文章目录
2022 EdgeViTs CVPR
港中文&三星提出EdgeViT:轻量级视觉Transformer新工作
论文链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.03436 100MB谨慎下载。打开页面巨慢
论文代码:还没有公布
1. 简介
1.1 摘要
在计算机视觉领域,基于Self-attention的模型(如(ViTs))已经成为CNN之外的一种极具竞争力的架构。尽管越来越强的变种具有越来越高的识别精度,但由于Self-attention的二次复杂度,现有的ViT在计算和模型大小方面都有较高的要求。 虽然之前的CNN的一些成功的设计选择(例如,卷积和分层结构)已经被引入到最近的ViT中,但它们仍然不足以满足移动设备有限的计算资源需求。这促使人们最近尝试开发基于最先进的MobileNet-v2的轻型MobileViT,但MobileViT与MobileNet-v2仍然存在性能差距。
在这项工作中,作者进一步推进这一研究方向,引入了EdgeViTs,一个新的轻量级ViTs家族,也是首次使基于Self-attention的视觉模型在准确性和设备效率之间的权衡中达到最佳轻量级CNN的性能。 这是通过引入一个基于Self-attention和卷积的最优集成的高成本的local-global-local(LGL)信息交换瓶颈来实现的。对于移动设备专用的评估,不依赖于不准确的proxies,如FLOPs的数量或参数,而是采用了一种直接关注设备延迟和能源效率的实用方法。
1.2 存在的问题
文章指出,目前基于VIT,做出轻量化的操作,一般有3种
- 使用具有空间分辨率(即token序列长度)的分层体系结构,在各个阶段逐步向下采样
- 用于控制输入token序列长度和参数共享的局部分组自我注意机制
- 池化注意方案以因子对key和value进行子抽样
这些的设计呢?趋势都是设计出更复杂,更强大的ViT,来挑战性能更好的CNN,但是呢还不能满足手机运行的实用效果
- 推理效率需要高(例如低延迟和能源消耗),这样运行成本就普遍负担得起,更多设备上的应用程序逗可以支持应用,这才是我们在实践中真正关心的直接指标。
- 模型尺寸(即参数量)对于现今的移动设备来说是负担得起的。
- 实现的简易性在实际应用中也是至关重要的。对于更广泛的部署,有必要使用通用深度学习框架(如ONNX、TensorRT和TorchScript)支持和优化的标准计算操作高效地实现模型,而不需要花费昂贵的代价为每个网络框架进行专门化设计。
本文贡献如下:
(1)我们从实际设备上部署和执行的角度研究轻量级ViT的设计;
(2)为了获得最佳的延展性和部署,我们提出了一种新的高效ViT家族,称为EdgeViT,它是基于使用标准初始模块的自注意力机制的最优分解而设计的。
(3)关于设备上的性能,为了现实部署的相关性,我们直接考虑不同模型的延迟和能源消耗,而不是依赖于其他标准,如FLOPs数量或参数量。
2. 网络
2.1 总体设计
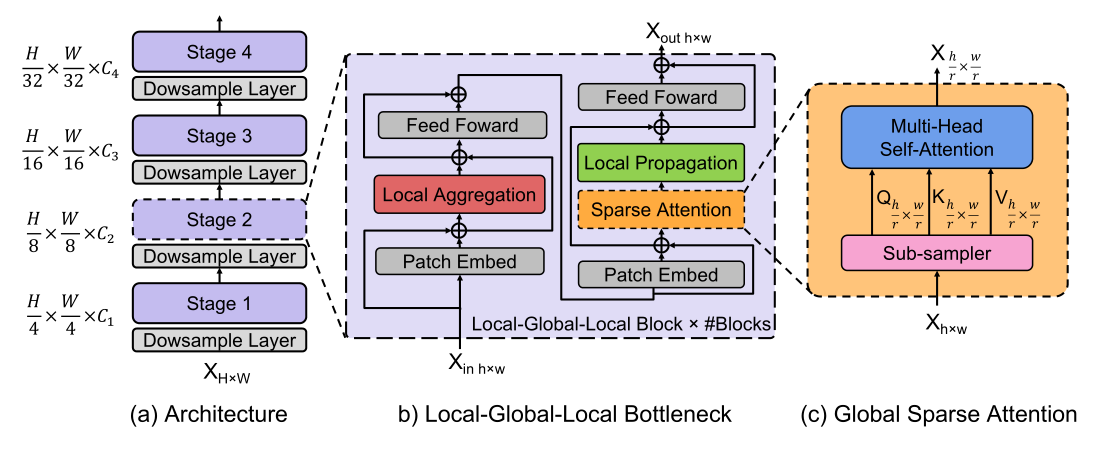
- 图a就是总体框架,类似于resnet结构。为了设计适合移动/边缘设备的轻量化ViT,我们采用最近ViT变体中使用的分层金字塔网络结构,
- 图b引入了一个开销高效的局部-全局-局部(LGL)bottleneck,LGL通过稀疏注意力模块进一步减少了自注意力的开销
- 图c,能实现更好的准确性和延迟平衡。
2.2 局部-全局-局部bottleneck(LGL)
- Self-attention已被证明是非常有效的学习全局信息或长距离空间依赖性的方法,这是视觉识别的关键。
- 另一方面,由于图像具有高度的空间冗余(例如,附近的Patch在语义上是相似的),将注意力集中到所有的空间Patch上,即使是在一个下采样的特征映射中,也是低效的。
因此,与以前在每个空间位置执行Self-attention的Transformer Block相比,LGL Bottleneck只对输入Token的子集计算Self-attention,但支持完整的空间交互,如在标准的Multi-Head Self-attention(MHSA)中。既会减少Token的作用域,同时也保留建模全局和局部上下文的底层信息流。
这里引入了3种有效的操作:
- Local aggregation:仅集成来自局部近似Token信号的局部聚合
- Global sparse attention:建模一组代表性Token之间的长期关系,其中每个Token都被视为一个局部窗口的代表;
- Local propagation:将委托学习到的全局上下文信息扩散到具有相同窗口的非代表Token。
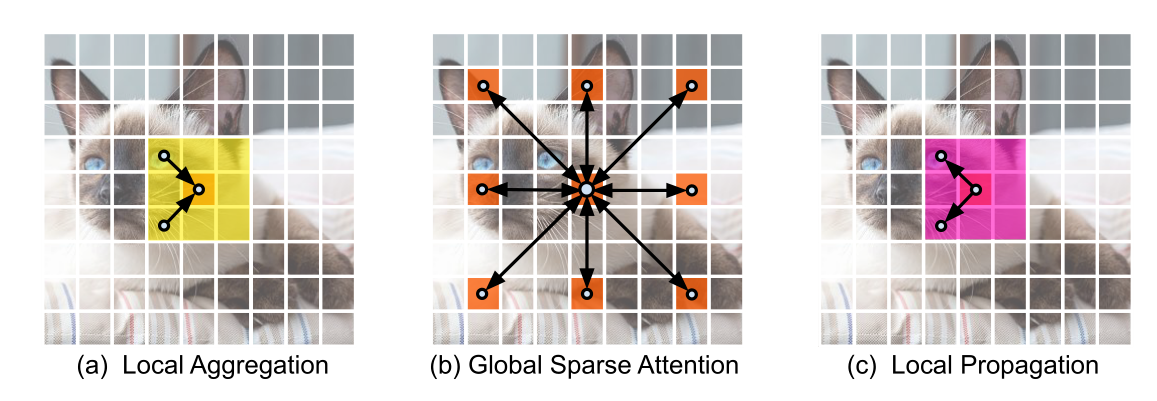
将这些结合起来,LGL Bottleneck就能够以低计算成本在同一特征映射中的任何一对Token之间进行信息交换。下面将详细说明每一个组成部分:
Local aggregation
对于每个Token,利用Depth-wise和Point-wise卷积在大小为k×k的局部窗口中聚合信息(图3(a))。
class LocalAgg(nn.Module):
"""
局部模块,LocalAgg
卷积操作能够有效的提取局部特征
为了能够降低计算量,使用 逐点卷积+深度可分离卷积实现
"""
def __init__(self, channels):
super(LocalAgg, self).__init__()
self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(channels)
# 逐点卷积,相当于全连接层。增加非线性,提高特征提取能力
self.pointwise_conv_0 = nn.Conv2d(channels, channels, kernel_size=1, bias=False)
# 深度可分离卷积
self.depthwise_conv = nn.Conv2d(channels, channels, padding=1, kernel_size=3, groups=channels, bias=False)
# 归一化
self.pointwise_prenorm_1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(channels)
