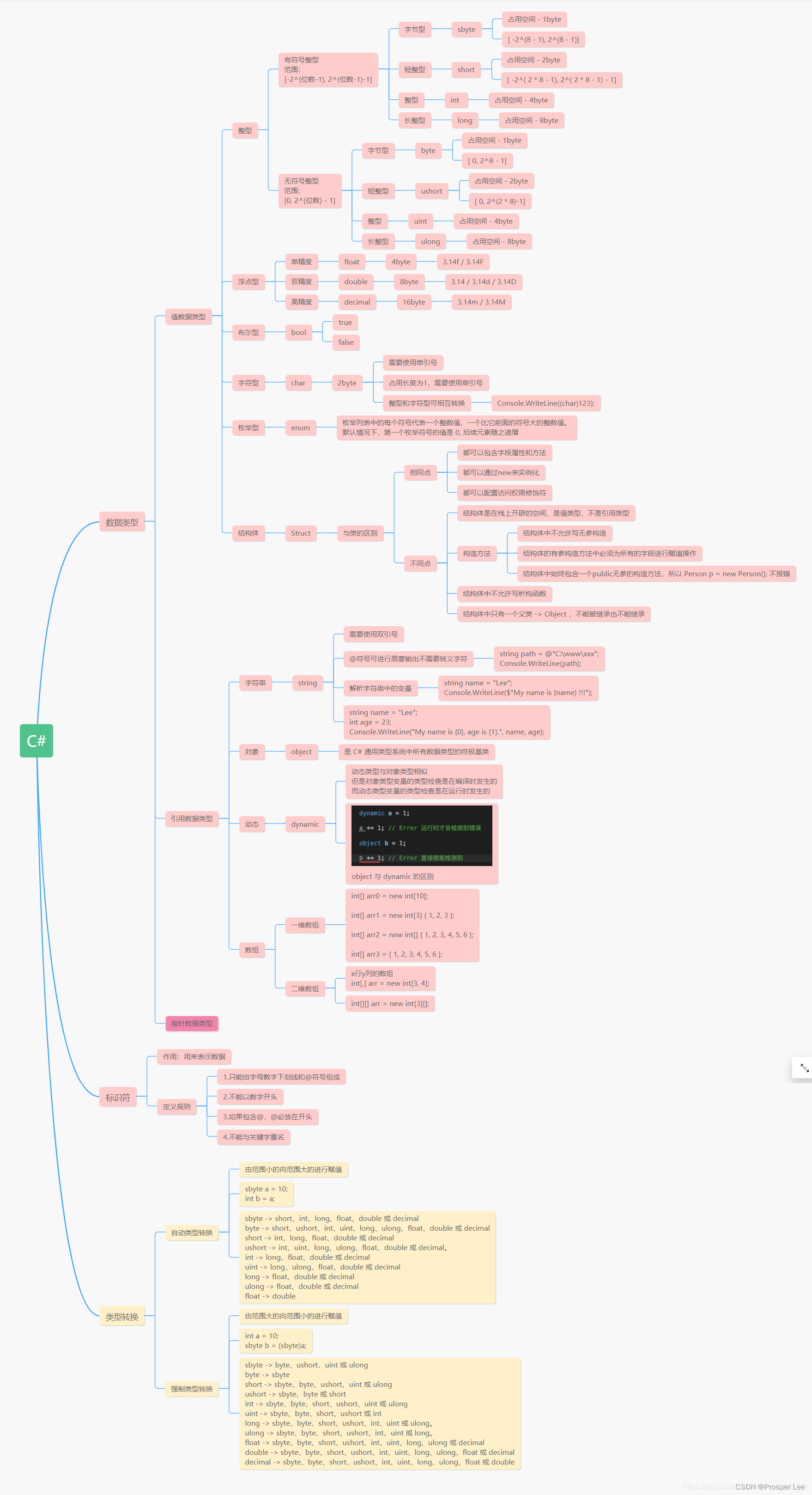
命名约定
| 命名约定 | 示例 | 适用场合 |
|---|---|---|
| 驼峰样式 | cost、orderDetail、dateOfBirth | 局部变量、私有变量 |
| 标题样式 | String、Int32、Cost、DateOfBirth、Run | 类型、非私有字段以及其他成员(如方法) |
变量
文本
字符
char a = 'A';
char b = 'L';
内插字符串
string name = "Lee";
Console.WriteLine($"Hello, {
name}!"); // Hello, Lee!
