策略模式是一种解耦的方法,它对算法进行封装,使得算法的调用和算法本身分离。使用策略模式,客户端代码不需要调整,算法之间可以互相替换,因为不同的算法实现的是同一个接口。
目录
策略模式
在策略模式(Strategy Pattern)中,一个类的行为或其算法可以在运行时更改。这种类型的设计模式属于行为型模式。
在策略模式中,我们创建表示各种策略的对象和一个行为随着策略对象改变而改变的 context 对象。策略对象改变 context 对象的执行算法。
===介绍===
意图:定义一系列的算法,把它们一个个封装起来, 并且使它们可相互替换。
主要解决:在有多种算法相似的情况下,使用 if...else 所带来的复杂和难以维护。
何时使用:一个系统有许多许多类,而区分它们的只是他们直接的行为。
如何解决:将这些算法封装成一个一个的类,任意地替换。
关键代码:实现同一个接口。
应用实例: 1、诸葛亮的锦囊妙计,每一个锦囊就是一个策略。 2、旅行的出游方式,选择骑自行车、坐汽车,每一种旅行方式都是一个策略。 3、JAVA AWT 中的 LayoutManager。
优点: 1、算法可以自由切换。 2、避免使用多重条件判断。 3、扩展性良好。
缺点: 1、策略类会增多。 2、所有策略类都需要对外暴露。
使用场景: 1、如果在一个系统里面有许多类,它们之间的区别仅在于它们的行为,那么使用策略模式可以动态地让一个对象在许多行为中选择一种行为。 2、一个系统需要动态地在几种算法中选择一种。 3、如果一个对象有很多的行为,如果不用恰当的模式,这些行为就只好使用多重的条件选择语句来实现。
注意事项:如果一个系统的策略多于四个,就需要考虑使用混合模式,解决策略类膨胀的问题。
===实现===
我们将创建一个定义活动的 Strategy 接口和实现了 Strategy 接口的实体策略类。Context 是一个使用了某种策略的类。
StrategyPatternDemo,我们的演示类使用 Context 和策略对象来演示 Context 在它所配置或使用的策略改变时的行为变化。
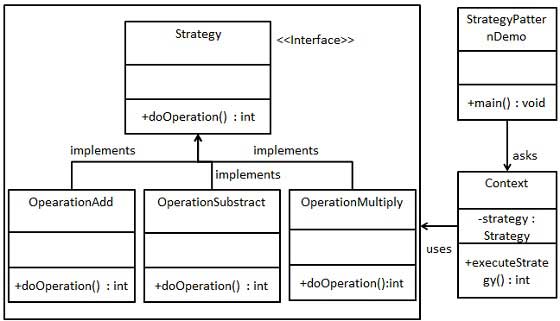
步骤 1
创建一个接口。Strategy.java
public interface Strategy {
public int doOperation(int num1, int num2);
}步骤 2
创建实现接口的实体类。OperationAdd.java
public class OperationAdd implements Strategy{
@Override
public int doOperation(int num1, int num2) {
return num1 + num2;
}
}OperationSubtract.java
public class OperationSubtract implements Strategy{
@Override
public int doOperation(int num1, int num2) {
return num1 - num2;
}
}OperationMultiply.java
public class OperationMultiply implements Strategy{
@Override
public int doOperation(int num1, int num2) {
return num1 * num2;
}
}步骤 3
创建 Context 类。Context.java
public class Context {
private Strategy strategy;
public Context(Strategy strategy){
this.strategy = strategy;
}
public int executeStrategy(int num1, int num2){
return strategy.doOperation(num1, num2);
}
}步骤 4
使用 Context 来查看当它改变策略 Strategy 时的行为变化。StrategyPatternDemo.java
public class StrategyPatternDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Context context = new Context(new OperationAdd());
System.out.println("10 + 5 = " + context.executeStrategy(10, 5));
context = new Context(new OperationSubtract());
System.out.println("10 - 5 = " + context.executeStrategy(10, 5));
context = new Context(new OperationMultiply());
System.out.println("10 * 5 = " + context.executeStrategy(10, 5));
}
}步骤 5
执行程序,输出结果:
10 + 5 = 15
10 - 5 = 5
10 * 5 = 50避免写IF逻辑语句
策略模式可以避免逻辑种存在大量if else 语句。
public class ContextSpringFactory {
private Map<String, Strategy> stgMap = new HashMap<String, Strategy>();
/**
* Getter method for property <tt>stgMap</tt>.
*
* @return property value of stgMap
*/
public Map<String, Strategy> getStgMap() {
return stgMap;
}
/**
* Setter method for property <tt>stgMap</tt>.
