前言
随着人工智能的不断发展,机器学习这门技术也越来越重要,很多人都开启了学习机器学习,本文就介绍了机器学习的基础内容。来源于哔哩哔哩博主“霹雳吧啦Wz”,博主学习作为笔记记录,欢迎大家一起讨论学习交流。
一、代码使用简介

1. trans_voc2yolo.py
"""
本脚本有两个功能:
1.将voc数据集标注信息(.xml)转为yolo标注格式(.txt),并将图像文件复制到相应文件夹
2.根据json标签文件,生成对应names标签(my_data_label.names)
"""
import os
from tqdm import tqdm
from lxml import etree
import json
import shutil
# voc数据集根目录以及版本
voc_root = "./data/VOCdevkit"
voc_version = "VOC2012"
# 转换的训练集以及验证集对应txt文件
train_txt = "train.txt"
val_txt = "val.txt"
# 转换后的文件保存目录
save_file_root = "./my_yolo_dataset"
# label标签对应json文件
label_json_path = './data/pascal_voc_classes.json'
# 拼接出voc的images目录,xml目录,txt目录
voc_images_path = os.path.join(voc_root, voc_version, "JPEGImages")
voc_xml_path = os.path.join(voc_root, voc_version, "Annotations")
train_txt_path = os.path.join(voc_root, voc_version, "ImageSets", "Main", train_txt)
val_txt_path = os.path.join(voc_root, voc_version, "ImageSets", "Main", val_txt)
# 检查文件/文件夹都是否存在
assert os.path.exists(voc_images_path), "VOC images path not exist..."
assert os.path.exists(voc_xml_path), "VOC xml path not exist..."
assert os.path.exists(train_txt_path), "VOC train txt file not exist..."
assert os.path.exists(val_txt_path), "VOC val txt file not exist..."
assert os.path.exists(label_json_path), "label_json_path does not exist..."
if os.path.exists(save_file_root) is False:
os.makedirs(save_file_root)
def parse_xml_to_dict(xml):
"""
将xml文件解析成字典形式,参考tensorflow的recursive_parse_xml_to_dict
Args:
xml: xml tree obtained by parsing XML file contents using lxml.etree
Returns:
Python dictionary holding XML contents.
"""
if len(xml) == 0: # 遍历到底层,直接返回tag对应的信息
return {
xml.tag: xml.text}
result = {
}
for child in xml:
child_result = parse_xml_to_dict(child) # 递归遍历标签信息
if child.tag != 'object':
result[child.tag] = child_result[child.tag]
else:
if child.tag not in result: # 因为object可能有多个,所以需要放入列表里
result[child.tag] = []
result[child.tag].append(child_result[child.tag])
return {
xml.tag: result}
def translate_info(file_names: list, save_root: str, class_dict: dict, train_val='train'):
"""
将对应xml文件信息转为yolo中使用的txt文件信息
:param file_names:
:param save_root:
:param class_dict:
:param train_val:
:return:
"""
save_txt_path = os.path.join(save_root, train_val, "labels")
if os.path.exists(save_txt_path) is False:
os.makedirs(save_txt_path)
save_images_path = os.path.join(save_root, train_val, "images")
if os.path.exists(save_images_path) is False:
os.makedirs(save_images_path)
for file in tqdm(file_names, desc="translate {} file...".format(train_val)):
# 检查下图像文件是否存在
img_path = os.path.join(voc_images_path, file + ".jpg")
assert os.path.exists(img_path), "file:{} not exist...".format(img_path)
# 检查xml文件是否存在
xml_path = os.path.join(voc_xml_path, file + ".xml")
assert os.path.exists(xml_path), "file:{} not exist...".format(xml_path)
# read xml
with open(xml_path) as fid:
xml_str = fid.read()
xml = etree.fromstring(xml_str)
data = parse_xml_to_dict(xml)["annotation"]
img_height = int(data["size"]["height"])
img_width = int(data["size"]["width"])
# write object info into txt
assert "object" in data.keys(), "file: '{}' lack of object key.".format(xml_path)
if len(data["object"]) == 0:
# 如果xml文件中没有目标就直接忽略该样本
print("Warning: in '{}' xml, there are no objects.".format(xml_path))
continue
with open(os.path.join(save_txt_path, file + ".txt"), "w") as f:
for index, obj in enumerate(data["object"]):
# 获取每个object的box信息
xmin = float(obj["bndbox"]["xmin"])
xmax = float(obj["bndbox"]["xmax"])
ymin = float(obj["bndbox"]["ymin"])
ymax = float(obj["bndbox"]["ymax"])
class_name = obj["name"]
class_index = class_dict[class_name] - 1 # 目标id从0开始
# 进一步检查数据,有的标注信息中可能有w或h为0的情况,这样的数据会导致计算回归loss为nan
if xmax <= xmin or ymax <= ymin:
print("Warning: in '{}' xml, there are some bbox w/h <=0".format(xml_path))
continue
# 将box信息转换到yolo格式
xcenter = xmin + (xmax - xmin) / 2
ycenter = ymin + (ymax - ymin) / 2
w = xmax - xmin
h = ymax - ymin
# 绝对坐标转相对坐标,保存6位小数
xcenter = round(xcenter / img_width, 6)
ycenter = round(ycenter / img_height, 6)
w = round(w / img_width, 6)
h = round(h / img_height, 6)
info = [str(i) for i in [class_index, xcenter, ycenter, w, h]]
if index == 0:
f.write(" ".join(info))
else:
f.write("\n" + " ".join(info))
# copy image into save_images_path
path_copy_to = os.path.join(save_images_path, img_path.split(os.sep)[-1])
if os.path.exists(path_copy_to) is False:
shutil.copyfile(img_path, path_copy_to)
def create_class_names(class_dict: dict):
keys = class_dict.keys()
with open("./data/my_data_label.names", "w") as w:
for index, k in enumerate(keys):
if index + 1 == len(keys):
w.write(k)
else:
w.write(k + "\n")
def main():
# read class_indict
json_file = open(label_json_path, 'r')
class_dict = json.load(json_file)
# 读取train.txt中的所有行信息,删除空行
with open(train_txt_path, "r") as r:
train_file_names = [i for i in r.read().splitlines() if len(i.strip()) > 0]
# voc信息转yolo,并将图像文件复制到相应文件夹
translate_info(train_file_names, save_file_root, class_dict, "train")
# 读取val.txt中的所有行信息,删除空行
with open(val_txt_path, "r") as r:
val_file_names = [i for i in r.read().splitlines() if len(i.strip()) > 0]
# voc信息转yolo,并将图像文件复制到相应文件夹
translate_info(val_file_names, save_file_root, class_dict, "val")
# 创建my_data_label.names文件
create_class_names(class_dict)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
这个部分代码是把VOC 数据集的.xml文件转换为YOLO格式的.txt文件,会生成my_yolo_dataset的train和val对应的图片images和标签labels,以及标签的名字my_data_label.names。数据集一定要好好检测,要不然可能转换不成功。
2.calculate_dataset.py
"""
该脚本有3个功能:
1.统计训练集和验证集的数据并生成相应.txt文件
2.创建data.data文件,记录classes个数, train以及val数据集文件(.txt)路径和label.names文件路径
3.根据yolov3-spp.cfg创建my_yolov3.cfg文件修改其中的predictor filters以及yolo classes参数(这两个参数是根据类别数改变的)
"""
import os
train_annotation_dir = "./my_yolo_dataset/train/labels"
val_annotation_dir = "./my_yolo_dataset/val/labels"
classes_label = "./data/my_data_label.names"
cfg_path = "./cfg/yolov3-spp.cfg"
assert os.path.exists(train_annotation_dir), "train_annotation_dir not exist!"
assert os.path.exists(val_annotation_dir), "val_annotation_dir not exist!"
assert os.path.exists(classes_label), "classes_label not exist!"
assert os.path.exists(cfg_path), "cfg_path not exist!"
def calculate_data_txt(txt_path, dataset_dir):
# create my_data.txt file that record image list
with open(txt_path, "w") as w:
for file_name in os.listdir(dataset_dir):
if file_name == "classes.txt":
continue
img_path = os.path.join(dataset_dir.replace("labels", "images"),
file_name.split(".")[0]) + ".jpg"
line = img_path + "\n"
assert os.path.exists(img_path), "file:{} not exist!".format(img_path)
w.write(line)
def create_data_data(create_data_path, label_path, train_path, val_path, classes_info):
# create my_data.data file that record classes, train, valid and names info.
# shutil.copyfile(label_path, "./data/my_data_label.names")
with open(create_data_path, "w") as w:
w.write("classes={}".format(len(classes_info)) + "\n") # 记录类别个数
w.write("train={}".format(train_path) + "\n") # 记录训练集对应txt文件路径
w.write("valid={}".format(val_path) + "\n") # 记录验证集对应txt文件路径
w.write("names=data/my_data_label.names" + "\n") # 记录label.names文件路径
def change_and_create_cfg_file(classes_info, save_cfg_path="./cfg/my_yolov3.cfg"):
