartbeatCount.incrementAndGet());
}
}
- 定义客户端的Handler,继承刚才定义的抽象类
package cuit.pymjl.handler;
import cuit.pymjl.transport.NettyClient;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
/**
* @author Pymjl
* @version 1.0
* @date 2022/6/23 19:01
**/
public class ClientHandler extends AbstractCustomHeartbeatHandler {
private NettyClient client;
private AtomicInteger cnt;
public ClientHandler(NettyClient client) {
super("client");
this.client = client;
this.cnt = new AtomicInteger(0);
}
@Override
protected void handleData(ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext, ByteBuf byteBuf) {
byte[] data = new byte[byteBuf.readableBytes() - 5];
byteBuf.skipBytes(5);
byteBuf.readBytes(data);
String content = new String(data);
System.out.println(name + " get content from server: " + content);
}
@Override
protected void handleAllIdle(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) {
// 当客户端发送了五个心跳包后,停止发送,触发服务端的读事件,关闭连接
if (cnt.incrementAndGet() > 5) {
return;
}
super.handleAllIdle(ctx);
sendPingMsg(ctx);
}
/**
* 当连接关闭后,客户端重新连接服务端
*
* @param ctx ctx
* @throws Exception 异常
*/
@Override
public void channelInactive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
super.channelInactive(ctx);
client.doConnect();
}
}
- 定义ServerHandler
package cuit.pymjl.handler;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
/**
* @author Pymjl
* @version 1.0
* @date 2022/6/23 19:06
**/
public class ServerHandler extends AbstractCustomHeartbeatHandler {
public ServerHandler() {
super("server");
}
@Override
protected void handleData(ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext, ByteBuf buf) {
byte[] data = new byte[buf.readableBytes() - 5];
ByteBuf responseBuf = Unpooled.copiedBuffer(buf);
buf.skipBytes(5);
buf.readBytes(data);
String content = new String(data);
System.out.println(name + " get content: " + content);
channelHandlerContext.write(responseBuf);
}
@Override
protected void handleReaderIdle(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) {
super.handleReaderIdle(ctx);
System.err.println("---client " + ctx.channel().remoteAddress().toString() + " reader timeout, close it---");
ctx.close();
}
}
- 定义服务端
NettyServer
package cuit.pymjl.transport;
import cuit.pymjl.handler.ServerHandler;
import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.Channel;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelPipeline;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;