*
* @param stgMap value to be assigned to property stgMap
*/
public void setStgMap(Map<String, Strategy> stgMap) {
this.stgMap = stgMap;
}
public void doAction(String strType,int a,int b) {
this.stgMap.get(strType).executeStrategy(a,b);
}
} Spring源码策略模式
策略解析工具类
判定解析对象的类型,分析环境、资源、BeanFactory和类加载的处理策略。
package org.springframework.context.annotation;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import org.springframework.beans.BeanInstantiationException;
import org.springframework.beans.BeanUtils;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.Aware;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanClassLoaderAware;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactoryAware;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanDefinitionRegistry;
import org.springframework.context.EnvironmentAware;
import org.springframework.context.ResourceLoaderAware;
import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;
import org.springframework.core.io.ResourceLoader;
import org.springframework.lang.Nullable;
import org.springframework.util.Assert;
/**
* Common delegate code for the handling of parser strategies, e.g.
* {@code TypeFilter}, {@code ImportSelector}, {@code ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar}
*
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @author Phillip Webb
* @since 4.3.3
*/
abstract class ParserStrategyUtils {
/**
* Instantiate a class using an appropriate constructor and return the new
* instance as the specified assignable type. The returned instance will
* have {@link BeanClassLoaderAware}, {@link BeanFactoryAware},
* {@link EnvironmentAware}, and {@link ResourceLoaderAware} contracts
* invoked if they are implemented by the given object.
* @since 5.2
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
static <T> T instantiateClass(Class<?> clazz, Class<T> assignableTo, Environment environment,
ResourceLoader resourceLoader, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
Assert.notNull(clazz, "Class must not be null");
Assert.isAssignable(assignableTo, clazz);
if (clazz.isInterface()) {
throw new BeanInstantiationException(clazz, "Specified class is an interface");
}
ClassLoader classLoader = (registry instanceof ConfigurableBeanFactory ?
((ConfigurableBeanFactory) registry).getBeanClassLoader() : resourceLoader.getClassLoader());
T instance = (T) createInstance(clazz, environment, resourceLoader, registry, classLoader);
ParserStrategyUtils.invokeAwareMethods(instance, environment, resourceLoader, registry, classLoader);
return instance;
}
private static Object createInstance(Class<?> clazz, Environment environment,
ResourceLoader resourceLoader, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry,
@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
Constructor<?>[] constructors = clazz.getDeclaredConstructors();
if (constructors.length == 1 && constructors[0].getParameterCount() > 0) {
try {
Constructor<?> constructor = constructors[0];
Object[] args = resolveArgs(constructor.getParameterTypes(),
environment, resourceLoader, registry, classLoader);
return BeanUtils.instantiateClass(constructor, args);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
throw new BeanInstantiationException(clazz, "No suitable constructor found", ex);
}
}
return BeanUtils.instantiateClass(clazz);
}
private static Object[] resolveArgs(Class<?>[] parameterTypes,
Environment environment, ResourceLoader resourceLoader,
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
Object[] parameters = new Object[parameterTypes.length];
for (int i = 0; i < parameterTypes.length; i++) {
parameters[i] = resolveParameter(parameterTypes[i], environment,
resourceLoader, registry, classLoader);
}
return parameters;
}
@Nullable
private static Object resolveParameter(Class<?> parameterType,
Environment environment, ResourceLoader resourceLoader,
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
if (parameterType == Environment.class) {
return environment;
}
if (parameterType == ResourceLoader.class) {
return resourceLoader;
}
if (parameterType == BeanFactory.class) {
return (registry instanceof BeanFactory ? registry : null);
}
if (parameterType == ClassLoader.class) {
return classLoader;
}
throw new IllegalStateException("Illegal method parameter type: " + parameterType.getName());
}
private static void invokeAwareMethods(Object parserStrategyBean, Environment environment,
ResourceLoader resourceLoader, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
if (parserStrategyBean instanceof Aware) {
if (parserStrategyBean instanceof BeanClassLoaderAware && classLoader != null) {
((BeanClassLoaderAware) parserStrategyBean).setBeanClassLoader(classLoader);
}
if (parserStrategyBean instanceof BeanFactoryAware && registry instanceof BeanFactory) {
((BeanFactoryAware) parserStrategyBean).setBeanFactory((BeanFactory) registry);
}
if (parserStrategyBean instanceof EnvironmentAware) {
((EnvironmentAware) parserStrategyBean).setEnvironment(environment);
}
if (parserStrategyBean instanceof ResourceLoaderAware) {
((ResourceLoaderAware) parserStrategyBean).setResourceLoader(resourceLoader);
}
}
}
}
版本解析策略
设置上下文对象版本对应处理的策略:策略类->FixedVersionStrategy和ContentVersionStrategy。
private RootBeanDefinition parseVersionResolver(ParserContext context, Element element, @Nullable Object source) {