# create my_yolov3.cfg file changed predictor filters and yolo classes param.
# this operation only deal with yolov3-spp.cfg
filters_lines = [636, 722, 809]
classes_lines = [643, 729, 816]
cfg_lines = open(cfg_path, "r").readlines()
for i in filters_lines:
assert "filters" in cfg_lines[i-1], "filters param is not in line:{}".format(i-1)
output_num = (5 + len(classes_info)) * 3
cfg_lines[i-1] = "filters={}\n".format(output_num)
for i in classes_lines:
assert "classes" in cfg_lines[i-1], "classes param is not in line:{}".format(i-1)
cfg_lines[i-1] = "classes={}\n".format(len(classes_info))
with open(save_cfg_path, "w") as w:
w.writelines(cfg_lines)
def main():
# 统计训练集和验证集的数据并生成相应txt文件
train_txt_path = "data/my_train_data.txt"
val_txt_path = "data/my_val_data.txt"
calculate_data_txt(train_txt_path, train_annotation_dir)
calculate_data_txt(val_txt_path, val_annotation_dir)
classes_info = [line.strip() for line in open(classes_label, "r").readlines() if len(line.strip()) > 0]
# 创建data.data文件,记录classes个数, train以及val数据集文件(.txt)路径和label.names文件路径
create_data_data("./data/my_data.data", classes_label, train_txt_path, val_txt_path, classes_info)
# 根据yolov3-spp.cfg创建my_yolov3.cfg文件修改其中的predictor filters以及yolo classes参数(这两个参数是根据类别数改变的)
change_and_create_cfg_file(classes_info)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
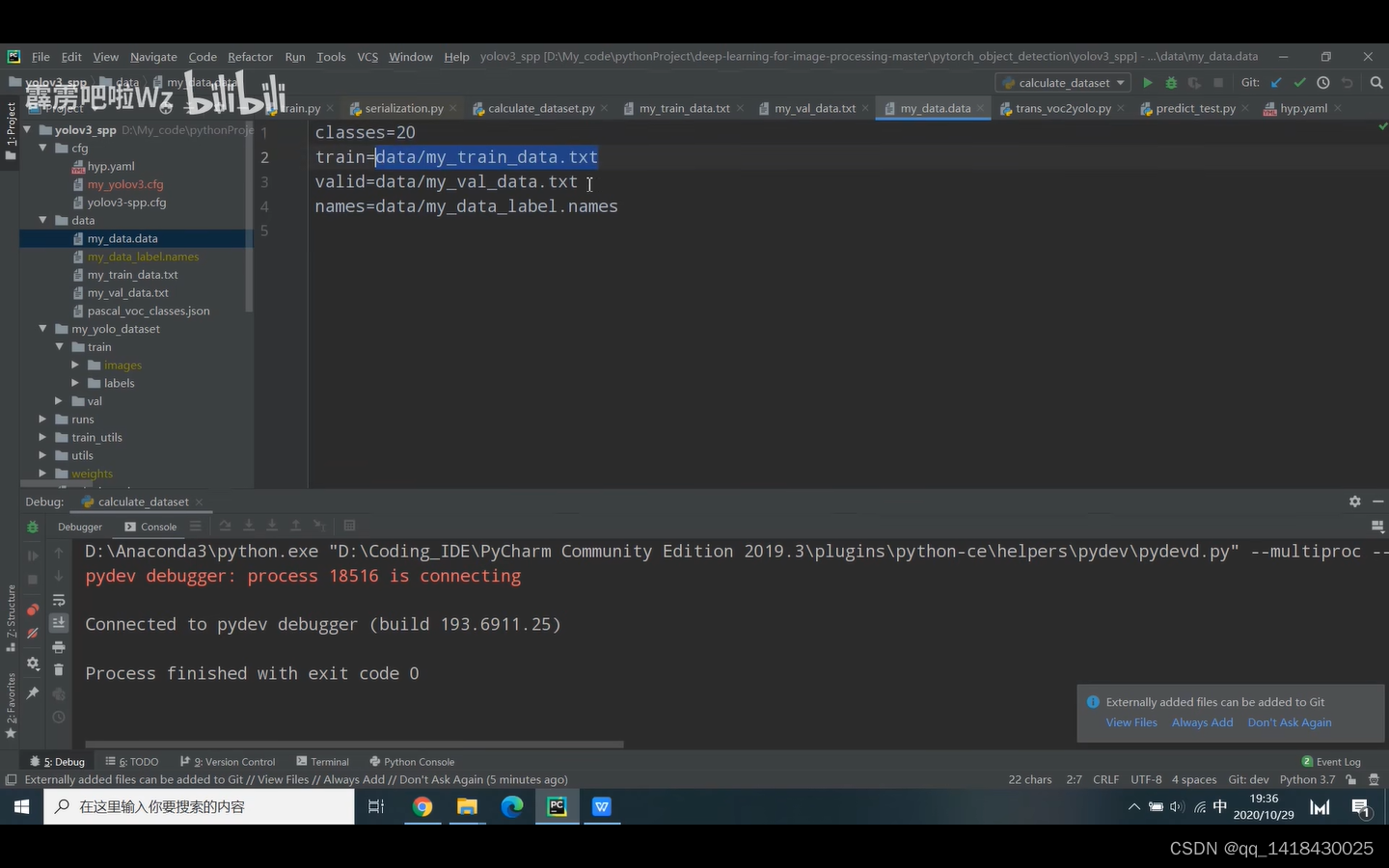
在这个文件下,生成my_val_data.txt文件(val路径)+my_train_data.txt文件(train路径)+my_data.data文件(包含类别数目,train=data/my_train_data.txt,valid=data/my_val_data.txt,names=data/my_data_label.names)
3.train.py(训练完成后,怎么打开终端进行查看训练保存的结果:打开Run文件夹下更目录,按住Shift+鼠标右键,输入tensorboard.exe --logdir “./”,打开浏览器输入网址即可查看)
import datetime
import argparse
import yaml
import torch.optim as optim
import torch.optim.lr_scheduler as lr_scheduler
from torch.utils.tensorboard import SummaryWriter
from models import *
from build_utils.datasets import *
from build_utils.utils import *
from train_utils import train_eval_utils as train_util
from train_utils import get_coco_api_from_dataset
def train(hyp):
device = torch.device(opt.device if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
print("Using {} device training.".format(device.type))
wdir = "weights" + os.sep # weights dir
best = wdir + "best.pt"
results_file = "results{}.txt".format(datetime.datetime.now().strftime("%Y%m%d-%H%M%S"))
cfg = opt.cfg
data = opt.data
epochs = opt.epochs
batch_size = opt.batch_size
accumulate = max(round(64 / batch_size), 1) # accumulate n times before optimizer update (bs 64)
weights = opt.weights # initial training weights
imgsz_train = opt.img_size
imgsz_test = opt.img_size # test image sizes
multi_scale = opt.multi_scale
# Image sizes
# 图像要设置成32的倍数
gs = 32 # (pixels) grid size
assert math.fmod(imgsz_test, gs) == 0, "--img-size %g must be a %g-multiple" % (imgsz_test, gs)
grid_min, grid_max = imgsz_test // gs, imgsz_test // gs
if multi_scale:
imgsz_min = opt.img_size // 1.5
imgsz_max = opt.img_size // 0.667
# 将给定的最大,最小输入尺寸向下调整到32的整数倍
grid_min, grid_max = imgsz_min // gs, imgsz_max // gs
imgsz_min, imgsz_max = int(grid_min * gs), int(grid_max * gs)
imgsz_train = imgsz_max # initialize with max size
print("Using multi_scale training, image range[{}, {}]".format(imgsz_min, imgsz_max))
# configure run
# init_seeds() # 初始化随机种子,保证结果可复现
data_dict = parse_data_cfg(data)
train_path = data_dict["train"]
test_path = data_dict["valid"]
nc = 1 if opt.single_cls else int(data_dict["classes"]) # number of classes
hyp["cls"] *= nc / 80 # update coco-tuned hyp['cls'] to current dataset
hyp["obj"] *= imgsz_test / 320
# Remove previous results
for f in glob.glob(results_file):
os.remove(f)
# Initialize model
model = Darknet(cfg).to(device)
# 是否冻结权重,只训练predictor的权重
if opt.freeze_layers:
# 索引减一对应的是predictor的索引,YOLOLayer并不是predictor
output_layer_indices = [idx - 1 for idx, module in enumerate(model.module_list) if
isinstance(module, YOLOLayer)]
# 冻结除predictor和YOLOLayer外的所有层
freeze_layer_indeces = [x for x in range(len(model.module_list)) if
(x not in output_layer_indices) and
(x - 1 not in output_layer_indices)]
# Freeze non-output layers
# 总共训练3x2=6个parameters
for idx in freeze_layer_indeces:
for parameter in model.module_list[idx].parameters():
parameter.requires_grad_(False)
else:
# 如果freeze_layer为False,默认仅训练除darknet53之后的部分
# 若要训练全部权重,删除以下代码
darknet_end_layer = 74 # only yolov3spp cfg
# Freeze darknet53 layers
# 总共训练21x3+3x2=69个parameters
for idx in range(darknet_end_layer + 1): # [0, 74]
for parameter in model.module_list[idx].parameters():
parameter.requires_grad_(False)
# optimizer
pg = [p for p in model.parameters() if p.requires_grad]
optimizer = optim.SGD(pg, lr=hyp["lr0"], momentum=hyp["momentum"],
weight_decay=hyp["weight_decay"], nesterov=True)
scaler = torch.cuda.amp.GradScaler() if opt.amp else None
start_epoch = 0
best_map = 0.0
if weights.endswith(".pt") or weights.endswith(".pth"):
ckpt = torch.load(weights, map_location=device)
# load model
try:
ckpt["model"] = {
k: v for k, v in ckpt["model"].items() if model.state_dict()[k].numel() == v.numel()}
model.load_state_dict(ckpt["model"], strict=False)
except KeyError as e:
s = "%s is not compatible with %s. Specify --weights '' or specify a --cfg compatible with %s. " \
"See https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov3/issues/657" % (opt.weights, opt.cfg, opt.weights)
raise KeyError(s) from e
# load optimizer
if ckpt["optimizer"] is not None:
optimizer.load_state_dict(ckpt["optimizer"])
if "best_map" in ckpt.keys():
best_map = ckpt["best_map"]
# load results
if ckpt.get("training_results") is not None:
with open(results_file, "w") as file:
file.write(ckpt["training_results"]) # write results.txt
# epochs
start_epoch = ckpt["epoch"] + 1
if epochs < start_epoch:
print('%s has been trained for %g epochs. Fine-tuning for %g additional epochs.' %
(opt.weights, ckpt['epoch'], epochs))
epochs += ckpt['epoch'] # finetune additional epochs
if opt.amp and "scaler" in ckpt:
scaler.load_state_dict(ckpt["scaler"])
del ckpt
# Scheduler https://arxiv.org/pdf/1812.01187.pdf
lf = lambda x: ((1 + math.cos(x * math.pi / epochs)) / 2) * (1 - hyp["lrf"]) + hyp["lrf"] # cosine
scheduler = lr_scheduler.LambdaLR(optimizer, lr_lambda=lf)
scheduler.last_epoch = start_epoch # 指定从哪个epoch开始
# Plot lr schedule
# y = []
# for _ in range(epochs):
# scheduler.step()
# y.append(optimizer.param_groups[0]['lr'])
# plt.plot(y, '.-', label='LambdaLR')
# plt.xlabel('epoch')
# plt.ylabel('LR')
# plt.tight_layout()
# plt.savefig('LR.png', dpi=300)
# model.yolo_layers = model.module.yolo_layers
# dataset
# 训练集的图像尺寸指定为multi_scale_range中最大的尺寸
train_dataset = LoadImagesAndLabels(train_path, imgsz_train, batch_size,
augment=True,
hyp=hyp, # augmentation hyperparameters
rect=opt.rect, # rectangular training
cache_images=opt.cache_images,
single_cls=opt.single_cls)
# 验证集的图像尺寸指定为img_size(512)
val_dataset = LoadImagesAndLabels(test_path, imgsz_test, batch_size,
hyp=hyp,
rect=True, # 将每个batch的图像调整到合适大小,可减少运算量(并不是512x512标准尺寸)
cache_images=opt.cache_images,
single_cls=opt.single_cls)
# dataloader
nw = min([os.cpu_count(), batch_size if batch_size > 1 else 0, 8]) # number of workers
train_dataloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(train_dataset,
batch_size=batch_size,
num_workers=nw,
# Shuffle=True unless rectangular training is used
shuffle=not opt.rect,
pin_memory=True,
collate_fn=train_dataset.collate_fn)
val_datasetloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(val_dataset,
batch_size=batch_size,
num_workers=nw,
pin_memory=True,
collate_fn=val_dataset.collate_fn)
# Model parameters
model.nc = nc # attach number of classes to model
model.hyp = hyp # attach hyperparameters to model
model.gr = 1.0 # giou loss ratio (obj_loss = 1.0 or giou)
# 计算每个类别的目标个数,并计算每个类别的比重
# model.class_weights = labels_to_class_weights(train_dataset.labels, nc).to(device) # attach class weights
# start training
# caching val_data when you have plenty of memory(RAM)
# coco = None
coco = get_coco_api_from_dataset(val_dataset)
print("starting traning for %g epochs..." % epochs)
print('Using %g dataloader workers' % nw)
for epoch in range(start_epoch, epochs):
mloss, lr = train_util.train_one_epoch(model, optimizer, train_dataloader,
device, epoch,
accumulate=accumulate, # 迭代多少batch才训练完64张图片
img_size=imgsz_train, # 输入图像的大小