import io.netty.handler.codec.LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder;
import io.netty.handler.timeout.IdleStateHandler;
/**
* @author Pymjl
* @version 1.0
* @date 2022/6/23 19:05
**/
public class NettyServer {
/**
* 端口
*/
private final int port;
public NettyServer(int port) {
this.port = port;
}
public void run() {
NioEventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1);
NioEventLoopGroup workGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(4);
try {
ServerBootstrap bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
bootstrap
.group(bossGroup, workGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline p = socketChannel.pipeline();
//添加心跳检测的Handler,监听读空闲,当10秒内没有读到数据,则触发读空闲事件,关闭channel
p.addLast(new IdleStateHandler(10, 0, 0));
//Netty提供的自定义的消息解码器,用于解码消息的长度,并且把消息体封装到ByteBuf中(如若不明白请自行百度)
p.addLast(new LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder(1024, 0, 4, -4, 0));
//添加自定义的消息处理器,用于处理消息
p.addLast(new ServerHandler());
}
});
Channel ch = bootstrap.bind(port).sync().channel();
System.out.println("server start success, port: " + port);
ch.closeFuture().sync();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
- 定义客户端
NettyClient
package cuit.pymjl.transport;
import cuit.pymjl.handler.AbstractCustomHeartbeatHandler;
import cuit.pymjl.handler.ClientHandler;
import io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.channel.*;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel;
import io.netty.handler.codec.LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder;
import io.netty.handler.timeout.IdleStateHandler;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* @author Pymjl
* @version 1.0
* @date 2022/6/23 18:26
**/
public class NettyClient {
private NioEventLoopGroup workGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(4);
private Channel channel;
private Bootstrap bootstrap;
private final String host;
private final Integer port;
public NettyClient(String host, int port) {
this.host = host;
this.port = port;
}
/**
* 发送数据
*
* @throws Exception 异常
*/
public void sendData() throws Exception {
Random random = new Random(System.currentTimeMillis());
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
if (channel != null && channel.isActive()) {
//构建消息内容
String content = "client msg " + i;
//分配缓冲区
ByteBuf buf = channel.alloc().buffer(5 + content.getBytes().length);
//写入消息长度(4字节)
buf.writeInt(5 + content.getBytes().length);
//写入消息类型(1字节)
