孩子兄弟表示法
树转化为二叉树
孩子兄弟表示法又称二叉树表示法,即以二叉链表作为树的存储结构。孩子兄弟表示法使每个结点包括三部分内容:结点值、指向结点第一个孩子结点的指针,及指向结点下一个兄弟结点的指针(沿此域可以找到结点的所有兄弟结点)
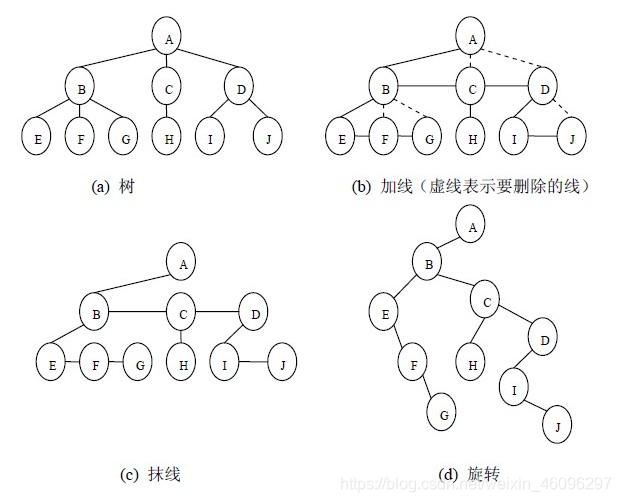
将树转换成二叉树的步骤是:
(1)加线。就是在所有兄弟结点之间加一条连线;
(2)抹线。就是对树中的每个结点,只保留他与第一个孩子结点之间的连线,删除它与其它孩子结点之间的连线;
(3)旋转。就是以树的根结点为轴心,将整棵树顺时针旋转一定角度,使之结构层次分明。
二叉树
之前在构造二叉树的时候,指针为左孩子和右孩子。
typedef struct BTree
{
elementype data;
struct BTree *lef_child, *rig_child;
}*T_NODE,Bnode;
一棵树有多个子树的情况下其定义为:
typedef struct NTree
{
elementype data;
struct NTree *fis_child, *next_sib;
}*Node;
所以在输入树元素的时候,左边都是第一个孩子,右边都是兄弟。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
typedef int Status;
typedef char elementype;
typedef struct NTree
{
elementype data;
struct NTree *fis_child, *next_sib;
}*Node;
//初始化
Status InitTree(Node &tree)
{
tree = new NTree;
tree->data = NULL;
tree->fis_child = NULL;
tree->next_sib = NULL;
return 0;
}
//添加内容
Status CreatTree(Node &tree)
{
if (tree != NULL)
{
tree = new NTree;
cout <<"please input a data" << endl;
elementype x;
cin >> x;
tree->data = x;
if (tree->data == '#')
{
cout << "The node branch is empty" << endl;
tree = NULL;
//return NULL;
}
else
{
cout << "please input " << tree->data << " first child" <<endl;
CreatTree(tree->fis_child);
cout << "please input " << tree->data << " child of sibling" << endl;
CreatTree(tree->next_sib);
}
}
return 0;
}
//——————————————输出————————————————
//前序输出
Status OutputTree(Node &tree)
{
if (tree == NULL)
{
cout << "The Tree is empty" << endl;
return NULL;
}
cout << tree->data << endl;
if (tree->fis_child != NULL)
{
OutputTree(tree->fis_child);
}
if (tree->next_sib != NULL)
{
OutputTree(tree->next_sib);
}
return 0;
}
//中序输出
Status OutTree_mid(Node &tree)
{
if (tree == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
if (tree->fis_child != NULL)
{
OutTree_mid(tree->fis_child);
}
cout << tree->data << endl;
if (tree->next_sib != NULL)
{
OutTree_mid(tree->next_sib);
}
return 0;
}
//后序输出
Status OutTreeafter(Node &tree)
{
if (tree == NULL)
return NULL;
if (tree->fis_child != NULL)
{
OutTreeafter(tree->fis_child);
}
if (tree->next_sib != NULL)
{
OutTreeafter(tree->next_sib);
}
cout << tree->data << endl;
return 0;
}
//——————————————输出————————————————
//copy
Status CopyTree(Node &tree,Node &TTT)
{
if (tree == NULL)
{
TTT = NULL;
return 0;
}
else
{
TTT = new NTree;
TTT->data = tree->data;
CopyTree(tree->fis_child,TTT->fis_child);
CopyTree(tree->next_sib,TTT->next_sib);
//return 0;
}
return 0;
}
int main()
{
Node T,Tcopy;
cout << "——————InitTree——————" << endl;
InitTree(T);
cout << "——————CreatTRee——————" << endl;
CreatTree(T);
cout << "——————Preamble output——————" << endl;
OutputTree(T);
cout << "——————Middle order output——————" << endl;
OutTree_mid(T);
cout << "——————Sequential output——————" << endl;
OutTreeafter(T);
cout << "——————Copy a binary tree——————" << endl;
CopyTree(T,Tcopy);
//OutTreeafter(Tcopy);
return 0;
}
关于二叉树的具体操作可点击
二叉树的链式表示|前序输出|后续输出|中序输出|销毁等操作
关于线索二叉树的理解和实现
单链表|双向链表|二叉树|线索二叉树|转换解释和应用