# 逐点卷积,相当于全连接层,增加非线性,提高特征提取能力
self.pointwise_conv_1 = nn.Conv2d(channels, channels, kernel_size=1, bias=False)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.bn(x)
x = self.pointwise_conv_0(x)
x = self.depthwise_conv(x)
x = self.pointwise_prenorm_1(x)
x = self.pointwise_conv_1(x)
return x
Global sparse attention
对均匀分布在空间中的稀疏代表性Token集进行采样,每个r×r窗口有一个代表性Token。这里,r表示子样本率。然后,只对这些被选择的Token应用Self-attention(图3(b))。这与所有现有的ViTs不同,在那里,所有的空间Token都作为Self-attention计算中的query被涉及到。
class GlobalSparseAttention(nn.Module):
"""
全局模块,选取特定的tokens,进行全局作用
"""
def __init__(self, channels, r, heads):
"""
Args:
channels: 通道数
r: 下采样倍率
heads: 注意力头的数目
这里使用的是多头注意力机制,MHSA,multi-head self-attention
"""
super(GlobalSparseAttention, self).__init__()
#
self.head_dim = channels // heads
# 扩张的
self.scale = self.head_dim ** -0.5
self.num_heads = heads
# 使用平均池化,来进行特征提取
self.sparse_sampler = nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size=1, stride=r)
# 计算qkv
self.qkv = nn.Conv2d(channels, channels * 3, kernel_size=1, bias=False)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.sparse_sampler(x)
B, C, H, W = x.shape
q, k, v = self.qkv(x).view(B, self.num_heads, -1, H * W).split([self.head_dim,self.head_dim,self.head_dim],dim=2)
# 计算特征图 attention map
attn = (q.transpose(-2, -1) @ k).softmax(-1)
# value和特征图进行计算,得出全局注意力的结果
x = (v @ attn.transpose(-2, -1)).view(B, -1, H, W)
# print(x.shape)
return x
Local propagation
通过转置卷积将代表性 Token 中编码的全局上下文信息传播到它们的相邻的 Token 中(图 3©)。
class LocalPropagation(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, channels, r):
super(LocalPropagation, self).__init__()
# 组归一化
self.norm = nn.GroupNorm(num_groups=1, num_channels=channels)
# 使用转置卷积 恢复 GlobalSparseAttention模块 r倍的下采样率
self.local_prop = nn.ConvTranspose2d(channels,
channels,
kernel_size=r,
stride=r,
groups=channels)
# 使用逐点卷积
self.proj = nn.Conv2d(channels, channels, kernel_size=1, bias=False)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.local_prop(x)
x = self.norm(x)
x = self.proj(x)
return x
最终, LGL bottleneck 可以表达为:
X = L o c a l A g g ( N o r m ( X i n ) ) + X i n Y = F F N ( N o r m ( X ) ) + X Z = L o c a l P r o p ( G l o b a l S p a r s e A t t e n ( N o r m ( Y ) ) ) + Y X o u t = F F N ( N o r m ( Z ) ) + Z \begin{aligned} X&=LocalAgg(Norm(X_{in}))+X_{in} \\ Y&=FFN(Norm(X))+X \\ Z&=LocalProp(GlobalSparseAtten(Norm(Y)))+Y \\ X_{out}&=FFN(Norm(Z))+Z \end{aligned} XYZXout=LocalAgg(Norm(Xin))+Xin=FFN(Norm(X))+X=LocalProp(GlobalSparseAtten(Norm(Y)))+Y=FFN(Norm(Z))+Z
LGL 的代码为
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
class Residual(nn.Module):
"""
残差网络
"""
def __init__(self, module):
super().__init__()
self.module = module
def forward(self, x):
return x + self.module(x)