字面字符串
string filePath1 = "C:\txxx\\xxx\\xxx.txt";
Console.WriteLine(filePath1); // C: xxx\xxx\xxx.txt
逐字字符串
string filePath2 = @"C:\txxx\nxxx\rxxx.txt";
Console.WriteLine(filePath2); // C:\txxx\nxxx\rxxx.txt
数字
整型
uint a = 1; // 无符号整型
int b = -2; // 整数类型
Console.WriteLine(a + b == -1.0); // True
浮点型
float c = 1;
float d = 0.1F;
float e = 0.2f;
Console.WriteLine(d + e == 0.3); // False
双精度浮点型
double f = 0.1;
double g = 0.2f;
Console.WriteLine(f + g == 0.3); // False
// 不是数字
Console.WriteLine(double.NaN); // NaN
Console.WriteLine(double.IsNaN(double.NaN)); // True
// 最小正数
Console.WriteLine(double.Epsilon); // 4.94065645841247E-324
// 判断值是否无限大
Console.WriteLine(double.IsInfinity(1)); // True
精准数据类型
扫描二维码关注公众号,回复:
14618973 查看本文章


decimal h = 0.1M;
decimal i = 0.2m;
Console.WriteLine(h + i == 0.3M); // True
布尔值
bool a = true;
bool b = false;
任意类型 object dynamic
object
object name = "Lee";
Console.WriteLine(((string)name).Length); // 3
object num1 = "123";
object num2 = 123;
Console.WriteLine((int)num1 + (int)num2); // 未经处理的异常: System.InvalidCastException: 指定的转换无效。
dynamic
dynamic name = "ProsperLee";
Console.WriteLine(name.Length); // 10
声明局部变量
var name = "ProsperLee";
Console.WriteLine(name.Length); // 10
获取类型的默认值
Console.WriteLine(default(DateTime)); // 0001/1/1 0:00:00
Console.WriteLine(default(char) == '\0'); // True
Console.WriteLine(default(string) == null); // True
Console.WriteLine(default(uint) == 0); // True
Console.WriteLine(default(int) == 0); // True
Console.WriteLine(default(float) == 0); // True
Console.WriteLine(default(double) == 0); // True
Console.WriteLine(default(decimal) == 0); // True
Console.WriteLine(default(bool)); // False
Console.WriteLine(default(object) == null); // True
数组
string[] names = {
"Lee", "Tom", "Lucy" };
foreach (string name in names)
{
Console.WriteLine(name); // Lee Tom Lucy
}
object[] list1 = {
"Lee", 123, true, 1.23m };
dynamic[] list2 = {
"Lee", 123, true, 1.23m };
foreach (object d in list1)
{
Console.WriteLine(d); // Lee 123 True 1.23
}
foreach (var d in list2)
{
Console.WriteLine(d); // Lee 123 True 1.23
}
数组定义方法
int[] arr0 = new int[10];
int[] arr1 = new int[3] {
1, 2, 3 };
int[] arr2 = new int[] {
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 };
int[] arr3 = {
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 };
x 行 y 列 的二维数组
int[,] arr = new int[3, 4];
arr[0, 1] = 12;
foreach (int item in arr)
{
Console.WriteLine(item);
}
params 传参形式
class MainClass
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[] arr = {
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 };
ForArray(arr); // 1 2 3 4 5 6
ForArray(new int[5]); // 0 0 0 0 0
ForArray(new int[] {
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 }); // 1 2 3 4 5 6
ForArray(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6); // 1 2 3 4 5 6
}
//public static void ForArray(int[] array)