ManagedMap<String, Object> strategyMap = new ManagedMap<>();
strategyMap.setSource(source);
RootBeanDefinition versionResolverDef = new RootBeanDefinition(VersionResourceResolver.class);
versionResolverDef.setSource(source);
versionResolverDef.setRole(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE);
versionResolverDef.getPropertyValues().addPropertyValue("strategyMap", strategyMap);
for (Element beanElement : DomUtils.getChildElements(element)) {
String[] patterns = StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray(beanElement.getAttribute("patterns"));
Object strategy = null;
if (FIXED_VERSION_STRATEGY_ELEMENT.equals(beanElement.getLocalName())) {
ConstructorArgumentValues cargs = new ConstructorArgumentValues();
cargs.addIndexedArgumentValue(0, beanElement.getAttribute("version"));
RootBeanDefinition strategyDef = new RootBeanDefinition(FixedVersionStrategy.class);
strategyDef.setSource(source);
strategyDef.setRole(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE);
strategyDef.setConstructorArgumentValues(cargs);
strategy = strategyDef;
}
else if (CONTENT_VERSION_STRATEGY_ELEMENT.equals(beanElement.getLocalName())) {
RootBeanDefinition strategyDef = new RootBeanDefinition(ContentVersionStrategy.class);
strategyDef.setSource(source);
strategyDef.setRole(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE);
strategy = strategyDef;
}
else if (VERSION_STRATEGY_ELEMENT.equals(beanElement.getLocalName())) {
Element childElement = DomUtils.getChildElementsByTagName(beanElement, "bean", "ref").get(0);
strategy = context.getDelegate().parsePropertySubElement(childElement, null);
}
for (String pattern : patterns) {
strategyMap.put(pattern, strategy);
}
}
return versionResolverDef;
}VersionPathStrategy定义:
package org.springframework.web.servlet.resource;
import org.springframework.lang.Nullable;
/**
* A strategy for extracting and embedding a resource version in its URL path.
*
* @author Brian Clozel
* @author Rossen Stoyanchev
* @since 4.1
*/
public interface VersionPathStrategy {
/**
* Extract the resource version from the request path.
* @param requestPath the request path to check
* @return the version string or {@code null} if none was found
*/
@Nullable
String extractVersion(String requestPath);
/**
* Remove the version from the request path. It is assumed that the given
* version was extracted via {@link #extractVersion(String)}.
* @param requestPath the request path of the resource being resolved
* @param version the version obtained from {@link #extractVersion(String)}
* @return the request path with the version removed
*/
String removeVersion(String requestPath, String version);
/**
* Add a version to the given request path.
* @param requestPath the requestPath
* @param version the version
* @return the requestPath updated with a version string
*/
String addVersion(String requestPath, String version);
}VersionStrategy定义:
package org.springframework.web.servlet.resource;
import org.springframework.core.io.Resource;
/**
* An extension of {@link VersionPathStrategy} that adds a method
* to determine the actual version of a {@link Resource}.
*
* @author Brian Clozel
* @author Rossen Stoyanchev
* @since 4.1
* @see VersionResourceResolver
*/
public interface VersionStrategy extends VersionPathStrategy {
/**
* Determine the version for the given resource.
* @param resource the resource to check
* @return the version (never {@code null})
*/
String getResourceVersion(Resource resource);
}
AbstractVersionStrategy定义:
package org.springframework.web.servlet.resource;
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
import org.apache.commons.logging.Log;
import org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory;
import org.springframework.lang.Nullable;
import org.springframework.util.Assert;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils;
/**
* Abstract base class for {@link VersionStrategy} implementations.
*
* <p>Supports versions as:
* <ul>
* <li>prefix in the request path, like "version/static/myresource.js"
* <li>file name suffix in the request path, like "static/myresource-version.js"
* </ul>
*
* <p>Note: This base class does <i>not</i> provide support for generating the
* version string.
*
* @author Brian Clozel
* @author Rossen Stoyanchev
* @since 4.1
*/
public abstract class AbstractVersionStrategy implements VersionStrategy {
protected final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(getClass());
private final VersionPathStrategy pathStrategy;
protected AbstractVersionStrategy(VersionPathStrategy pathStrategy) {
Assert.notNull(pathStrategy, "VersionPathStrategy is required");
this.pathStrategy = pathStrategy;
}
public VersionPathStrategy getVersionPathStrategy() {
return this.pathStrategy;
}
@Override
@Nullable
public String extractVersion(String requestPath) {
return this.pathStrategy.extractVersion(requestPath);
}
@Override
public String removeVersion(String requestPath, String version) {
return this.pathStrategy.removeVersion(requestPath, version);
}
@Override
public String addVersion(String requestPath, String version) {
return this.pathStrategy.addVersion(requestPath, version);
}
/**
* A prefix-based {@code VersionPathStrategy},
* e.g. {@code "{version}/path/foo.js"}.
