将模型视图 和 投影结合起来运用的实例。
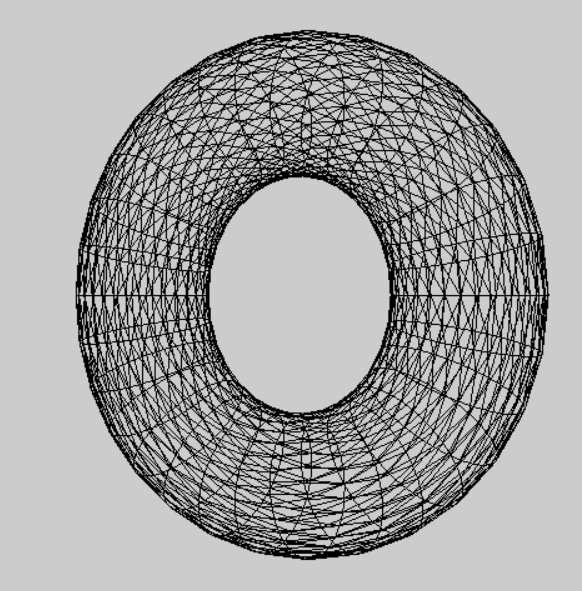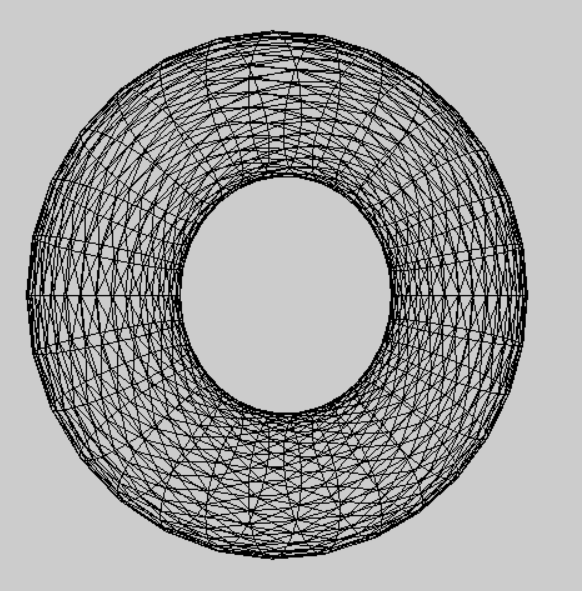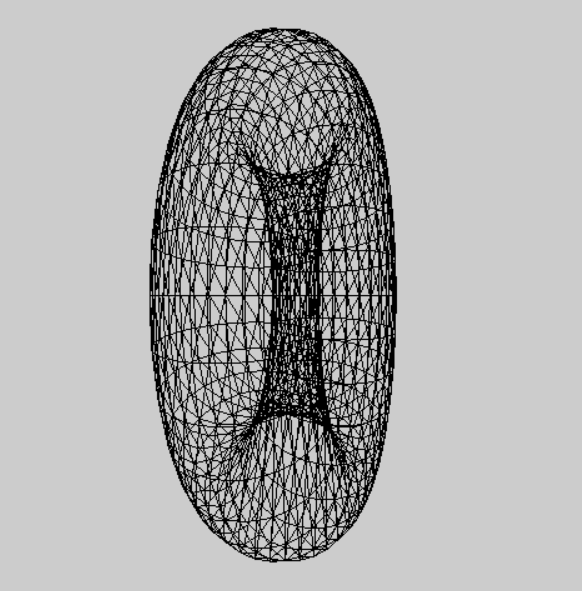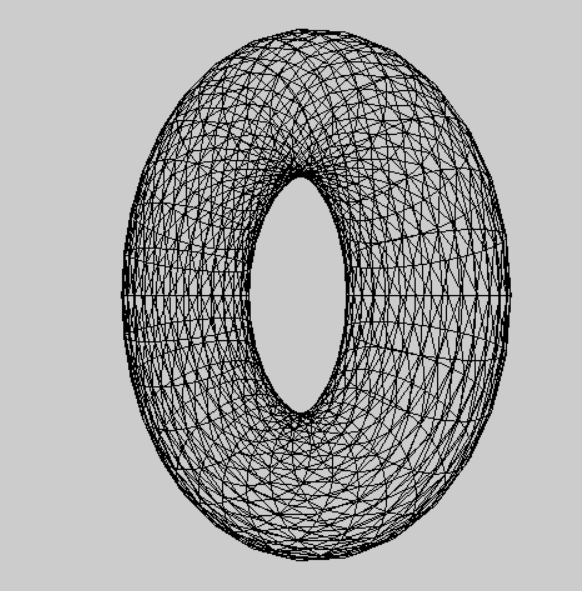
在ChangeSize函数里即视口发生变换时回调的函数,进行了设置投影矩阵为透视投影,其中防止 (float)w/(float)h , 除数不为0,情况用 if(h==0) h = 1; 来避免。
在RenderScene函数里 进行了创建平移矩阵 和 旋转矩阵 并用m3dMatrixMultiply44 合并为一个 mModelview 模型视图矩阵,又将它和 viewFrustum:GetProjectionMatrix()投影矩阵 相差得到 mModelViewProjection 模型视图投影矩阵,最终应用到着色器上绘制批次。
其中有个新的类 CStopWatch类 作为静态对象出现 获取rotTimer.GetElapsedSeconds() 时间毫秒 去改变yRot 旋转角度 这种做法比之前的直接 对yRot += 1 好处是它跟随时间而变化,而不是跟随帧率而变化快慢,而是帧率高是则刷新频率流畅,反之不流畅。
最后为了将当前坐标系浓缩到单元正方体内[-1,1] 通过用投影矩阵乘以模型视图矩阵来完成。
// ModelviewProjection.cpp
// OpenGL SuperBible
// Demonstrates OpenGL the ModelviewProjection matrix
// Program by Richard S. Wright Jr.