multi_scale=multi_scale,
grid_min=grid_min, # grid的最小尺寸
grid_max=grid_max, # grid的最大尺寸
gs=gs, # grid step: 32
print_freq=50, # 每训练多少个step打印一次信息
warmup=True,
scaler=scaler)
# update scheduler
scheduler.step()
if opt.notest is False or epoch == epochs - 1:
# evaluate on the test dataset
result_info = train_util.evaluate(model, val_datasetloader,
coco=coco, device=device)
coco_mAP = result_info[0]
voc_mAP = result_info[1]
coco_mAR = result_info[8]
# write into tensorboard
if tb_writer:
tags = ['train/giou_loss', 'train/obj_loss', 'train/cls_loss', 'train/loss', "learning_rate",
"mAP@[IoU=0.50:0.95]", "mAP@[IoU=0.5]", "mAR@[IoU=0.50:0.95]"]
for x, tag in zip(mloss.tolist() + [lr, coco_mAP, voc_mAP, coco_mAR], tags):
tb_writer.add_scalar(tag, x, epoch)
# write into txt
with open(results_file, "a") as f:
# 记录coco的12个指标加上训练总损失和lr
result_info = [str(round(i, 4)) for i in result_info + [mloss.tolist()[-1]]] + [str(round(lr, 6))]
txt = "epoch:{} {}".format(epoch, ' '.join(result_info))
f.write(txt + "\n")
# update best mAP(IoU=0.50:0.95)
if coco_mAP > best_map:
best_map = coco_mAP
if opt.savebest is False:
# save weights every epoch
with open(results_file, 'r') as f:
save_files = {
'model': model.state_dict(),
'optimizer': optimizer.state_dict(),
'training_results': f.read(),
'epoch': epoch,
'best_map': best_map}
if opt.amp:
save_files["scaler"] = scaler.state_dict()
torch.save(save_files, "./weights/yolov3spp-{}.pt".format(epoch))
else:
# only save best weights
if best_map == coco_mAP:
with open(results_file, 'r') as f:
save_files = {
'model': model.state_dict(),
'optimizer': optimizer.state_dict(),
'training_results': f.read(),
'epoch': epoch,
'best_map': best_map}
if opt.amp:
save_files["scaler"] = scaler.state_dict()
torch.save(save_files, best.format(epoch))
if __name__ == '__main__':
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument('--epochs', type=int, default=30)
parser.add_argument('--batch-size', type=int, default=4)
parser.add_argument('--cfg', type=str, default='cfg/my_yolov3.cfg', help="*.cfg path")
parser.add_argument('--data', type=str, default='data/my_data.data', help='*.data path')
parser.add_argument('--hyp', type=str, default='cfg/hyp.yaml', help='hyperparameters path')
parser.add_argument('--multi-scale', type=bool, default=True,
help='adjust (67%% - 150%%) img_size every 10 batches')
parser.add_argument('--img-size', type=int, default=512, help='test size')
parser.add_argument('--rect', action='store_true', help='rectangular training')
parser.add_argument('--savebest', type=bool, default=False, help='only save best checkpoint')
parser.add_argument('--notest', action='store_true', help='only test final epoch')
parser.add_argument('--cache-images', action='store_true', help='cache images for faster training')
parser.add_argument('--weights', type=str, default='weights/yolov3-spp-ultralytics-512.pt',
help='initial weights path')
parser.add_argument('--name', default='', help='renames results.txt to results_name.txt if supplied')
parser.add_argument('--device', default='cuda:0', help='device id (i.e. 0 or 0,1 or cpu)')
parser.add_argument('--single-cls', action='store_true', help='train as single-class dataset')
parser.add_argument('--freeze-layers', type=bool, default=False, help='Freeze non-output layers')
# 是否使用混合精度训练(需要GPU支持混合精度)
parser.add_argument("--amp", default=False, help="Use torch.cuda.amp for mixed precision training")
opt = parser.parse_args()
# 检查文件是否存在
opt.cfg = check_file(opt.cfg)
opt.data = check_file(opt.data)
opt.hyp = check_file(opt.hyp)
print(opt)
with open(opt.hyp) as f:
hyp = yaml.load(f, Loader=yaml.FullLoader)
print('Start Tensorboard with "tensorboard --logdir=runs", view at http://localhost:6006/')
tb_writer = SummaryWriter(comment=opt.name)
train(hyp)
二、配置文件解析
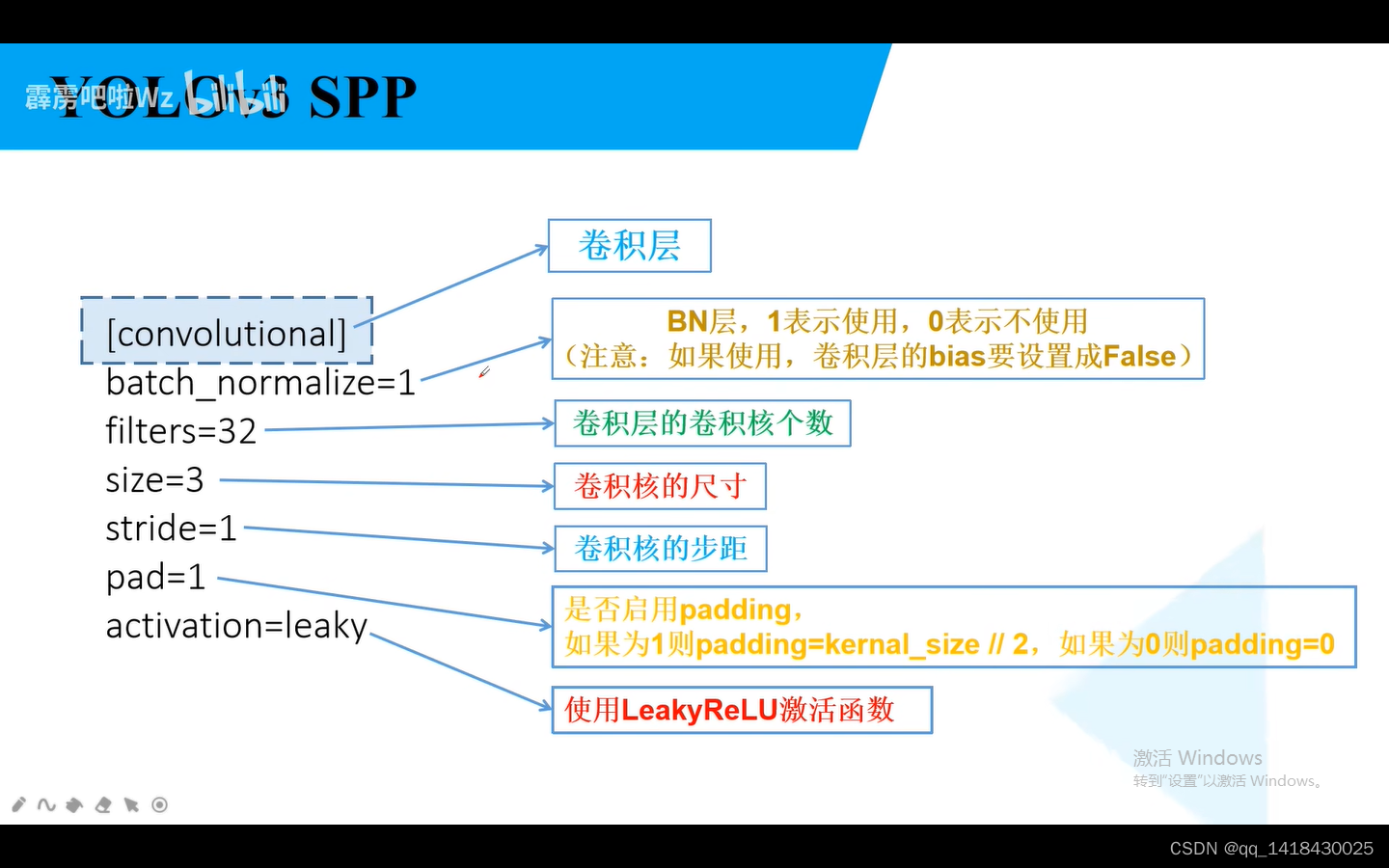
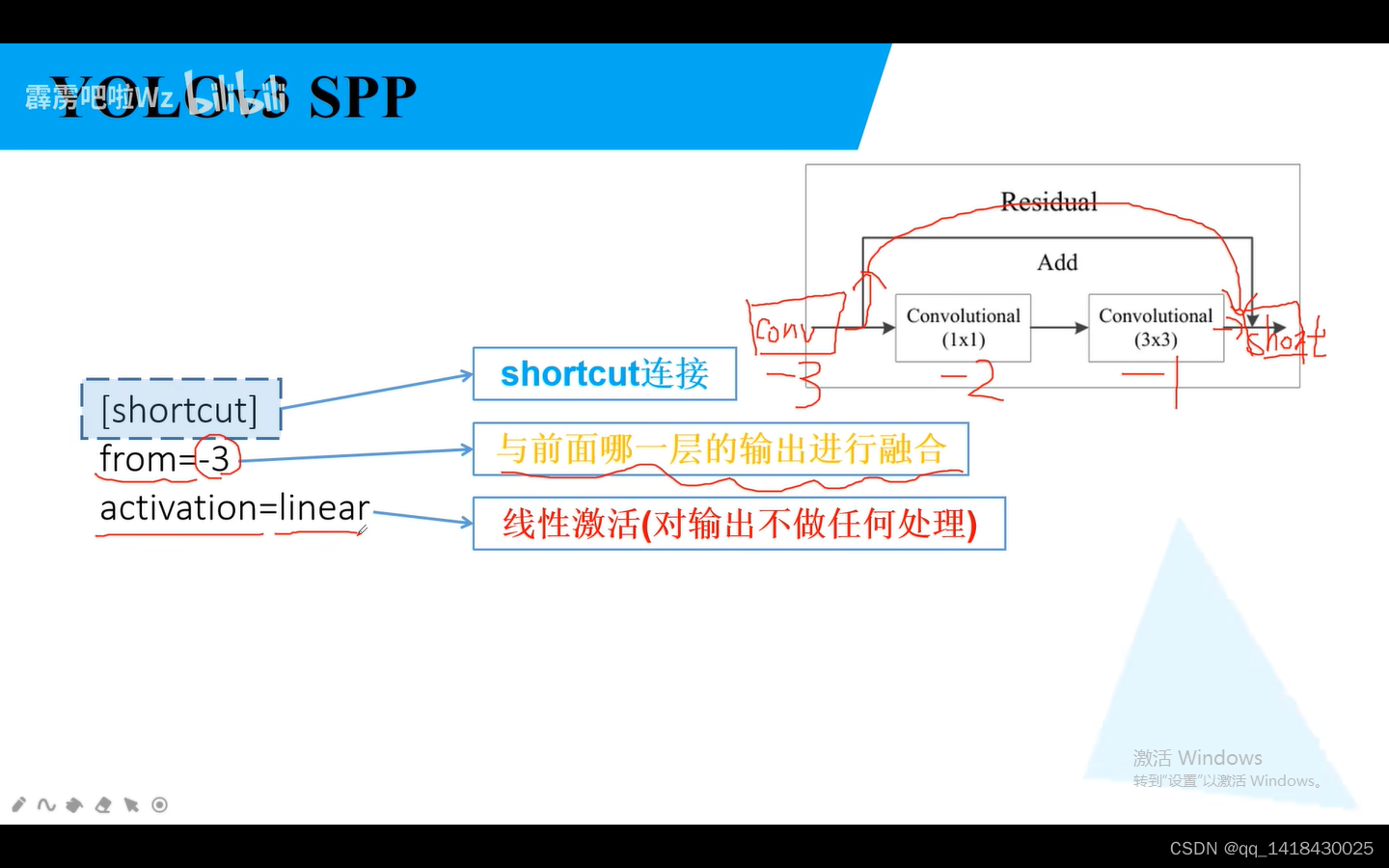
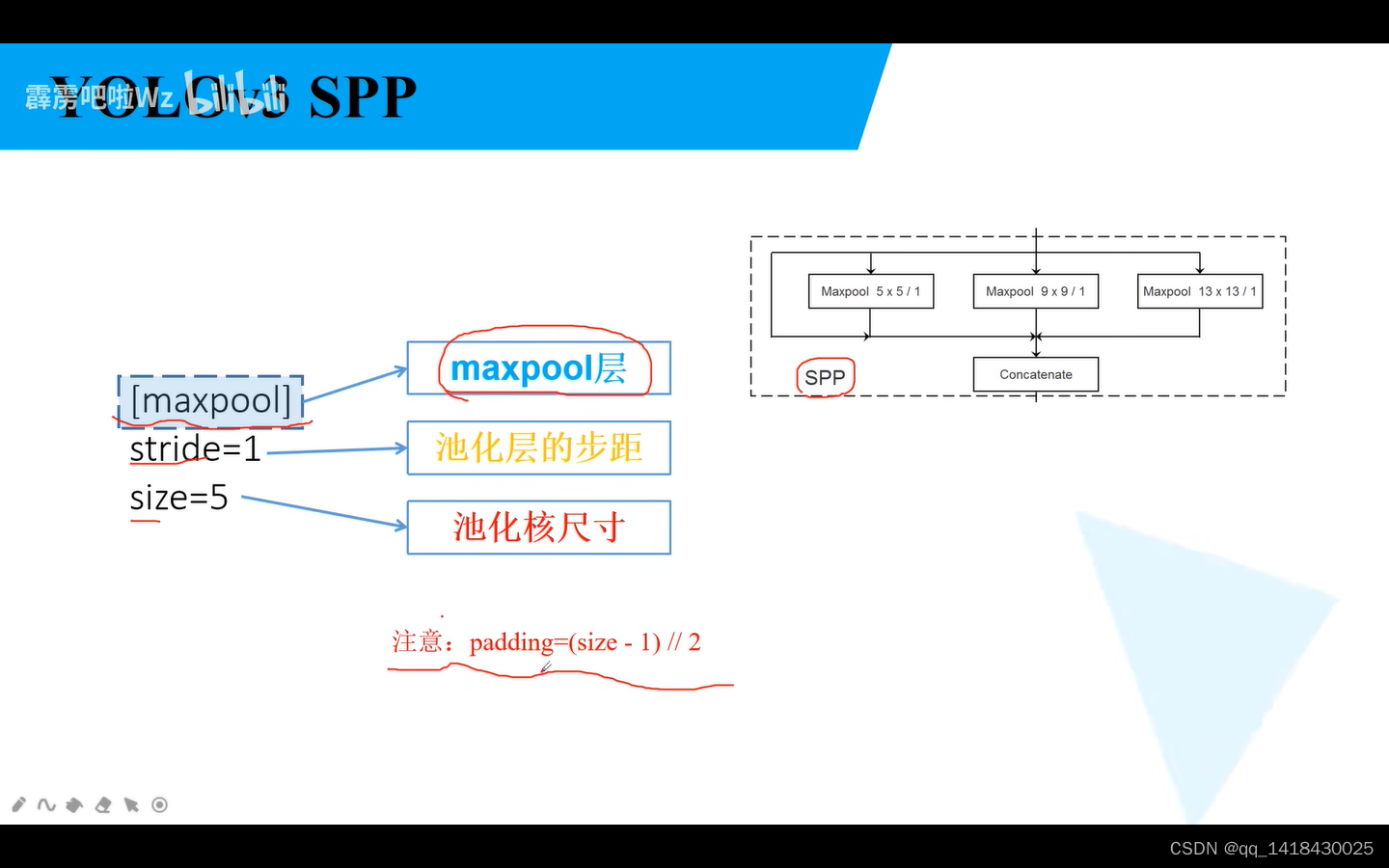
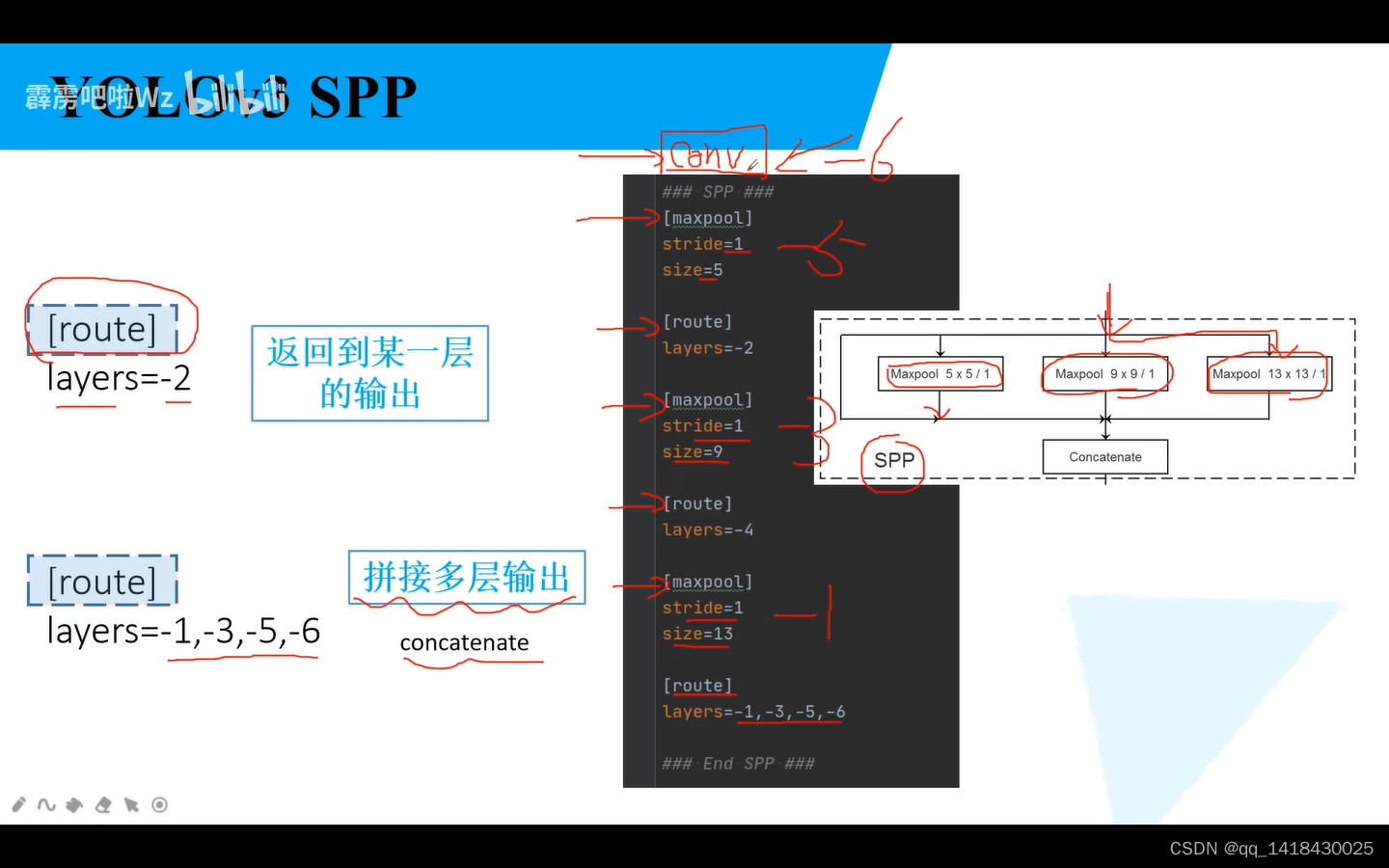
1.parse_config.py(解析网络文件的配置文件)
import os
import numpy as np
def parse_model_cfg(path: str):
# 检查文件是否存在
if not path.endswith(".cfg") or not os.path.exists(path):
raise FileNotFoundError("the cfg file not exist...")