//{
// foreach (int item in array)
// {
// Console.WriteLine(item);
// }
//}
public static void ForArray(params int[] array)
{
foreach (int item in array)
{
Console.WriteLine(item);
}
}
}
二分查找
- 利用二分查找查询升序数组中指定元素的下标
class MainClass { public static void Main(string[] args) { int[] array = { 1, 2, 4, 5, 6, 8 }; Console.WriteLine(FindIndex(array, 6)); } /// <summary> /// 利用二分查找查询升序数组中指定元素的下标 /// </summary> /// <param name="array">目标数组</param> /// <param name="num">要查找的数</param> /// <returns>元素下标</returns> public static int FindIndex(int[] array, int num) { int index = -1; int min = 0; int max = array.Length - 1; while (max >= min) { int mid = (min + max) / 2; if (array[mid] == num) { index = mid; break; } else if (array[mid] > num) { max = mid - 1; } else { min = mid + 1; } } return index; } }
数组选择排序
public static int[] SortArray(int[] array)
{
for (int i = 0; i < array.Length - 1; i++) {
for(int j = i + 1; j < array.Length; j++) {
if (array[i] > array[j])
{
int num = array[i];
array[i] = array[j];
array[j] = num;
}
}
}
return array;
}
foreach (int item in SortArray(new int[] {
1, 3, 5, 1, 5, -1, 24, 12 })) {
Console.WriteLine(item); // -1 1 1 3 5 5 12 24
}
数组冒泡排序
public static int[] SortArray(int[] array)
{
for(int i = 0; i < array.Length - 1; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; i + j < array.Length - 1; j++)
{
if (array[j] > array[j + 1]) {
int num = array[j];
array[j] = array[j + 1];
array[j + 1] = num;
}
}
}
return array;
}
foreach (int item in SortArray(new int[] {
1, 3, 5, 1, 5, -1, 24, 12 })) {
Console.WriteLine(item); // -1 1 1 3 5 5 12 24
}
数据处理
处理空值
int num = new Random().Next(0, 10);
int? a;
if (num > 5) a = num; else a = null;
Console.WriteLine(a); // [0, 10) or null
检查null
int num = new Random().Next(0, 10);
string str;
if (num > 5) str = "ProsperLee"; else str = null;
Console.WriteLine(str?.Length); // 10 or null
Console.WriteLine(str?.Length ?? 123); // 10 or 123
格式化字符串
格式:
{ index [, alignment ] [ :formatString ] }
// 苹果:10个;总价:¥20.00;
Console.WriteLine(
format: "苹果:{0}个;总价:{1:C};",
arg0: 10,
arg1: 2 * 10
);
// 苹果:10个;总价:¥20.00;
string str = string.Format(
format: "苹果:{0}个;总价:{1:C};",
arg0: 10,
arg1: 2 * 10
);
Console.WriteLine(str);
// 苹果:10个;总价:¥20.00;
int num = 10;
int price = 2;
Console.WriteLine($"苹果:{
num}个;总价:{
num * price:C};");
运算符
一元运算符
++--
二元运算符
+-*/%
除法 /
- 整型之间的除法结果为商数
Console.WriteLine(10 / 3); // 3 - 含有浮点数参与的除法结果为浮点数
Console.WriteLine(10 / 3f); // 3.333333 Console.WriteLine(10.00 / 3); // 3.33333333333333 Console.WriteLine(10.5 / 3); // 3.5
赋值运算符
+=-=*=/=
逻辑运算符
&|^
异或 ^ 和 位异或 ^
true和false参与判断时- 如果两个结果相同,返回值为
falseConsole.WriteLine(true ^ true); // False Console.WriteLine(false ^ false); // False - 如果两个结果不同,返回值为
trueConsole.WriteLine(false ^ true); // True Console.WriteLine(true ^ false); // True
- 如果两个结果相同,返回值为
条件逻辑运算符(短路布尔运算符)
&&||
!