class ConditionalPositionalEncoding(nn.Module):
"""
条件编码信息
"""
def __init__(self, channels):
super(ConditionalPositionalEncoding, self).__init__()
self.conditional_positional_encoding = nn.Conv2d(channels, channels, kernel_size=3, padding=1, groups=channels,
bias=False)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conditional_positional_encoding(x)
return x
class MLP(nn.Module):
"""
FFN 模块
"""
def __init__(self, channels):
super(MLP, self).__init__()
expansion = 4
self.mlp_layer_0 = nn.Conv2d(channels, channels * expansion, kernel_size=1, bias=False)
self.mlp_act = nn.GELU()
self.mlp_layer_1 = nn.Conv2d(channels * expansion, channels, kernel_size=1, bias=False)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.mlp_layer_0(x)
x = self.mlp_act(x)
x = self.mlp_layer_1(x)
return x
class LocalAgg(nn.Module):
"""
局部模块,LocalAgg
卷积操作能够有效的提取局部特征
为了能够降低计算量,使用 逐点卷积+深度可分离卷积实现
"""
def __init__(self, channels):
super(LocalAgg, self).__init__()
self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(channels)
# 逐点卷积,相当于全连接层。增加非线性,提高特征提取能力
self.pointwise_conv_0 = nn.Conv2d(channels, channels, kernel_size=1, bias=False)
# 深度可分离卷积
self.depthwise_conv = nn.Conv2d(channels, channels, padding=1, kernel_size=3, groups=channels, bias=False)
# 归一化
self.pointwise_prenorm_1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(channels)
# 逐点卷积,相当于全连接层,增加非线性,提高特征提取能力
self.pointwise_conv_1 = nn.Conv2d(channels, channels, kernel_size=1, bias=False)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.bn(x)
x = self.pointwise_conv_0(x)
x = self.depthwise_conv(x)
x = self.pointwise_prenorm_1(x)
x = self.pointwise_conv_1(x)
return x
class GlobalSparseAttention(nn.Module):
"""
全局模块,选取特定的tokens,进行全局作用
"""
def __init__(self, channels, r, heads):
"""
Args:
channels: 通道数
r: 下采样倍率
heads: 注意力头的数目
这里使用的是多头注意力机制,MHSA,multi-head self-attention
"""
super(GlobalSparseAttention, self).__init__()
#
self.head_dim = channels // heads
# 扩张的
self.scale = self.head_dim ** -0.5
self.num_heads = heads
# 使用平均池化,来进行特征提取
self.sparse_sampler = nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size=1, stride=r)
# 计算qkv
self.qkv = nn.Conv2d(channels, channels * 3, kernel_size=1, bias=False)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.sparse_sampler(x)
B, C, H, W = x.shape
q, k, v = self.qkv(x).view(B, self.num_heads, -1, H * W).split([self.head_dim, self.head_dim, self.head_dim],
dim=2)
# 计算特征图 attention map
attn = (q.transpose(-2, -1) @ k).softmax(-1)
# value和特征图进行计算,得出全局注意力的结果
x = (v @ attn.transpose(-2, -1)).view(B, -1, H, W)
# print(x.shape)
return x
class LocalPropagation(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, channels, r):
super(LocalPropagation, self).__init__()
# 组归一化
self.norm = nn.GroupNorm(num_groups=1, num_channels=channels)