# 读取文件信息
with open(path, "r") as f:
lines = f.read().split("\n")
# 去除空行和注释行
lines = [x for x in lines if x and not x.startswith("#")]
# 去除每行开头和结尾的空格符
lines = [x.strip() for x in lines]
mdefs = [] # module definitions
for line in lines:
if line.startswith("["): # this marks the start of a new block
mdefs.append({
})
mdefs[-1]["type"] = line[1:-1].strip() # 记录module类型
# 如果是卷积模块,设置默认不使用BN(普通卷积层后面会重写成1,最后的预测层conv保持为0)
if mdefs[-1]["type"] == "convolutional":
mdefs[-1]["batch_normalize"] = 0
else:
key, val = line.split("=")
key = key.strip()
val = val.strip()
if key == "anchors":
# anchors = 10,13, 16,30, 33,23, 30,61, 62,45, 59,119, 116,90, 156,198, 373,326
val = val.replace(" ", "") # 将空格去除
mdefs[-1][key] = np.array([float(x) for x in val.split(",")]).reshape((-1, 2)) # np anchors
elif (key in ["from", "layers", "mask"]) or (key == "size" and "," in val):
mdefs[-1][key] = [int(x) for x in val.split(",")]
else:
# TODO: .isnumeric() actually fails to get the float case
if val.isnumeric(): # return int or float 如果是数值的情况
mdefs[-1][key] = int(val) if (int(val) - float(val)) == 0 else float(val)
else:
mdefs[-1][key] = val # return string 是字符的情况
# check all fields are supported
supported = ['type', 'batch_normalize', 'filters', 'size', 'stride', 'pad', 'activation', 'layers', 'groups',
'from', 'mask', 'anchors', 'classes', 'num', 'jitter', 'ignore_thresh', 'truth_thresh', 'random',
'stride_x', 'stride_y', 'weights_type', 'weights_normalization', 'scale_x_y', 'beta_nms', 'nms_kind',
'iou_loss', 'iou_normalizer', 'cls_normalizer', 'iou_thresh', 'probability']
# 遍历检查每个模型的配置
for x in mdefs[1:]: # 0对应net配置
# 遍历每个配置字典中的key值
for k in x:
if k not in supported:
raise ValueError("Unsupported fields:{} in cfg".format(k))
return mdefs
def parse_data_cfg(path):
# Parses the data configuration file
if not os.path.exists(path) and os.path.exists('data' + os.sep + path): # add data/ prefix if omitted
path = 'data' + os.sep + path
with open(path, 'r') as f:
lines = f.readlines()
options = dict()
for line in lines:
line = line.strip()
if line == '' or line.startswith('#'):
continue
key, val = line.split('=')
options[key.strip()] = val.strip()
return options
三、网络搭建
1.modules.py
from build_utils.layers import *
from build_utils.parse_config import *
ONNX_EXPORT = False
def create_modules(modules_defs: list, img_size):
"""
Constructs module list of layer blocks from module configuration in module_defs
:param modules_defs: 通过.cfg文件解析得到的每个层结构的列表
:param img_size:
:return:
"""
img_size = [img_size] * 2 if isinstance(img_size, int) else img_size
# 删除解析cfg列表中的第一个配置(对应[net]的配置)
modules_defs.pop(0) # cfg training hyperparams (unused)
output_filters = [3] # input channels
module_list = nn.ModuleList()
# 统计哪些特征层的输出会被后续的层使用到(可能是特征融合,也可能是拼接)
routs = [] # list of layers which rout to deeper layers
yolo_index = -1
# 遍历搭建每个层结构
for i, mdef in enumerate(modules_defs):
modules = nn.Sequential()
if mdef["type"] == "convolutional":
bn = mdef["batch_normalize"] # 1 or 0 / use or not
filters = mdef["filters"]
k = mdef["size"] # kernel size
stride = mdef["stride"] if "stride" in mdef else (mdef['stride_y'], mdef["stride_x"])
if isinstance(k, int):
modules.add_module("Conv2d", nn.Conv2d(in_channels=output_filters[-1],
out_channels=filters,
kernel_size=k,
stride=stride,
padding=k // 2 if mdef["pad"] else 0,
bias=not bn))
else:
raise TypeError("conv2d filter size must be int type.")
if bn:
modules.add_module("BatchNorm2d", nn.BatchNorm2d(filters))
else:
# 如果该卷积操作没有bn层,意味着该层为yolo的predictor
routs.append(i) # detection output (goes into yolo layer)
if mdef["activation"] == "leaky":
modules.add_module("activation", nn.LeakyReLU(0.1, inplace=True))
else:
pass
elif mdef["type"] == "BatchNorm2d":
pass
elif mdef["type"] == "maxpool":
k = mdef["size"] # kernel size
stride = mdef["stride"]
modules = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=k, stride=stride, padding=(k - 1) // 2)
elif mdef["type"] == "upsample":
if ONNX_EXPORT: # explicitly state size, avoid scale_factor
g = (yolo_index + 1) * 2 / 32 # gain
modules = nn.Upsample(size=tuple(int(x * g) for x in img_size))
else:
modules = nn.Upsample(scale_factor=mdef["stride"])
elif mdef["type"] == "route": # [-2], [-1,-3,-5,-6], [-1, 61]
layers = mdef["layers"]
filters = sum([output_filters[l + 1 if l > 0 else l] for l in layers])
routs.extend([i + l if l < 0 else l for l in layers])
modules = FeatureConcat(layers=layers)
elif mdef["type"] == "shortcut":
layers = mdef["from"]
filters = output_filters[-1]
# routs.extend([i + l if l < 0 else l for l in layers])
routs.append(i + layers[0])
modules = WeightedFeatureFusion(layers=layers, weight="weights_type" in mdef)
elif mdef["type"] == "yolo":
yolo_index += 1 # 记录是第几个yolo_layer [0, 1, 2]
stride = [32, 16, 8] # 预测特征层对应原图的缩放比例
modules = YOLOLayer(anchors=mdef["anchors"][mdef["mask"]], # anchor list
nc=mdef["classes"], # number of classes
img_size=img_size,
stride=stride[yolo_index])
# Initialize preceding Conv2d() bias (https://arxiv.org/pdf/1708.02002.pdf section 3.3)
try:
j = -1
# bias: shape(255,) 索引0对应Sequential中的Conv2d
# view: shape(3, 85)
b = module_list[j][0].bias.view(modules.na, -1)
b.data[:, 4] += -4.5 # obj
b.data[:, 5:] += math.log(0.6 / (modules.nc - 0.99)) # cls (sigmoid(p) = 1/nc)
module_list[j][0].bias = torch.nn.Parameter(b.view(-1), requires_grad=True)
except Exception as e:
print('WARNING: smart bias initialization failure.', e)
else:
print("Warning: Unrecognized Layer Type: " + mdef["type"])
# Register module list and number of output filters
module_list.append(modules)
output_filters.append(filters)
routs_binary = [False] * len(modules_defs)
for i in routs:
routs_binary[i] = True
return module_list, routs_binary
class YOLOLayer(nn.Module):
"""
对YOLO的输出进行处理
"""
def __init__(self, anchors, nc, img_size, stride):
super(YOLOLayer, self).__init__()
self.anchors = torch.Tensor(anchors)
self.stride = stride # layer stride 特征图上一步对应原图上的步距 [32, 16, 8]
self.na = len(anchors) # number of anchors (3)
self.nc = nc # number of classes (80)
self.no = nc + 5 # number of outputs (85: x, y, w, h, obj, cls1, ...)
self.nx, self.ny, self.ng = 0, 0, (0, 0) # initialize number of x, y gridpoints
# 将anchors大小缩放到grid尺度
self.anchor_vec = self.anchors / self.stride
# batch_size, na, grid_h, grid_w, wh,
# 值为1的维度对应的值不是固定值,后续操作可根据broadcast广播机制自动扩充
self.anchor_wh = self.anchor_vec.view(1, self.na, 1, 1, 2)
self.grid = None
if ONNX_EXPORT:
self.training = False
self.create_grids((img_size[1] // stride, img_size[0] // stride)) # number x, y grid points
def create_grids(self, ng=(13, 13), device="cpu"):
"""
更新grids信息并生成新的grids参数
:param ng: 特征图大小
:param device:
:return:
"""
self.nx, self.ny = ng
self.ng = torch.tensor(ng, dtype=torch.float)
# build xy offsets 构建每个cell处的anchor的xy偏移量(在feature map上的)
if not self.training: # 训练模式不需要回归到最终预测boxes
yv, xv = torch.meshgrid([torch.arange(self.ny, device=device),
torch.arange(self.nx, device=device)])
# batch_size, na, grid_h, grid_w, wh
self.grid = torch.stack((xv, yv), 2).view((1, 1, self.ny, self.nx, 2)).float()
if self.anchor_vec.device != device:
self.anchor_vec = self.anchor_vec.to(device)
self.anchor_wh = self.anchor_wh.to(device)
def forward(self, p):
if ONNX_EXPORT:
bs = 1 # batch size
else:
bs, _, ny, nx = p.shape # batch_size, predict_param(255), grid(13), grid(13)
if (self.nx, self.ny) != (nx, ny) or self.grid is None: # fix no grid bug
self.create_grids((nx, ny), p.device)
# view: (batch_size, 255, 13, 13) -> (batch_size, 3, 85, 13, 13)
# permute: (batch_size, 3, 85, 13, 13) -> (batch_size, 3, 13, 13, 85)
# [bs, anchor, grid, grid, xywh + obj + classes]
p = p.view(bs, self.na, self.no, self.ny, self.nx).permute(0, 1, 3, 4, 2).contiguous() # prediction
if self.training:
return p
elif ONNX_EXPORT:
# Avoid broadcasting for ANE operations
m = self.na * self.nx * self.ny # 3*
ng = 1. / self.ng.repeat(m, 1)
grid = self.grid.repeat(1, self.na, 1, 1, 1).view(m, 2)
anchor_wh = self.anchor_wh.repeat(1, 1, self.nx, self.ny, 1).view(m, 2) * ng
p = p.view(m, self.no)
# xy = torch.sigmoid(p[:, 0:2]) + grid # x, y
# wh = torch.exp(p[:, 2:4]) * anchor_wh # width, height
# p_cls = torch.sigmoid(p[:, 4:5]) if self.nc == 1 else \
# torch.sigmoid(p[:, 5:self.no]) * torch.sigmoid(p[:, 4:5]) # conf
p[:, :2] = (torch.sigmoid(p[:, 0:2]) + grid) * ng # x, y
p[:, 2:4] = torch.exp(p[:, 2:4]) * anchor_wh # width, height
p[:, 4:] = torch.sigmoid(p[:, 4:])
p[:, 5:] = p[:, 5:self.no] * p[:, 4:5]
return p
else: # inference
# [bs, anchor, grid, grid, xywh + obj + classes]
io = p.clone() # inference output
io[..., :2] = torch.sigmoid(io[..., :2]) + self.grid # xy 计算在feature map上的xy坐标
io[..., 2:4] = torch.exp(io[..., 2:4]) * self.anchor_wh # wh yolo method 计算在feature map上的wh
io[..., :4] *= self.stride # 换算映射回原图尺度
torch.sigmoid_(io[..., 4:])
return io.view(bs, -1, self.no), p # view [1, 3, 13, 13, 85] as [1, 507, 85]
class Darknet(nn.Module):
"""
YOLOv3 spp object detection model
"""
def __init__(self, cfg, img_size=(416, 416), verbose=False):
super(Darknet, self).__init__()
# 这里传入的img_size只在导出ONNX模型时起作用
self.input_size = [img_size] * 2 if isinstance(img_size, int) else img_size
# 解析网络对应的.cfg文件
self.module_defs = parse_model_cfg(cfg)
# 根据解析的网络结构一层一层去搭建
self.module_list, self.routs = create_modules(self.module_defs, img_size)
# 获取所有YOLOLayer层的索引
self.yolo_layers = get_yolo_layers(self)
# 打印下模型的信息,如果verbose为True则打印详细信息
self.info(verbose) if not ONNX_EXPORT else None # print model description
def forward(self, x, verbose=False):
return self.forward_once(x, verbose=verbose)
def forward_once(self, x, verbose=False):
# yolo_out收集每个yolo_layer层的输出
# out收集每个模块的输出
yolo_out, out = [], []
if verbose:
print('0', x.shape)
str = ""
for i, module in enumerate(self.module_list):
name = module.__class__.__name__
if name in ["WeightedFeatureFusion", "FeatureConcat"]: # sum, concat
if verbose:
l = [i - 1] + module.layers # layers
sh = [list(x.shape)] + [list(out[i].shape) for i in module.layers] # shapes
str = ' >> ' + ' + '.join(['layer %g %s' % x for x in zip(l, sh)])
x = module(x, out) # WeightedFeatureFusion(), FeatureConcat()
elif name == "YOLOLayer":
yolo_out.append(module(x))
else: # run module directly, i.e. mtype = 'convolutional', 'upsample', 'maxpool', 'batchnorm2d' etc.