按位和二元位移运算符
&|^
表达式 数字 参与判断
Console.WriteLine(-10 ^ 10); // -4
// 1000 1010 原 -10
// 1111 0101 反 -10
// 1111 0110 补 -10
// 0000 1010 补 +10
// ------------------
// 1111 1100 补 计算结果 => 按位异或 1^0 1^0 1^0 1^0 0^1 1^0 1^1 0^0
// 1000 0011 反 求反
// 1000 0100 原 求原
// -(2^2) = -4
Console.WriteLine(10 ^ 10); // 0
// 0000 1010 原反补 +10
// 0000 1010 原反补 +10
// --------------------
// 0000 0000 原反补 计算结果 0
Console.WriteLine(6 ^ 10); // 12
// 0000 0110 原反补 +6
// 0000 1010 原反补 +10
// --------------------
// 0000 1100 原反补 计算结果 8 + 4 = 12
位或 |
Console.WriteLine(-10 | 10); // -2
// 1000 1010 原 -10
// 1111 0101 反 -10
// 1111 0110 补 -10
// 0000 1010 原反补 +10
// 1111 1110 补 计算结果
// 1000 0001 反 求反
// 1000 0010 原 求原 -2
Console.WriteLine(10 | 2); // 10
// 0000 1010 原反补
// 0000 0010 原反补
// 0000 1010 原反补 10
Console.WriteLine(10 | 12); // 14
// 0000 1010 原反补
// 0000 1100 原反补
// 0000 1110 原反补 14
位与 &
Console.WriteLine(-10 & 10); // 2
// 1000 1010 原
// 1111 0101 反
// 1111 0110 补
// 0000 1010 原反补
// 0000 0010 原反补 2
Console.WriteLine(10 & 2); // 2
// 0000 1010 原反补
// 0000 0010 原反补
// 0000 0010 原反补 2
Console.WriteLine(10 & 12); // 8
// 0000 1010 原反补
// 0000 1100 原反补
// 0000 1000 原反补 8
位反 ~
Console.WriteLine(~10);
// 0000 1010 原反补 +10
// 1111 0101 补 ~10
// 1000 1010 反
// 1000 1011 原
// -11
Console.WriteLine(~-10);
// 1000 1010 原 -10
// 1111 0101 反 -10
// 1111 0110 补 -10
// 0000 1001 原反补 ~-10
// 9
Console.WriteLine(~-8);
// 1000 1000 原 -8
// 1111 0111 反 -8
// 1111 1000 补 -8
// 0000 0111 原反补 ~-8
// 8
<<>>
位左移 << 和 位右移 >>
Console.WriteLine(10 << 2); // 40 => 10 * 2^2 = 40
// ---- 0000 1010 ----
// ---- 0000 1010 00--
// ---- --00 1010 00--
// 0010 1000
// 2^5 + 2^3 = 40
Console.WriteLine(10 >> 2); // 2 => 10 / 2^2 = 2
// ---- 0000 1010 ----
// --00 0000 1010 ----
// --00 0000 10-- ----
// 0000 0010
// 2^1 = 2
Console.WriteLine(-8 << 2); // -32 => -(8 * 2^2) = -32
// => -(8 << 2)
// ---- 0000 1000 ----
// ---- 0000 1000 00--
// ---- --00 1000 00--
// 0010 0000
// 32
Console.WriteLine(-8 >> 2); // -2 => -(8 / 2^2) = -2
// => -(8 >> 2)
// ---- 0000 1000 ----
// --00 0000 1000 ----
// --00 0000 10-- ----
// 0000 0010
// 2
运算符的重载 operator
struct Point {
public double x;
public double y;
public Point(double x, double y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
// 加号方法
public static Point operator +(Point p1, Point p2)
{
return new Point(p1.x + p2.x, p1.y + p2.y);
}
// 参数类型
public static Point operator +(Point p1, int a)
{
return new Point(p1.x + a, p1.y + a);
}
// 返回类型