# 使用转置卷积 恢复 GlobalSparseAttention模块 r倍的下采样率
self.local_prop = nn.ConvTranspose2d(channels,
channels,
kernel_size=r,
stride=r,
groups=channels)
# 使用逐点卷积
self.proj = nn.Conv2d(channels, channels, kernel_size=1, bias=False)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.local_prop(x)
x = self.norm(x)
x = self.proj(x)
return x
class LGL(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, channels, r, heads):
super(LGL, self).__init__()
self.cpe1 = ConditionalPositionalEncoding(channels)
self.LocalAgg = LocalAgg(channels)
self.mlp1 = MLP(channels)
self.cpe2 = ConditionalPositionalEncoding(channels)
self.GlobalSparseAttention = GlobalSparseAttention(channels, r, heads)
self.LocalPropagation = LocalPropagation(channels, r)
self.mlp2 = MLP(channels)
def forward(self, x):
# 1. 经过 位置编码操作
x = self.cpe1(x) + x
# 2. 经过第一步的 局部操作
x = self.LocalAgg(x) + x
# 3. 经过一个前馈网络
x = self.mlp1(x) + x
# 4. 经过一个位置编码操作
x = self.cpe2(x) + x
# 5. 经过一个全局捕捉的操作。长和宽缩小 r倍。然后通过一个
# 6. 经过一个 局部操作部
x = self.LocalPropagation(self.GlobalSparseAttention(x)) + x
# 7. 经过一个前馈网络
x = self.mlp2(x) + x
return x
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 64通道,图片大小为32*32
x = torch.randn(size=(1, 64, 32, 32))
# 64通道,下采样2倍,8个头的注意力
model = LGL(64, 2, 8)
out = model(x)
print(out.shape)
3. 代码
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
# edgevits的配置信息
edgevit_configs = {
'XXS': {
'channels': (36, 72, 144, 288),
'blocks': (1, 1, 3, 2),
'heads': (1, 2, 4, 8)
}
,
'XS': {
'channels': (48, 96, 240, 384),
'blocks': (1, 1, 2, 2),
'heads': (1, 2, 4, 8)
}
,
'S': {
'channels': (48, 96, 240, 384),
'blocks': (1, 2, 3, 2),
'heads': (1, 2, 4, 8)
}
}
HYPERPARAMETERS = {
'r': (4, 2, 2, 1)
}
class Residual(nn.Module):
"""
残差网络
"""
def __init__(self, module):
super().__init__()
self.module = module
def forward(self, x):
return x + self.module(x)
class ConditionalPositionalEncoding(nn.Module):
"""
"""
def __init__(self, channels):
super(ConditionalPositionalEncoding, self).__init__()
self.conditional_positional_encoding = nn.Conv2d(channels, channels, kernel_size=3, padding=1, groups=channels,
bias=False)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conditional_positional_encoding(x)
return x
class MLP(nn.Module):
"""
FFN 模块
"""
def __init__(self, channels):
super(MLP, self).__init__()
expansion = 4
self.mlp_layer_0 = nn.Conv2d(channels, channels * expansion, kernel_size=1, bias=False)
self.mlp_act = nn.GELU()
self.mlp_layer_1 = nn.Conv2d(channels * expansion, channels, kernel_size=1, bias=False)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.mlp_layer_0(x)
x = self.mlp_act(x)
x = self.mlp_layer_1(x)
return x
class LocalAgg(nn.Module):
"""
局部模块,LocalAgg
卷积操作能够有效的提取局部特征
为了能够降低计算量,使用 逐点卷积+深度可分离卷积实现
"""