x = module(x)
out.append(x if self.routs[i] else [])
if verbose:
print('%g/%g %s -' % (i, len(self.module_list), name), list(x.shape), str)
str = ''
if self.training: # train
return yolo_out
elif ONNX_EXPORT: # export
# x = [torch.cat(x, 0) for x in zip(*yolo_out)]
# return x[0], torch.cat(x[1:3], 1) # scores, boxes: 3780x80, 3780x4
p = torch.cat(yolo_out, dim=0)
# # 根据objectness虑除低概率目标
# mask = torch.nonzero(torch.gt(p[:, 4], 0.1), as_tuple=False).squeeze(1)
# # onnx不支持超过一维的索引(pytorch太灵活了)
# # p = p[mask]
# p = torch.index_select(p, dim=0, index=mask)
#
# # 虑除小面积目标,w > 2 and h > 2 pixel
# # ONNX暂不支持bitwise_and和all操作
# mask_s = torch.gt(p[:, 2], 2./self.input_size[0]) & torch.gt(p[:, 3], 2./self.input_size[1])
# mask_s = torch.nonzero(mask_s, as_tuple=False).squeeze(1)
# p = torch.index_select(p, dim=0, index=mask_s) # width-height 虑除小目标
#
# if mask_s.numel() == 0:
# return torch.empty([0, 85])
return p
else: # inference or test
x, p = zip(*yolo_out) # inference output, training output
x = torch.cat(x, 1) # cat yolo outputs
return x, p
def info(self, verbose=False):
"""
打印模型的信息
:param verbose:
:return:
"""
torch_utils.model_info(self, verbose)
def get_yolo_layers(self):
"""
获取网络中三个"YOLOLayer"模块对应的索引
:param self:
:return:
"""
return [i for i, m in enumerate(self.module_list) if m.__class__.__name__ == 'YOLOLayer'] # [89, 101, 113]
四、自定义数据集
1.datasets.py
import math
import os
import random
import shutil
from pathlib import Path
import cv2
import numpy as np
import torch
from PIL import Image, ExifTags
from torch.utils.data import Dataset
from tqdm import tqdm
from build_utils.utils import xyxy2xywh, xywh2xyxy
help_url = 'https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov3/wiki/Train-Custom-Data'
img_formats = ['.bmp', '.jpg', '.jpeg', '.png', '.tif', '.dng']
# get orientation in exif tag
# 找到图像exif信息中对应旋转信息的key值
for orientation in ExifTags.TAGS.keys():
if ExifTags.TAGS[orientation] == "Orientation":
break
def exif_size(img):
"""
获取图像的原始img size
通过exif的orientation信息判断图像是否有旋转,如果有旋转则返回旋转前的size
:param img: PIL图片
:return: 原始图像的size
"""
# Returns exif-corrected PIL size
s = img.size # (width, height)
try:
rotation = dict(img._getexif().items())[orientation]
if rotation == 6: # rotation 270 顺时针翻转90度
s = (s[1], s[0])
elif rotation == 8: # ratation 90 逆时针翻转90度
s = (s[1], s[0])
except:
# 如果图像的exif信息中没有旋转信息,则跳过
pass
return s
class LoadImagesAndLabels(Dataset): # for training/testing
def __init__(self,
path, # 指向data/my_train_data.txt路径或data/my_val_data.txt路径
# 这里设置的是预处理后输出的图片尺寸
# 当为训练集时,设置的是训练过程中(开启多尺度)的最大尺寸
# 当为验证集时,设置的是最终使用的网络大小
img_size=416,
batch_size=16,
augment=False, # 训练集设置为True(augment_hsv),验证集设置为False
hyp=None, # 超参数字典,其中包含图像增强会使用到的超参数
rect=False, # 是否使用rectangular training
cache_images=False, # 是否缓存图片到内存中
single_cls=False, pad=0.0, rank=-1):
try:
path = str(Path(path))
# parent = str(Path(path).parent) + os.sep
if os.path.isfile(path): # file
# 读取对应my_train/val_data.txt文件,读取每一行的图片路劲信息
with open(path, "r") as f:
f = f.read().splitlines()
else:
raise Exception("%s does not exist" % path)
# 检查每张图片后缀格式是否在支持的列表中,保存支持的图像路径
# img_formats = ['.bmp', '.jpg', '.jpeg', '.png', '.tif', '.dng']
self.img_files = [x for x in f if os.path.splitext(x)[-1].lower() in img_formats]
self.img_files.sort() # 防止不同系统排序不同,导致shape文件出现差异
except Exception as e:
raise FileNotFoundError("Error loading data from {}. {}".format(path, e))
# 如果图片列表中没有图片,则报错
n = len(self.img_files)
assert n > 0, "No images found in %s. See %s" % (path, help_url)
# batch index
# 将数据划分到一个个batch中
bi = np.floor(np.arange(n) / batch_size).astype(np.int)
# 记录数据集划分后的总batch数
nb = bi[-1] + 1 # number of batches
self.n = n # number of images 图像总数目
self.batch = bi # batch index of image 记录哪些图片属于哪个batch
self.img_size = img_size # 这里设置的是预处理后输出的图片尺寸
self.augment = augment # 是否启用augment_hsv
self.hyp = hyp # 超参数字典,其中包含图像增强会使用到的超参数
self.rect = rect # 是否使用rectangular training
# 注意: 开启rect后,mosaic就默认关闭
self.mosaic = self.augment and not self.rect # load 4 images at a time into a mosaic (only during training)
# Define labels
# 遍历设置图像对应的label路径
# (./my_yolo_dataset/train/images/2009_004012.jpg) -> (./my_yolo_dataset/train/labels/2009_004012.txt)
self.label_files = [x.replace("images", "labels").replace(os.path.splitext(x)[-1], ".txt")
for x in self.img_files]
# Read image shapes (wh)
# 查看data文件下是否缓存有对应数据集的.shapes文件,里面存储了每张图像的width, height
sp = path.replace(".txt", ".shapes") # shapefile path
try:
with open(sp, "r") as f: # read existing shapefile
s = [x.split() for x in f.read().splitlines()]
# 判断现有的shape文件中的行数(图像个数)是否与当前数据集中图像个数相等
# 如果不相等则认为是不同的数据集,故重新生成shape文件
assert len(s) == n, "shapefile out of aync"
except Exception as e:
# print("read {} failed [{}], rebuild {}.".format(sp, e, sp))
# tqdm库会显示处理的进度
# 读取每张图片的size信息
if rank in [-1, 0]:
image_files = tqdm(self.img_files, desc="Reading image shapes")
else:
image_files = self.img_files
s = [exif_size(Image.open(f)) for f in image_files]
# 将所有图片的shape信息保存在.shape文件中
np.savetxt(sp, s, fmt="%g") # overwrite existing (if any)
# 记录每张图像的原始尺寸
self.shapes = np.array(s, dtype=np.float64)
# Rectangular Training https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov3/issues/232
# 如果为ture,训练网络时,会使用类似原图像比例的矩形(让最长边为img_size),而不是img_size x img_size
# 注意: 开启rect后,mosaic就默认关闭
if self.rect:
# Sort by aspect ratio
s = self.shapes # wh
# 计算每个图片的高/宽比
ar = s[:, 1] / s[:, 0] # aspect ratio
# argsort函数返回的是数组值从小到大的索引值
# 按照高宽比例进行排序,这样后面划分的每个batch中的图像就拥有类似的高宽比
irect = ar.argsort()
# 根据排序后的顺序重新设置图像顺序、标签顺序以及shape顺序
self.img_files = [self.img_files[i] for i in irect]
self.label_files = [self.label_files[i] for i in irect]
self.shapes = s[irect] # wh
ar = ar[irect]
# set training image shapes
# 计算每个batch采用的统一尺度
shapes = [[1, 1]] * nb # nb: number of batches
for i in range(nb):
ari = ar[bi == i] # bi: batch index
# 获取第i个batch中,最小和最大高宽比
mini, maxi = ari.min(), ari.max()
# 如果高/宽小于1(w > h),将w设为img_size
if maxi < 1:
shapes[i] = [maxi, 1]
# 如果高/宽大于1(w < h),将h设置为img_size
elif mini > 1:
shapes[i] = [1, 1 / mini]
# 计算每个batch输入网络的shape值(向上设置为32的整数倍)
self.batch_shapes = np.ceil(np.array(shapes) * img_size / 32. + pad).astype(np.int) * 32
# cache labels
self.imgs = [None] * n # n为图像总数
# label: [class, x, y, w, h] 其中的xywh都为相对值
self.labels = [np.zeros((0, 5), dtype=np.float32)] * n
extract_bounding_boxes, labels_loaded = False, False
nm, nf, ne, nd = 0, 0, 0, 0 # number mission, found, empty, duplicate
# 这里分别命名是为了防止出现rect为False/True时混用导致计算的mAP错误
# 当rect为True时会对self.images和self.labels进行从新排序
if rect is True:
np_labels_path = str(Path(self.label_files[0]).parent) + ".rect.npy" # saved labels in *.npy file
else:
np_labels_path = str(Path(self.label_files[0]).parent) + ".norect.npy"
if os.path.isfile(np_labels_path):
x = np.load(np_labels_path, allow_pickle=True)
if len(x) == n:
# 如果载入的缓存标签个数与当前计算的图像数目相同则认为是同一数据集,直接读缓存
self.labels = x
labels_loaded = True
# 处理进度条只在第一个进程中显示
if rank in [-1, 0]:
pbar = tqdm(self.label_files)
else:
pbar = self.label_files
# 遍历载入标签文件
for i, file in enumerate(pbar):
if labels_loaded is True:
# 如果存在缓存直接从缓存读取
l = self.labels[i]