public static int[] operator +(int a, Point p1)
{
return new int[]{
(int)(p1.x + a), (int)(p1.y + a) };
}
// 修改 & (正确但不合乎常理)
public static int[] operator &(int a, Point p1)
{
return new int[] {
(int)(p1.x + a), (int)(p1.y + a) };
}
// 减号方法
public static Point operator -(Point p1)
{
return new Point(-p1.x, -p1.y);
}
}
class MainClass
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
Point a = new Point(1, 2);
Console.WriteLine(a.x); // 1
Console.WriteLine(a.y); // 2
Point b = new Point(3, 4);
Console.WriteLine(b.x); // 3
Console.WriteLine(b.y); // 4
Point c = a + b;
Console.WriteLine(c.x); // 4
Console.WriteLine(c.y); // 6
Point d = new Point(1, 2);
Point e = -d;
Console.WriteLine(e.x); // -1
Console.WriteLine(e.y); // -2
Point f = new Point(1, 2);
int g = 10;
Point h = f + g;
Console.WriteLine(h.x); // 11
Console.WriteLine(h.y); // 12
int i = 1;
Point j = new Point(1, 2);
int[] k = i + j;
foreach (int item in k)
{
Console.WriteLine(item); // 2 3
}
int l = 1;
Point m = new Point(1, 2);
int[] n = l + m;
foreach (int item in n)
{
Console.WriteLine(item); // 2 3
}
}
}
特点
- 运算符重载方法的参数必须与运算符可操作的数据一致
- 一元运算符:操作一个数据
!-··· - 二元运算符:操作两个数据
*/··· - 三元运算符:操作三个数据
? :···
- 一元运算符:操作一个数据
哪些运算符可进行重载
- 全部可以进行重载:
- 算数运算符
- 关系运算符(重载必须成对)
比如重载了 > ,就必须重载 <
- 全部不可进行重载:
- 赋值运算符
- 部分可以进行重载:
- 逻辑运算符
- 可进行:
&|!^ - 不可进行:
&&||
- 可进行:
- 位运算符
- 可进行:
~
- 可进行:
- 逻辑运算符
语句
if... else if ... else ...
switch
int num = new Random().Next(0, 3);
switch (num)
{
case 1:
Console.WriteLine(1);
break;
case 2:
Console.WriteLine(2);
break;
default:
Console.WriteLine("default: 0");
break;
}
while
int count = 0;
while (count < 6)
{
Console.WriteLine(count); // 0 1 2 3 4 5
count++;
}
do { ... } while (...)
int i = 1;
do
{
Console.Write("{0} ", i);
i++;
} while (i <= 6);
for (int i = 0; i <= 6; i++) { ... }
foreach
string[] names = {
"Lee", "Tom", "Lucy" };
foreach (string name in names)
{
Console.WriteLine(name); // Lee Tom Lucy
}
类型转换
隐式类型转换
int a = 10;
double b = a;
Console.WriteLine(b); // 10
显示类型转换
double a = 1.53;
int b = (int)a;
Console.WriteLine(b); // 1
强制类型转换 System.Convert
int a = System.Convert.ToInt32("123");
Console.WriteLine(a); // 123
double b = System.Convert.ToDouble("123.456");
Console.WriteLine(b); // 123.456
圆整数字
规则
如果小数部分小于0.5,则向下圆整;如果小数部分大于0.5,则向上圆整;如果小数部分等于0.5,那么非小数部分为奇数时,则向上圆整,非小数部分为偶数时,则向下圆整;
double[] nums = {
1, 1.4, 1.49, 1.5, 2.5, 1.59, 1.99 };
foreach (double num in nums)
{
int n = System.Convert.ToInt32(num);
Console.WriteLine(n); // 1 1 1 2 2 2 2
}
控制圆整规则
Math.Round(...)