def __init__(self, channels):
super(LocalAgg, self).__init__()
self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(channels)
# 逐点卷积,相当于全连接层。增加非线性,提高特征提取能力
self.pointwise_conv_0 = nn.Conv2d(channels, channels, kernel_size=1, bias=False)
# 深度可分离卷积
self.depthwise_conv = nn.Conv2d(channels, channels, padding=1, kernel_size=3, groups=channels, bias=False)
# 归一化
self.pointwise_prenorm_1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(channels)
# 逐点卷积,相当于全连接层,增加非线性,提高特征提取能力
self.pointwise_conv_1 = nn.Conv2d(channels, channels, kernel_size=1, bias=False)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.bn(x)
x = self.pointwise_conv_0(x)
x = self.depthwise_conv(x)
x = self.pointwise_prenorm_1(x)
x = self.pointwise_conv_1(x)
return x
class GlobalSparseAttention(nn.Module):
"""
全局模块,选取特定的tokens,进行全局作用
"""
def __init__(self, channels, r, heads):
"""
Args:
channels: 通道数
r: 下采样倍率
heads: 注意力头的数目
这里使用的是多头注意力机制,MHSA,multi-head self-attention
"""
super(GlobalSparseAttention, self).__init__()
#
self.head_dim = channels // heads
# 扩张的
self.scale = self.head_dim ** -0.5
self.num_heads = heads
# 使用平均池化,来进行特征提取
self.sparse_sampler = nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size=1, stride=r)
# 计算qkv
self.qkv = nn.Conv2d(channels, channels * 3, kernel_size=1, bias=False)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.sparse_sampler(x)
B, C, H, W = x.shape
q, k, v = self.qkv(x).view(B, self.num_heads, -1, H * W).split([self.head_dim, self.head_dim, self.head_dim],
dim=2)
# 计算特征图 attention map
attn = (q.transpose(-2, -1) @ k).softmax(-1)
# value和特征图进行计算,得出全局注意力的结果
x = (v @ attn.transpose(-2, -1)).view(B, -1, H, W)
# print(x.shape)
return x
class LocalPropagation(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, channels, r):
super(LocalPropagation, self).__init__()
# 组归一化
self.norm = nn.GroupNorm(num_groups=1, num_channels=channels)
# 使用转置卷积 恢复 GlobalSparseAttention模块 r倍的下采样率
self.local_prop = nn.ConvTranspose2d(channels,
channels,
kernel_size=r,
stride=r,
groups=channels)
# 使用逐点卷积
self.proj = nn.Conv2d(channels, channels, kernel_size=1, bias=False)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.local_prop(x)
x = self.norm(x)
x = self.proj(x)
return x
class LGL(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, channels, r, heads):
super(LGL, self).__init__()
self.cpe1 = ConditionalPositionalEncoding(channels)
self.LocalAgg = LocalAgg(channels)
self.mlp1 = MLP(channels)
self.cpe2 = ConditionalPositionalEncoding(channels)
self.GlobalSparseAttention = GlobalSparseAttention(channels, r, heads)
self.LocalPropagation = LocalPropagation(channels, r)
self.mlp2 = MLP(channels)
def forward(self, x):
# 1. 经过 位置编码操作
x = self.cpe1(x) + x
# 2. 经过第一步的 局部操作
x = self.LocalAgg(x) + x
# 3. 经过一个前馈网络
x = self.mlp1(x) + x
