javaSE多线程练习
javaSE多线程练习
将Work3的代码补全
我们提供了一个类:
public class Foo {
public void first() { System.out.print(“first”); }
public void second() { System.out.print(“second”); }
public void third() { System.out.print(“third”); }
}
三个不同的线程 A、B、C 将会共用一个 Foo 实例。
一个将会调用 first() 方法
一个将会调用 second() 方法
还有一个将会调用 third() 方法
请设计修改程序,以确保 second() 方法在 first() 方法之后被执行,third() 方法在 second() 方法之后被执行。
示例 1:
输入: 1,2,3
输出: “firstsecondthird”
解释:
有三个线程会被异步启动。
输入 1,2,3 表示线程 A 将会调用 first() 方法,线程 B 将会调用 second() 方法,线程 C 将会调用 third() 方法。
正确的输出是 “firstsecondthird”。
示例 2:
输入: 1,3,2
输出: “firstsecondthird”
解释:
输入 1,3,2 表示线程 A 将会调用 first() 方法,线程 B 将会调用 third() 方法,线程 C 将会调用 second() 方法。
正确的输出是 “firstsecondthird”。
代码
public class Demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Foo foo = new Foo();
MyRun myRun1 = new MyRun(foo);
MyRun myRun2 = new MyRun(foo);
MyRun myRun3 = new MyRun(foo);
Thread thread1 = new Thread(myRun1);
Thread thread2 = new Thread(myRun2);
Thread thread3 = new Thread(myRun3);
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
myRun1.num = sc.nextInt();
myRun2.num = sc.nextInt();
myRun3.num = sc.nextInt();
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
thread3.start();
}
}
class Foo {
private boolean firstFinished;
private boolean secondFinished;
public Foo() {
}
public synchronized void first() {
System.out.println("first");
firstFinished = true;
this.notifyAll();
}
public synchronized void second() throws InterruptedException {
while (!firstFinished) {
this.wait();
}
System.out.println("second");
secondFinished = true;
this.notifyAll();
}
public synchronized void third() throws InterruptedException {
while (!secondFinished) {
this.wait();
}
System.out.println("third");
}
}
class MyRun implements Runnable {
Foo foo;
int num;
public MyRun(Foo foo) {
this.foo = foo;
}
@Override
public void run() {
if (num == 1) {
foo.first();
} else if (num == 2) {
try {
foo.second();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} else if (num == 3) {
try {
foo.third();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
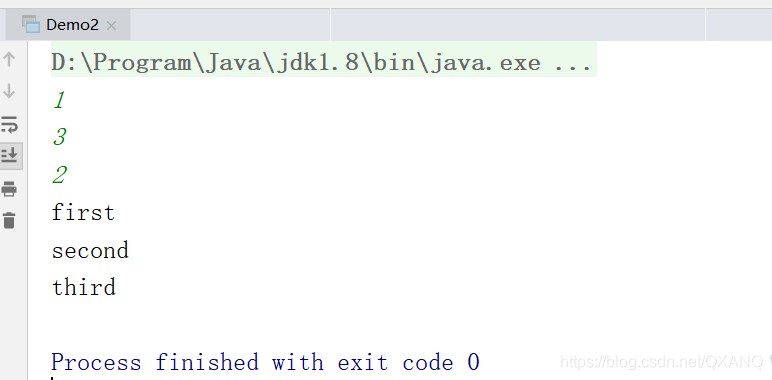
结果: