1、前言
在实际项目中,我们不仅需要实现应用的功能,也需要考虑整个应用的性能问题。当大量用户访问相同数据时,对数据库是个很大的考验。这时候如果使用数据缓存技术了,同样的数据就不需要通过访问数据库获取处理,在应用层面就可以拿到缓存数据,可以减轻数据库的压力、同时也能提高数据的响应速度。
那么在Spring Boot中提供哪些缓存支持呢?
Spring Framework中提供了对缓存数据的支持,核心是通过在方法中应用缓存方法,然后根据缓存中的已有可用信息来减少大量的执行次数。Spring Boot自动携带了缓存的基础配置,我们只需要使用注解@EnableCaching即可开启缓存功能。
举例说明;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.Cacheable;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class MathService {
@Cacheable("piDecimals")
public int computePiDecimal(int i) {
// ...
}
}
上述的举例是,缓存一个需要复杂计算的计算方法,那么具体是怎么执行的呢?
在computePiDecimal方法执行之前,会查找piDecimals的缓存,并从中取匹配i这个参数,如果数据存在,立刻把数据返回给调用者,然后这个方法computePiDecimal并不会执行。否则执行方法,在返回数据给调用者之前就更新数据到缓存中。
如果没有添加指定的缓存库,Spring Boot自动配置了一个简单的Simple Provider,通过concurrent maps保存缓存数据。比如上面的piDecimals缓存,当缓存存在时,调用方法时,会通过simple provider 直接返回。simple provider 不建议应用于正式生产环境,如果只是测试熟悉缓存技术还是不错的。
2、CacheManager缓存分类
Spring 定义 CacheManager 和 Cache 接口用来统一不同的缓存技术。例如 JCache、 EhCache、 Hazelcast、 Guava、 Redis 等。在使用 Spring 集成 Cache 的时候,我们需要注册实现的 CacheManager 的 Bean。Spring Boot 默认使用的是 SimpleCacheConfiguration,即使用 ConcurrentMapCacheManager 来实现的缓存。
CacheManager是专门用来缓存管理器,管理各种缓存组件的;
针对不同的缓存技术,实现了不同的 CacheManager ,Spring 定义了下表所示的 CacheManager:
| CacheManager | 描述 |
|---|---|
| SimpleCacheManager | 使用简单的 Collection 来存储缓存,主要用于测试 |
| ConcurrentMapCacheManager | 使用 ConcurrentMap 来存储缓存 |
| NoOpCacheManager | 仅测试用途,不会实际缓存数据 |
| EhCacheCacheManager | 使用 EhCache 作为缓存技术 |
| GuavaCacheManager | 使用 Google Guava 的 GuavaCache 作为缓存技术 |
| HazelcastCacheManager | 使用 Hazelcast 作为缓存技术 |
| JCacheCacheManager | 支持 JCache(JSR-107) 标准的实现作为缓存技术,如 ApacheCommonsJCS |
| RedisCacheManager | 使用 Redis 作为缓存技术 |
缓存接口有以下分类:
- Generic
- JCache (JSR-107) (EhCache 3, Hazelcast, Infinispan, and others)
- EhCache 2.x
- Hazelcast
- Infinispan
- Couchbase
- Redis
- Caffeine
- Simple
详细列举,请进入Spring Boot Cache
我们在这里将只讲解Simple和Redis,Simple用于测试,Redis用于实际用途。其他的平时不多用,可以自行了解。
3、具体实现
3.1、自定义是否开启缓存
是否开启缓存,有两种方法:
方法一:
在不同环境的配置文件中如application-dev.yml、application-test.yml、application-prod.yml,修改 spring.cache.type = none;
spring:
cache:
type: none
方法二:
自定义配置
application.yml
## 开启数据缓存
caching:
enabled: true
com.scaffold.test.config.CacheConfig
缓存配置文件
@Configuration
@EnableCaching
//配置文件读取是否启用此配置
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "caching", name = "enabled", havingValue = "true")
public class CacheConfig {
}
3.2、simpleCacheManage
3.2.1、概要介绍
simpleCacheManage 基于ConcurrentHashMap 实现,不依赖其他库,如果增加了注解@EnableCaching,默认开启缓存,可以通过设置cache-names限制缓存列表
设置缓存列表
application.yml
spring:
cache:
type: simple
cache-names: cache1,cache2
或者
增加配置文件 cacheConfig
@Configuration
public class CacheConfig {
@Bean
public CacheManager cacheManager() {
return new ConcurrentMapCacheManager("cache1", "cache2");
}
}
maven依赖
<!-- cache 依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-cache</artifactId>
</dependency>
注意:所有的注解是加到实现类方法上的
| 注解 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| @Cacheable | 在方法执行前 Spring 先查看缓存中是否有数据,若有,则直接返回缓存数据;若无数据,调用方法将方法返回值放入缓存中 |
| @CachePut | 无论怎样,都会将方法的返回值放到缓存中。 |
| @CacheEvict | 将一条或多条数据从缓存中删除 |
| @Caching | 可以通过 @Caching 注解组合多个注解策略在一个方法 |
@Cacheable、@CachePut、@CacheEvict 都有 value 属性,指定的是要使用的缓存名称;key 属性指定的是数据在缓存中存储的键。
3.2.2、代码实现
配置类
package com.scaffold.test.config;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnProperty;
import org.springframework.cache.CacheManager;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.EnableCaching;
import org.springframework.cache.concurrent.ConcurrentMapCacheManager;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import java.time.Duration;
/**
* 缓存配置文件
* 配置文件读取是否启用此配置
* @author alex
*/
@Configuration
@EnableCaching
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "caching", name = "enabled", havingValue = "true")
public class CacheConfig {
@Bean
public CacheManager cacheManager() {
return new ConcurrentMapCacheManager("cacheData");
}
}
实体类
com.scaffold.test.entity.Student
package com.scaffold.test.entity;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.EqualsAndHashCode;
import java.io.Serializable;
/**
* @author alex wong
*/
@Data
@EqualsAndHashCode(callSuper = false)
public class Student implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID=1L;
private int id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
}
service层
com.scaffold.test.service.StudentService
package com.scaffold.test.service;
import com.scaffold.test.entity.Student;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.service.IService;
import java.util.List;
/**
* <p>
* 服务类
* </p>
*
* @author alex wong
*/
public interface StudentService extends IService<Student> {
List<Student> findAll();
Student findStudent(Student student);
Student testStudent(String text);
void deleteStudent(Student student);
void saveStudent(Student student);
}
service实现类
com.scaffold.test.service.StudentService
package com.scaffold.test.service.impl;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.service.impl.ServiceImpl;
import com.scaffold.test.entity.Student;