# 4. 经过一个位置编码操作
x = self.cpe2(x) + x
# 5. 经过一个全局捕捉的操作。长和宽缩小 r倍。然后通过一个
# 6. 经过一个 局部操作部
x = self.LocalPropagation(self.GlobalSparseAttention(x)) + x
# 7. 经过一个前馈网络
x = self.mlp2(x) + x
return x
class DownSampleLayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dim_in, dim_out, r):
super(DownSampleLayer, self).__init__()
self.downsample = nn.Conv2d(dim_in,
dim_out,
kernel_size=r,
stride=r)
self.norm = nn.GroupNorm(num_groups=1, num_channels=dim_out)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.downsample(x)
x = self.norm(x)
return x
# if __name__ == '__main__':
# # 64通道,图片大小为32*32
# x = torch.randn(size=(1, 64, 32, 32))
# # 64通道,下采样2倍,8个头的注意力
# model = LGL(64, 2, 8)
# out = model(x)
# print(out.shape)
class EdgeViT(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, channels, blocks, heads, r=[4, 2, 2, 1], num_classes=1000, distillation=False):
super(EdgeViT, self).__init__()
self.distillation = distillation
l = []
in_channels = 3
# 主体部分
for stage_id, (num_channels, num_blocks, num_heads, sample_ratio) in enumerate(zip(channels, blocks, heads, r)):
# print(num_channels,num_blocks,num_heads,sample_ratio)
# print(in_channels)
l.append(DownSampleLayer(dim_in=in_channels, dim_out=num_channels, r=4 if stage_id == 0 else 2))
for _ in range(num_blocks):
l.append(LGL(channels=num_channels, r=sample_ratio, heads=num_heads))
in_channels = num_channels
self.main_body = nn.Sequential(*l)
self.pooling = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1)
self.classifier = nn.Linear(in_channels, num_classes, bias=True)
if self.distillation:
self.dist_classifier = nn.Linear(in_channels, num_classes, bias=True)
# print(self.main_body)
def forward(self, x):
# print(x.shape)
x = self.main_body(x)
x = self.pooling(x).flatten(1)
if self.distillation:
x = self.classifier(x), self.dist_classifier(x)
if not self.training:
x = 1 / 2 * (x[0] + x[1])
else:
x = self.classifier(x)
return x
def EdgeViT_XXS(pretrained=False):
model = EdgeViT(**edgevit_configs['XXS'])
if pretrained:
raise NotImplementedError
return model
def EdgeViT_XS(pretrained=False):
model = EdgeViT(**edgevit_configs['XS'])
if pretrained:
raise NotImplementedError
return model
def EdgeViT_S(pretrained=False):
model = EdgeViT(**edgevit_configs['S'])
if pretrained:
raise NotImplementedError
return model
if __name__ == '__main__':
x = torch.randn(size=(1, 3, 224, 224))
model = EdgeViT_S(False)
# y = model(x)
# print(y.shape)
from thop import profile
input = torch.randn(1, 3, 224, 224)
flops, params = profile(model, inputs=(input,))
print("flops:{:.3f}G".format(flops /1e9))
print("params:{:.3f}M".format(params /1e6))
参考链接
(2条消息) 轻量级网络EdgeViTs论文翻译_胖虎记录学习的博客-CSDN博客
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/516209737