#pragma comment(lib,"gltools.lib")
#include <GLTools.h> // OpenGL toolkit
#include <GLMatrixStack.h>
#include <GLFrame.h>
#include <GLFrustum.h>
#include <GLGeometryTransform.h>
#include <GLBatch.h>
#include <StopWatch.h>
#include <math.h>
#ifdef __APPLE__
#include <glut/glut.h>
#else
#define FREEGLUT_STATIC
#include <GL/glut.h>
#endif
// Global view frustum class
GLFrustum viewFrustum;
// The shader manager
GLShaderManager shaderManager;
// The torus
GLTriangleBatch torusBatch;
// Set up the viewport and the projection matrix
void ChangeSize(int w, int h)
{
// Prevent a divide by zero
if (h == 0)
h = 1;
// Set Viewport to window dimensions
glViewport(0, 0, w, h);
viewFrustum.SetPerspective(35.0f, float(w) / float(h), 1.0f, 1000.0f);
}
// Called to draw scene
void RenderScene(void)
{
// Set up time based animation
static CStopWatch rotTimer;
float yRot = rotTimer.GetElapsedSeconds() * 60.0f;
// Clear the window and the depth buffer
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT);
// Matrix Variables
M3DMatrix44f mTranslate, mRotate, mModelview, mModelViewProjection;
// Create a translation matrix to move the torus back and into sight
m3dTranslationMatrix44(mTranslate, 0.0f, 0.0f, -2.5f);
// Create a rotation matrix based on the current value of yRot
m3dRotationMatrix44(mRotate, m3dDegToRad(yRot), 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f);
// Add the rotation to the translation, store the result in mModelView
m3dMatrixMultiply44(mModelview, mTranslate, mRotate);
// Add the modelview matrix to the projection matrix,
// the final matrix is the ModelViewProjection matrix.
m3dMatrixMultiply44(mModelViewProjection, viewFrustum.GetProjectionMatrix(), mModelview);
// Pass this completed matrix to the shader, and render the torus
GLfloat vBlack[] = { 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f };
shaderManager.UseStockShader(GLT_SHADER_FLAT, mModelViewProjection, vBlack);
torusBatch.Draw();
// Swap buffers, and immediately refresh
glutSwapBuffers();
glutPostRedisplay();
}
// This function does any needed initialization on the rendering
// context.
void SetupRC()
{
// Black background
glClearColor(0.8f, 0.8f, 0.8f, 1.0f);
glEnable(GL_DEPTH_TEST);
shaderManager.InitializeStockShaders();
// This makes a torus
gltMakeTorus(torusBatch, 0.4f, 0.15f, 30, 30);
glPolygonMode(GL_FRONT_AND_BACK, GL_LINE);
}
///
// Main entry point for GLUT based programs
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
gltSetWorkingDirectory(argv[0]);
glutInit(&argc, argv);
glutInitDisplayMode(GLUT_DOUBLE | GLUT_RGBA | GLUT_DEPTH | GLUT_STENCIL);
glutInitWindowSize(800, 600);
glutCreateWindow("ModelViewProjection Example");
glutReshapeFunc(ChangeSize);
glutDisplayFunc(RenderScene);
GLenum err = glewInit();
if (GLEW_OK != err) {
fprintf(stderr, "GLEW Error: %s\n", glewGetErrorString(err));
return 1;
}
SetupRC();
glutMainLoop();
return 0;
}