*/
protected static class PrefixVersionPathStrategy implements VersionPathStrategy {
private final String prefix;
public PrefixVersionPathStrategy(String version) {
Assert.hasText(version, "Version must not be empty");
this.prefix = version;
}
@Override
@Nullable
public String extractVersion(String requestPath) {
return (requestPath.startsWith(this.prefix) ? this.prefix : null);
}
@Override
public String removeVersion(String requestPath, String version) {
return requestPath.substring(this.prefix.length());
}
@Override
public String addVersion(String path, String version) {
if (path.startsWith(".")) {
return path;
}
else {
return (this.prefix.endsWith("/") || path.startsWith("/") ?
this.prefix + path : this.prefix + '/' + path);
}
}
}
/**
* File name-based {@code VersionPathStrategy},
* e.g. {@code "path/foo-{version}.css"}.
*/
protected static class FileNameVersionPathStrategy implements VersionPathStrategy {
private static final Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile("-(\\S*)\\.");
@Override
@Nullable
public String extractVersion(String requestPath) {
Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(requestPath);
if (matcher.find()) {
String match = matcher.group(1);
return (match.contains("-") ? match.substring(match.lastIndexOf('-') + 1) : match);
}
else {
return null;
}
}
@Override
public String removeVersion(String requestPath, String version) {
return StringUtils.delete(requestPath, "-" + version);
}
@Override
public String addVersion(String requestPath, String version) {
String baseFilename = StringUtils.stripFilenameExtension(requestPath);
String extension = StringUtils.getFilenameExtension(requestPath);
return (baseFilename + '-' + version + '.' + extension);
}
}
}ContentVersionStrategy定义:
package org.springframework.web.servlet.resource;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.springframework.core.io.Resource;
import org.springframework.util.DigestUtils;
import org.springframework.util.FileCopyUtils;
/**
* A {@code VersionStrategy} that calculates an Hex MD5 hashes from the content
* of the resource and appends it to the file name, e.g.
* {@code "styles/main-e36d2e05253c6c7085a91522ce43a0b4.css"}.
*
* @author Brian Clozel
* @author Rossen Stoyanchev
* @since 4.1
* @see VersionResourceResolver
*/
public class ContentVersionStrategy extends AbstractVersionStrategy {
public ContentVersionStrategy() {
super(new FileNameVersionPathStrategy());
}
@Override
public String getResourceVersion(Resource resource) {
try {
byte[] content = FileCopyUtils.copyToByteArray(resource.getInputStream());
return DigestUtils.md5DigestAsHex(content);
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Failed to calculate hash for " + resource, ex);
}
}
}FixedVersionStrategy定义:
package org.springframework.web.servlet.resource;
import org.springframework.core.io.Resource;
/**
* A {@code VersionStrategy} that relies on a fixed version applied as a request
* path prefix, e.g. reduced SHA, version name, release date, etc.
*
* <p>This is useful for example when {@link ContentVersionStrategy} cannot be
* used such as when using JavaScript module loaders which are in charge of
* loading the JavaScript resources and need to know their relative paths.
*
* @author Brian Clozel
* @author Rossen Stoyanchev
* @since 4.1
* @see VersionResourceResolver
*/
public class FixedVersionStrategy extends AbstractVersionStrategy {
private final String version;
/**
* Create a new FixedVersionStrategy with the given version string.
* @param version the fixed version string to use
*/
public FixedVersionStrategy(String version) {
super(new PrefixVersionPathStrategy(version));
this.version = version;
}
@Override
public String getResourceVersion(Resource resource) {
return this.version;
}
}Handler命名映射策略
package org.springframework.web.servlet.handler;
import org.springframework.web.method.HandlerMethod;
/**
* A strategy for assigning a name to a handler method's mapping.
*
* <p>The strategy can be configured on
* {@link org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.AbstractHandlerMethodMapping
* AbstractHandlerMethodMapping}. It is used to assign a name to the mapping of
* every registered handler method. The names can then be queried via
* {@link org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.AbstractHandlerMethodMapping#getHandlerMethodsForMappingName(String)
* AbstractHandlerMethodMapping#getHandlerMethodsForMappingName}.
*
* <p>Applications can build a URL to a controller method by name with the help
* of the static method
* {@link org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.MvcUriComponentsBuilder#fromMappingName(String)
* MvcUriComponentsBuilder#fromMappingName} or in JSPs through the "mvcUrl"
* function registered by the Spring tag library.
*
* @author Rossen Stoyanchev
* @since 4.1
* @param <T> the mapping type
*/
@FunctionalInterface
public interface HandlerMethodMappingNamingStrategy<T> {
/**
* Determine the name for the given HandlerMethod and mapping.
* @param handlerMethod the handler method
* @param mapping the mapping
* @return the name
*/
String getName(HandlerMethod handlerMethod, T mapping);
}