任意类型转换字符串
Console.WriteLine(string.Empty.ToString() == ""); // True
二进制对象转换为字符串
用途:
对于将要存储或传输的二进制对象,例如图像或视频,有时不想发送原始位,因为不知道如何解释那些位,例如通过网络协议传输或由另一个操作系统读取及存储的二进制对象。
最安全的做法是将二进制对象转换成安全字符串,也就是Base64编码。
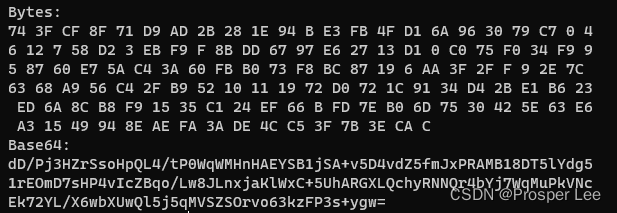
byte[] bytes = new byte[128];
new Random().NextBytes(bytes);
Console.WriteLine("Bytes:");
for (int i = 0; i < bytes.Length; i++)
{
Console.Write($"{
bytes[i]:X} ");
}
Console.WriteLine("Base64:");
Console.WriteLine(Convert.ToBase64String(bytes));
字符串转换为数值或日期和时间
int age = int.Parse("25");
DateTime birthday = DateTime.Parse("1997-02-11");
Console.WriteLine(age); // 25
Console.WriteLine(birthday); // 1997/2/11 0:00:00
TryParse:避免异常
int num1;
Console.WriteLine(int.TryParse("abc", out num1)); // False
Console.WriteLine(num1); // 0
Console.WriteLine(int.TryParse("12.34", out int num2)); // False
Console.WriteLine(num2); // 0
Console.WriteLine(int.TryParse("123", out int num3)); // True
Console.WriteLine(num3); // 123
异常捕获
try
{
int.Parse("abc");
}
catch (Exception err)
{
Console.WriteLine($"{
err.GetType()} ---> {
err.Message}"); // System.FormatException ---> 输入字符串的格式不正确。
}
检查溢出 checked
int count = int.MaxValue - 1;
Console.WriteLine(count); // 2147483646 继续累加
count++;
Console.WriteLine(count); // 2147483647 此时为最大值
count++;
Console.WriteLine(count); // -2147483648 此时溢出到了最小值上
count++;
Console.WriteLine(count); // -2147483647 继续累加
try
{
checked
{
int count = int.MaxValue - 1;
Console.WriteLine(count); // 2147483646 继续累加
count++;
Console.WriteLine(count); // 2147483647 此时为最大值
count++;
Console.WriteLine(count);
count++;
Console.WriteLine(count);
}
}
catch (Exception err)
{
Console.WriteLine($"{
err.GetType()} ---> {
err.Message}"); // System.OverflowException--->算术运算导致溢出。
}
自定义异常
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
try {
ScoreExceptionDemo();
}
catch (Exception e)
{
Console.WriteLine(e); // 自定义异常描述
}
}
static void ScoreExceptionDemo() {
ScoreException scoreException = new ScoreException("自定义异常描述");
throw scoreException;
}
}
// 自定义异常
class ScoreException : Exception {
public ScoreException(string message) : base(message) {
Console.WriteLine(message);
}
}
方法定义
[访问权限修饰符] [其他的修饰符] 返回值类型 方法名 ([行参列表]) { /* 方法体 */ }
public static string FunA(string str)
{
Console.WriteLine(str);
return str;
}
递归
- n的阶乘
class MainClass
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine(FunA(3));
}
public static int FunA(int n)
{
return n == 0 ? 1 : n * FunA(n - 1);
}
}
重载
在一个类中,如果由多个方法满足以下几个条件,那么这几个方法是重载关系
- 方法名相同
- 参数不同 (数量不同,类型不同)
- 跟返回值无关系
class MainClass
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
Add(1);
Add(1, 1f);
}
static void Add(int a, float b)
{
Console.WriteLine(a + b);
}
static int Add(int a)
{
return a;
}
}
ref 和 out
ref- 用来修饰参数
- 如果一个形参用
ref修饰,那么实参也需要用ref修饰 a的改变是因为用ref修饰的参数最终传的是实参的地址
public static void Change(ref int x) { x = 20; } int a = 10; Change(ref a); Console.WriteLine(a); // 20out- 用来修饰参数
- 如果一个形参用
out修饰,那么实参也需要用out修饰 a的改变是因为用out修饰的参数最终传的是实参的地址
public static void Change(out int x) { x = 20; } Change(out int a); Console.WriteLine(a);- 区别
- 在方法结束之前必须对
out参数赋值public static void Change(out int x) { } // Error 没有对参数x进行赋值 ref参数可以直接使用,而out参数需要进行赋值后才能使用(ref参数默认被赋值了而out参数默认没有被赋值)public static void Change(ref int x) { Console.WriteLine(x); // ok } public static void Change(out int x) { Console.WriteLine(x); // Error 使用了未赋值的变量x x = 20; Console.WriteLine(x); // ok }
- 在方法结束之前必须对