buf.writeByte(AbstractCustomHeartbeatHandler.CUSTOM_MSG);
//写入消息内容(字符串)
buf.writeBytes(content.getBytes());
//发送消息
channel.writeAndFlush(buf);
}
//随机睡眠0-20秒
Thread.sleep(random.nextInt(20000));
}
}
public void start() {
try {
bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
bootstrap
.group(workGroup)
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline p = socketChannel.pipeline();
//添加心跳检测的Handler,监听读写空闲,当5秒内没有数据交互,则触发读写空闲事件,发送心跳包
p.addLast(new IdleStateHandler(0, 0, 5));
//Netty提供的自定义的消息解码器,用于解码消息的长度,并且把消息体封装到ByteBuf中(如若不明白请自行百度)
p.addLast(new LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder(1024, 0, 4, -4, 0));
//自定义消息处理器,用于处理消息
p.addLast(new ClientHandler(NettyClient.this));
}
});
//连接服务器
doConnect();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public void doConnect() {
if (channel != null && channel.isActive()) {
return;
}
ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.connect(host, port);
future.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture futureListener) throws Exception {
if (futureListener.isSuccess()) {
channel = futureListener.channel();
System.out.println("Connect to server successfully!");
} else {
System.out.println("Failed to connect to server, try connect after 10s");
futureListener.channel().eventLoop().schedule(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
doConnect();
}
}, 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
}
});
}
}
测试
- 编写服务端主启动类
package cuit.pymjl;
import cuit.pymjl.transport.NettyServer;
/**
* @author Pymjl
* @version 1.0
* @date 2022/6/23 19:39
**/
public class ServerMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
NettyServer server = new NettyServer(12345);
server.run();
}
}
- 编写客户端主启动类
package cuit.pymjl;
import cuit.pymjl.transport.NettyClient;
/**
* @author Pymjl
* @version 1.0
* @date 2022/6/23 18:25
**/
public class ClientMain {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
NettyClient client = new NettyClient("127.0.0.1", 12345);
client.start();
client.sendData();
}
}
- 先启动服务端,再启动客户端,一段时间后,观看控制台输出:
客户端控制台输出:
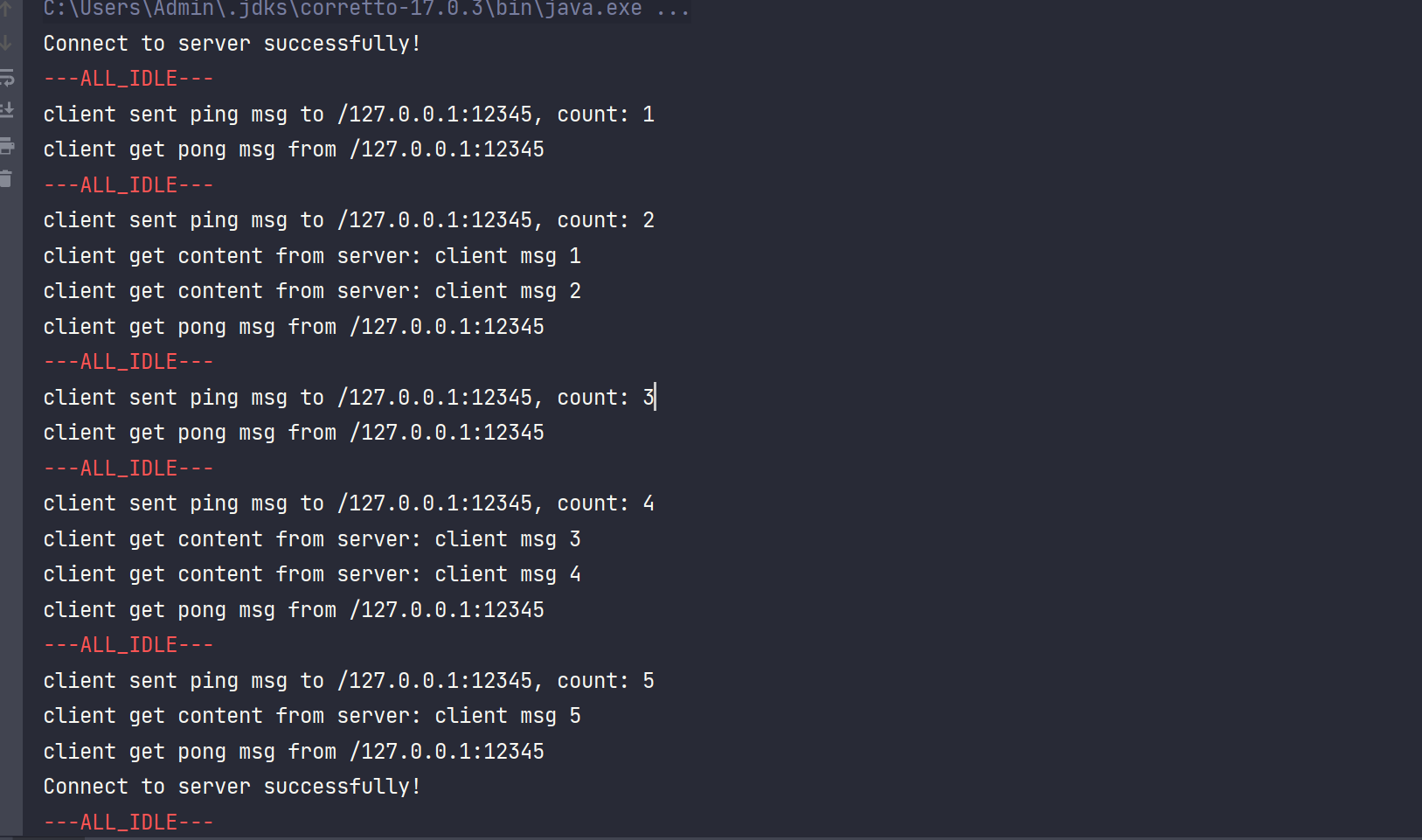
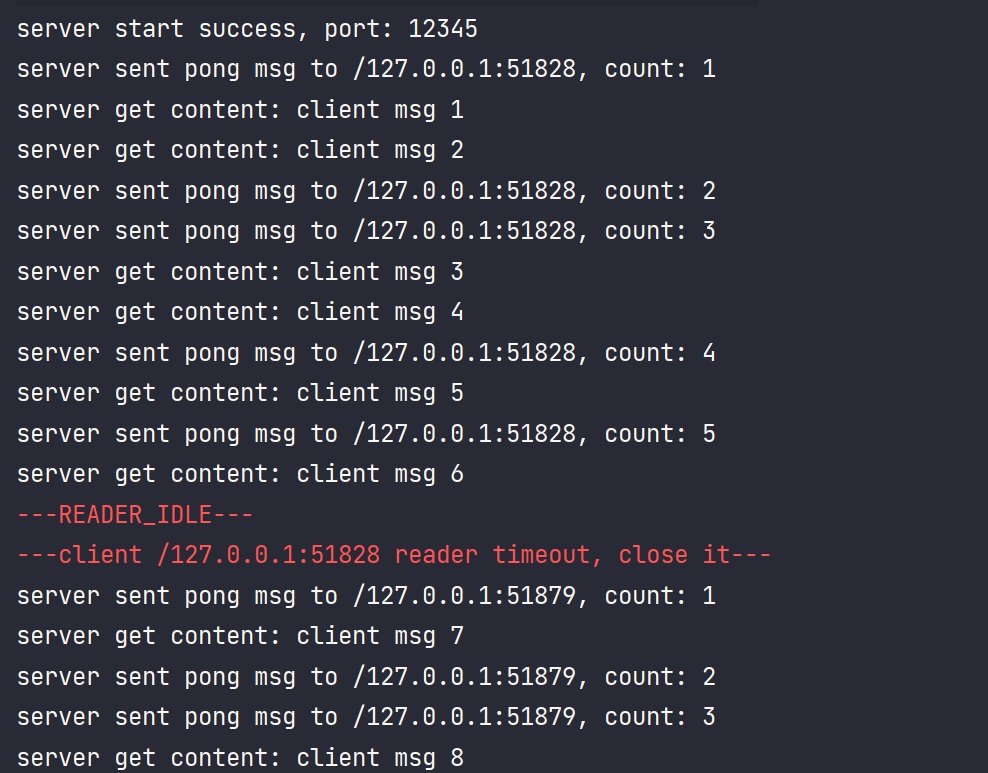
服务端控制台输出:
小结
通过观察控制台输出可知,客户端先向服务端发送数据,然后随即休眠了0~20秒,客户端休眠超过5秒就会触发读写空闲,向服务端发送PING心跳包,而服务端在收到服务PING后也会向客户端发送PONG心跳包。当服务端超过10秒没接收到客户端的消息,就会触发读空闲,然后关闭连接。当连接被关闭,客户端这边会触发channelInactive()方法,进行重新连接
好啦,关于Netty心跳机制的介绍就到这里,你可以点击这里克隆本篇博客完整的源代码
如果觉得写得还不错就请点个赞吧~
你的点赞、关注就是对我最大的鼓励
参考文章:
这样讲Netty中的心跳机制,还有谁不会?