else:
# 从文件读取标签信息
try:
with open(file, "r") as f:
# 读取每一行label,并按空格划分数据
l = np.array([x.split() for x in f.read().splitlines()], dtype=np.float32)
except Exception as e:
print("An error occurred while loading the file {}: {}".format(file, e))
nm += 1 # file missing
continue
# 如果标注信息不为空的话
if l.shape[0]:
# 标签信息每行必须是五个值[class, x, y, w, h]
assert l.shape[1] == 5, "> 5 label columns: %s" % file
assert (l >= 0).all(), "negative labels: %s" % file
assert (l[:, 1:] <= 1).all(), "non-normalized or out of bounds coordinate labels: %s" % file
# 检查每一行,看是否有重复信息
if np.unique(l, axis=0).shape[0] < l.shape[0]: # duplicate rows
nd += 1
if single_cls:
l[:, 0] = 0 # force dataset into single-class mode
self.labels[i] = l
nf += 1 # file found
# Extract object detection boxes for a second stage classifier
if extract_bounding_boxes:
p = Path(self.img_files[i])
img = cv2.imread(str(p))
h, w = img.shape[:2]
for j, x in enumerate(l):
f = "%s%sclassifier%s%g_%g_%s" % (p.parent.parent, os.sep, os.sep, x[0], j, p.name)
if not os.path.exists(Path(f).parent):
os.makedirs(Path(f).parent) # make new output folder
# 将相对坐标转为绝对坐标
# b: x, y, w, h
b = x[1:] * [w, h, w, h] # box
# 将宽和高设置为宽和高中的最大值
b[2:] = b[2:].max() # rectangle to square
# 放大裁剪目标的宽高
b[2:] = b[2:] * 1.3 + 30 # pad
# 将坐标格式从 x,y,w,h -> xmin,ymin,xmax,ymax
b = xywh2xyxy(b.reshape(-1, 4)).revel().astype(np.int)
# 裁剪bbox坐标到图片内
b[[0, 2]] = np.clip[b[[0, 2]], 0, w]
b[[1, 3]] = np.clip[b[[1, 3]], 0, h]
assert cv2.imwrite(f, img[b[1]:b[3], b[0]:b[2]]), "Failure extracting classifier boxes"
else:
ne += 1 # file empty
# 处理进度条只在第一个进程中显示
if rank in [-1, 0]:
# 更新进度条描述信息
pbar.desc = "Caching labels (%g found, %g missing, %g empty, %g duplicate, for %g images)" % (
nf, nm, ne, nd, n)
assert nf > 0, "No labels found in %s." % os.path.dirname(self.label_files[0]) + os.sep
# 如果标签信息没有被保存成numpy的格式,且训练样本数大于1000则将标签信息保存成numpy的格式
if not labels_loaded and n > 1000:
print("Saving labels to %s for faster future loading" % np_labels_path)
np.save(np_labels_path, self.labels) # save for next time
# Cache images into memory for faster training (Warning: large datasets may exceed system RAM)
if cache_images: # if training
gb = 0 # Gigabytes of cached images 用于记录缓存图像占用RAM大小
if rank in [-1, 0]:
pbar = tqdm(range(len(self.img_files)), desc="Caching images")
else:
pbar = range(len(self.img_files))
self.img_hw0, self.img_hw = [None] * n, [None] * n
for i in pbar: # max 10k images
self.imgs[i], self.img_hw0[i], self.img_hw[i] = load_image(self, i) # img, hw_original, hw_resized
gb += self.imgs[i].nbytes # 用于记录缓存图像占用RAM大小
if rank in [-1, 0]:
pbar.desc = "Caching images (%.1fGB)" % (gb / 1E9)
# Detect corrupted images https://medium.com/joelthchao/programmatically-detect-corrupted-image-8c1b2006c3d3
detect_corrupted_images = False
if detect_corrupted_images:
from skimage import io # conda install -c conda-forge scikit-image
for file in tqdm(self.img_files, desc="Detecting corrupted images"):
try:
_ = io.imread(file)
except Exception as e:
print("Corrupted image detected: {}, {}".format(file, e))
def __len__(self):
return len(self.img_files)
def __getitem__(self, index):
hyp = self.hyp
if self.mosaic:
# load mosaic
img, labels = load_mosaic(self, index)
shapes = None
else:
# load image
img, (h0, w0), (h, w) = load_image(self, index)
# letterbox
shape = self.batch_shapes[self.batch[index]] if self.rect else self.img_size # final letterboxed shape
img, ratio, pad = letterbox(img, shape, auto=False, scale_up=self.augment)
shapes = (h0, w0), ((h / h0, w / w0), pad) # for COCO mAP rescaling
# load labels
labels = []
x = self.labels[index]
if x.size > 0:
# Normalized xywh to pixel xyxy format
labels = x.copy() # label: class, x, y, w, h
labels[:, 1] = ratio[0] * w * (x[:, 1] - x[:, 3] / 2) + pad[0] # pad width
labels[:, 2] = ratio[1] * h * (x[:, 2] - x[:, 4] / 2) + pad[1] # pad height
labels[:, 3] = ratio[0] * w * (x[:, 1] + x[:, 3] / 2) + pad[0]
labels[:, 4] = ratio[1] * h * (x[:, 2] + x[:, 4] / 2) + pad[1]
if self.augment:
# Augment imagespace
if not self.mosaic:
img, labels = random_affine(img, labels,
degrees=hyp["degrees"],
translate=hyp["translate"],
scale=hyp["scale"],
shear=hyp["shear"])
# Augment colorspace
augment_hsv(img, h_gain=hyp["hsv_h"], s_gain=hyp["hsv_s"], v_gain=hyp["hsv_v"])
nL = len(labels) # number of labels
if nL:
# convert xyxy to xywh
labels[:, 1:5] = xyxy2xywh(labels[:, 1:5])
# Normalize coordinates 0-1
labels[:, [2, 4]] /= img.shape[0] # height
labels[:, [1, 3]] /= img.shape[1] # width
if self.augment:
# random left-right flip
lr_flip = True # 随机水平翻转
if lr_flip and random.random() < 0.5:
img = np.fliplr(img)
if nL:
labels[:, 1] = 1 - labels[:, 1] # 1 - x_center
# random up-down flip
ud_flip = False
if ud_flip and random.random() < 0.5:
img = np.flipud(img)
if nL:
labels[:, 2] = 1 - labels[:, 2] # 1 - y_center
labels_out = torch.zeros((nL, 6)) # nL: number of labels
if nL:
labels_out[:, 1:] = torch.from_numpy(labels)
# Convert BGR to RGB, and HWC to CHW(3x512x512)
img = img[:, :, ::-1].transpose(2, 0, 1)
img = np.ascontiguousarray(img)
return torch.from_numpy(img), labels_out, self.img_files[index], shapes, index
def coco_index(self, index):
"""该方法是专门为cocotools统计标签信息准备,不对图像和标签作任何处理"""
o_shapes = self.shapes[index][::-1] # wh to hw
# load labels
x = self.labels[index]
labels = x.copy() # label: class, x, y, w, h
return torch.from_numpy(labels), o_shapes
@staticmethod
def collate_fn(batch):
img, label, path, shapes, index = zip(*batch) # transposed
for i, l in enumerate(label):
l[:, 0] = i # add target image index for build_targets()
return torch.stack(img, 0), torch.cat(label, 0), path, shapes, index
def load_image(self, index):
# loads 1 image from dataset, returns img, original hw, resized hw
img = self.imgs[index]
if img is None: # not cached
path = self.img_files[index]
img = cv2.imread(path) # BGR
assert img is not None, "Image Not Found " + path
h0, w0 = img.shape[:2] # orig hw
# img_size 设置的是预处理后输出的图片尺寸
r = self.img_size / max(h0, w0) # resize image to img_size
if r != 1: # if sizes are not equal
interp = cv2.INTER_AREA if r < 1 and not self.augment else cv2.INTER_LINEAR
img = cv2.resize(img, (int(w0 * r), int(h0 * r)), interpolation=interp)
return img, (h0, w0), img.shape[:2] # img, hw_original, hw_resized
else:
return self.imgs[index], self.img_hw0[index], self.img_hw[index] # img, hw_original, hw_resized
def load_mosaic(self, index):
"""
将四张图片拼接在一张马赛克图像中
:param self:
:param index: 需要获取的图像索引
:return:
"""
# loads images in a mosaic
labels4 = [] # 拼接图像的label信息
s = self.img_size
# 随机初始化拼接图像的中心点坐标
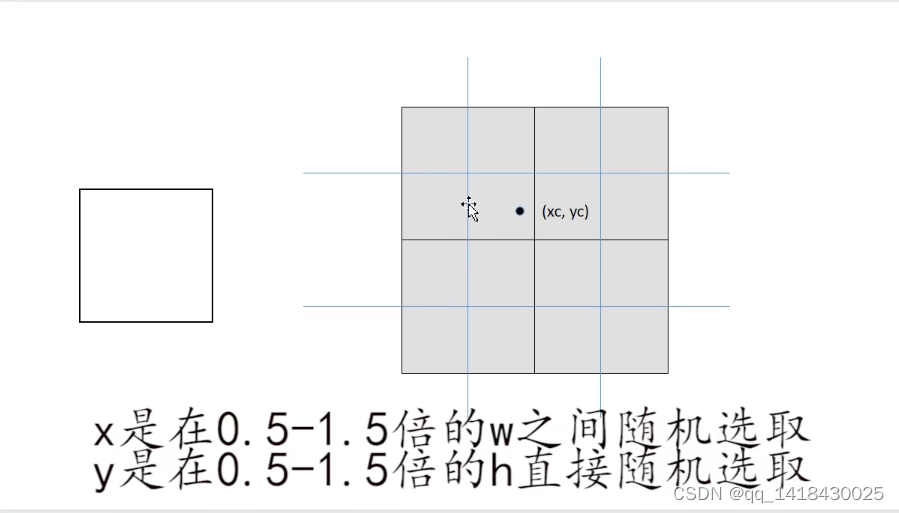
xc, yc = [int(random.uniform(s * 0.5, s * 1.5)) for _ in range(2)] # mosaic center x, y
# 从dataset中随机寻找三张图像进行拼接
indices = [index] + [random.randint(0, len(self.labels) - 1) for _ in range(3)] # 3 additional image indices
# 遍历四张图像进行拼接
for i, index in enumerate(indices):
# load image
img, _, (h, w) = load_image(self, index)
# place img in img4
if i == 0: # top left
# 创建马赛克图像
img4 = np.full((s * 2, s * 2, img.shape[2]), 114, dtype=np.uint8) # base image with 4 tiles
# 计算马赛克图像中的坐标信息(将图像填充到马赛克图像中)
x1a, y1a, x2a, y2a = max(xc - w, 0), max(yc - h, 0), xc, yc # xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax (large image)
# 计算截取的图像区域信息(以xc,yc为第一张图像的右下角坐标填充到马赛克图像中,丢弃越界的区域)
x1b, y1b, x2b, y2b = w - (x2a - x1a), h - (y2a - y1a), w, h # xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax (small image)
elif i == 1: # top right
# 计算马赛克图像中的坐标信息(将图像填充到马赛克图像中)
x1a, y1a, x2a, y2a = xc, max(yc - h, 0), min(xc + w, s * 2), yc
# 计算截取的图像区域信息(以xc,yc为第二张图像的左下角坐标填充到马赛克图像中,丢弃越界的区域)
x1b, y1b, x2b, y2b = 0, h - (y2a - y1a), min(w, x2a - x1a), h
elif i == 2: # bottom left
# 计算马赛克图像中的坐标信息(将图像填充到马赛克图像中)
x1a, y1a, x2a, y2a = max(xc - w, 0), yc, xc, min(s * 2, yc + h)
# 计算截取的图像区域信息(以xc,yc为第三张图像的右上角坐标填充到马赛克图像中,丢弃越界的区域)
x1b, y1b, x2b, y2b = w - (x2a - x1a), 0, max(xc, w), min(y2a - y1a, h)
elif i == 3: # bottom right
# 计算马赛克图像中的坐标信息(将图像填充到马赛克图像中)
x1a, y1a, x2a, y2a = xc, yc, min(xc + w, s * 2), min(s * 2, yc + h)
# 计算截取的图像区域信息(以xc,yc为第四张图像的左上角坐标填充到马赛克图像中,丢弃越界的区域)
x1b, y1b, x2b, y2b = 0, 0, min(w, x2a - x1a), min(y2a - y1a, h)
# 将截取的图像区域填充到马赛克图像的相应位置
img4[y1a:y2a, x1a:x2a] = img[y1b:y2b, x1b:x2b] # img4[ymin:ymax, xmin:xmax]
# 计算pad(图像边界与马赛克边界的距离,越界的情况为负值)
padw = x1a - x1b
padh = y1a - y1b
# Labels 获取对应拼接图像的labels信息
# [class_index, x_center, y_center, w, h]
x = self.labels[index]
labels = x.copy() # 深拷贝,防止修改原数据
if x.size > 0: # Normalized xywh to pixel xyxy format
# 计算标注数据在马赛克图像中的坐标(绝对坐标)
labels[:, 1] = w * (x[:, 1] - x[:, 3] / 2) + padw # xmin
labels[:, 2] = h * (x[:, 2] - x[:, 4] / 2) + padh # ymin
labels[:, 3] = w * (x[:, 1] + x[:, 3] / 2) + padw # xmax
labels[:, 4] = h * (x[:, 2] + x[:, 4] / 2) + padh # ymax
labels4.append(labels)
# Concat/clip labels
if len(labels4):
labels4 = np.concatenate(labels4, 0)
# 设置上下限防止越界
np.clip(labels4[:, 1:], 0, 2 * s, out=labels4[:, 1:]) # use with random_affine
# Augment
# 随机旋转,缩放,平移以及错切
img4, labels4 = random_affine(img4, labels4,
degrees=self.hyp['degrees'],
translate=self.hyp['translate'],
scale=self.hyp['scale'],
shear=self.hyp['shear'],
border=-s // 2) # border to remove
return img4, labels4
def random_affine(img, targets=(), degrees=10, translate=.1, scale=.1, shear=10, border=0):
"""随机旋转,缩放,平移以及错切"""
# torchvision.transforms.RandomAffine(degrees=(-10, 10), translate=(.1, .1), scale=(.9, 1.1), shear=(-10, 10))
# https://medium.com/uruvideo/dataset-augmentation-with-random-homographies-a8f4b44830d4
# 这里可以参考我写的博文: https://blog.csdn.net/qq_37541097/article/details/119420860
# targets = [cls, xyxy]
# 最终输出的图像尺寸,等于img4.shape / 2
height = img.shape[0] + border * 2
width = img.shape[1] + border * 2
# Rotation and Scale
# 生成旋转以及缩放矩阵
R = np.eye(3) # 生成对角阵
a = random.uniform(-degrees, degrees) # 随机旋转角度
s = random.uniform(1 - scale, 1 + scale) # 随机缩放因子
R[:2] = cv2.getRotationMatrix2D(angle=a, center=(img.shape[1] / 2, img.shape[0] / 2), scale=s)
# Translation
# 生成平移矩阵
T = np.eye(3)
T[0, 2] = random.uniform(-translate, translate) * img.shape[0] + border # x translation (pixels)
T[1, 2] = random.uniform(-translate, translate) * img.shape[1] + border # y translation (pixels)
# Shear
# 生成错切矩阵
S = np.eye(3)
S[0, 1] = math.tan(random.uniform(-shear, shear) * math.pi / 180) # x shear (deg)
S[1, 0] = math.tan(random.uniform(-shear, shear) * math.pi / 180) # y shear (deg)
# Combined rotation matrix
M = S @ T @ R # ORDER IS IMPORTANT HERE!!
if (border != 0) or (M != np.eye(3)).any(): # image changed
# 进行仿射变化
img = cv2.warpAffine(img, M[:2], dsize=(width, height), flags=cv2.INTER_LINEAR, borderValue=(114, 114, 114))
# Transform label coordinates
n = len(targets)
if n:
# warp points
xy = np.ones((n * 4, 3))
xy[:, :2] = targets[:, [1, 2, 3, 4, 1, 4, 3, 2]].reshape(n * 4, 2) # x1y1, x2y2, x1y2, x2y1
# [4*n, 3] -> [n, 8]
xy = (xy @ M.T)[:, :2].reshape(n, 8)
# create new boxes
# 对transform后的bbox进行修正(假设变换后的bbox变成了菱形,此时要修正成矩形)
x = xy[:, [0, 2, 4, 6]] # [n, 4]
y = xy[:, [1, 3, 5, 7]] # [n, 4]
xy = np.concatenate((x.min(1), y.min(1), x.max(1), y.max(1))).reshape(4, n).T # [n, 4]
# reject warped points outside of image
# 对坐标进行裁剪,防止越界
xy[:, [0, 2]] = xy[:, [0, 2]].clip(0, width)
xy[:, [1, 3]] = xy[:, [1, 3]].clip(0, height)
w = xy[:, 2] - xy[:, 0]
h = xy[:, 3] - xy[:, 1]
# 计算调整后的每个box的面积
area = w * h
# 计算调整前的每个box的面积
area0 = (targets[:, 3] - targets[:, 1]) * (targets[:, 4] - targets[:, 2])
# 计算每个box的比例
ar = np.maximum(w / (h + 1e-16), h / (w + 1e-16)) # aspect ratio
# 选取长宽大于4个像素,且调整前后面积比例大于0.2,且比例小于10的box
i = (w > 4) & (h > 4) & (area / (area0 * s + 1e-16) > 0.2) & (ar < 10)
targets = targets[i]
targets[:, 1:5] = xy[i]
return img, targets
def augment_hsv(img, h_gain=0.5, s_gain=0.5, v_gain=0.5):
# 这里可以参考我写的博文:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_37541097/article/details/119478023
r = np.random.uniform(-1, 1, 3) * [h_gain, s_gain, v_gain] + 1 # random gains
hue, sat, val = cv2.split(cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2HSV))
dtype = img.dtype # uint8
x = np.arange(0, 256, dtype=np.int16)
lut_hue = ((x * r[0]) % 180).astype(dtype)
lut_sat = np.clip(x * r[1], 0, 255).astype(dtype)
lut_val = np.clip(x * r[2], 0, 255).astype(dtype)
img_hsv = cv2.merge((cv2.LUT(hue, lut_hue), cv2.LUT(sat, lut_sat), cv2.LUT(val, lut_val))).astype(dtype)
cv2.cvtColor(img_hsv, cv2.COLOR_HSV2BGR, dst=img) # no return needed
def letterbox(img: np.ndarray,
new_shape=(416, 416),
color=(114, 114, 114),
auto=True,
scale_fill=False,
scale_up=True):
"""
将图片缩放调整到指定大小
:param img:
:param new_shape:
:param color:
:param auto:
:param scale_fill:
:param scale_up:
:return:
"""
shape = img.shape[:2] # [h, w]
if isinstance(new_shape, int):
new_shape = (new_shape, new_shape)
# scale ratio (new / old)
r = min(new_shape[0] / shape[0], new_shape[1] / shape[1])
if not scale_up: # only scale down, do not scale up (for better test mAP) 对于大于指定输入大小的图片进行缩放,小于的不变
r = min(r, 1.0)
# compute padding
ratio = r, r # width, height ratios
new_unpad = int(round(shape[1] * r)), int(round(shape[0] * r))
dw, dh = new_shape[1] - new_unpad[0], new_shape[0] - new_unpad[1] # wh padding
if auto: # minimun rectangle 保证原图比例不变,将图像最大边缩放到指定大小
# 这里的取余操作可以保证padding后的图片是32的整数倍
dw, dh = np.mod(dw, 32), np.mod(dh, 32) # wh padding
elif scale_fill: # stretch 简单粗暴的将图片缩放到指定尺寸
dw, dh = 0, 0
new_unpad = new_shape
ratio = new_shape[0] / shape[1], new_shape[1] / shape[0] # wh ratios
dw /= 2 # divide padding into 2 sides 将padding分到上下,左右两侧
dh /= 2
# shape:[h, w] new_unpad:[w, h]
if shape[::-1] != new_unpad:
img = cv2.resize(img, new_unpad, interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
top, bottom = int(round(dh - 0.1)), int(round(dh + 0.1)) # 计算上下两侧的padding
left, right = int(round(dw - 0.1)), int(round(dw + 0.1)) # 计算左右两侧的padding
img = cv2.copyMakeBorder(img, top, bottom, left, right, cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT, value=color) # add border
return img, ratio, (dw, dh)
def create_folder(path="./new_folder"):
# Create floder
if os.path.exists(path):
shutil.rmtree(path) # dalete output folder
os.makedirs(path) # make new output folder