import com.scaffold.test.mapper.StudentMapper;
import com.scaffold.test.service.StudentService;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CacheEvict;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CachePut;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.Cacheable;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import java.util.List;
/**
* <p>
* 服务实现类
* </p>
*
* @author alex wong
*/
@Slf4j
@Service
public class StudentServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<StudentMapper, Student> implements StudentService {
@Resource
private StudentMapper studentMapper;
@Override
@Cacheable(value = "cacheData")
public List<Student> findAll(){
return studentMapper.selectAll();
}
/**
* 缓存查询数据
* @Cacheable 缓存数据到缓存 student 中
* 其中缓存名称为 student 数据的 key 是 student 的 id
* @param student s
* @return
*/
@Override
@Cacheable(value = "cacheData", key = "#student.id")
public Student findStudent(Student student) {
log.warn("增加了student为{}的数据缓存", student);
int id = student.getId();
if(id == 0){
return null;
}
return studentMapper.findStudent(student);
}
/**
* 删除缓存
* @CacheEvict 从缓存 student 中删除
* 其中缓存名称为 student 数据的 key 是 student 的 id
* @param student s
*/
@Override
@CacheEvict(value = "cacheData", key = "#student.id")
public void deleteStudent(Student student) {
log.warn("删除了student为{}的数据缓存", student);
}
/**
* @CachePut 缓存新增的或更新的数据到缓存
* 其中缓存名称为 student 数据的 key 是 student 的 id
* @param student
*/
@Override
@CachePut(value = "cacheData", key = "#student.id")
public void saveStudent(Student student) {
log.warn("保存了id、key 为{}的数据缓存", student);
studentMapper.insertStudent(student);
}
@Override
@Cacheable(value = "cacheData", key = "#text")
public Student testStudent(String text) {
System.out.println("test" + text);
Student student = new Student();
student.setName(text);
return student;
}
}
dao层(data access object数据访问层)
com.scaffold.test.mapper.StudentMapper
package com.scaffold.test.mapper;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.mapper.BaseMapper;
import com.scaffold.test.entity.Student;
import java.util.List;
/**
* <p>
* Mapper 接口
* </p>
*
* @author alex wong
*/
public interface StudentMapper extends BaseMapper<Student> {
List<Student> selectAll();
Student findStudent(Student student);
int insertStudent(Student student);
}
src/main/resources/mapper/StudentMapper.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.scaffold.test.mapper.StudentMapper">
<!-- 通用查询映射结果 -->
<resultMap id="BaseResultMap" type="com.scaffold.test.entity.Student">
<result column="id" property="id"/>
<result column="name" property="name"/>
<result column="age" property="age"/>
</resultMap>
<!-- 通用查询结果列 -->
<sql id="Base_Column_List">
id,
name, age
</sql>
<sql id="Where_Condition">
<where>
<if test="id != null and id != ''">
id=#{id}
</if>
<if test="name != null and name != ''">
and name=#{name}
</if>
<if test="age != null and age != ''">
and age=#{age}
</if>
</where>
</sql>
<insert id="insertStudent">
insert student
(id, name, age)
values
(#{id}, #{name}, #{age})
</insert>
<select id="selectAll" resultMap="BaseResultMap">
select * from student
</select>
<select id="findStudent" resultType="com.scaffold.test.entity.Student">
select * from student
<include refid="Where_Condition"></include>
</select>
</mapper>
sql
SET NAMES utf8mb4;
SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS = 0;
-- ----------------------------
-- Table structure for student
-- ----------------------------
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `student`;
CREATE TABLE `student` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL,
`name` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci NOT NULL,
`age` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci;
-- ----------------------------
-- Records of student
-- ----------------------------
INSERT INTO `student` VALUES (1, '1', 2323);
INSERT INTO `student` VALUES (2, '2', 2323);
INSERT INTO `student` VALUES (3, '3', 2323);
SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS = 1;
Controller层
com.scaffold.test.controller.StudentController
package com.scaffold.test.controller;
import com.scaffold.test.entity.Student;
import com.scaffold.test.service.StudentService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.List;
/**
* <p>
* 前端控制器
* </p>
*
* @author alex wong
*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/student")
public class StudentController {
@Autowired
private StudentService studentService;
@GetMapping("list")
public List<Student> getAll(){
return studentService.findAll();
}
@GetMapping("add")
public void addStudent(Student student){
studentService.saveStudent(student);
}
@GetMapping("find")
public Student findStudent(Student student){
return studentService.findStudent(student);
}
@GetMapping("delete")
public void deleteStudent(Student student){
studentService.deleteStudent(student);
}
@GetMapping("test")
public Student test(@RequestParam String text){
return studentService.testStudent(text);
}
}
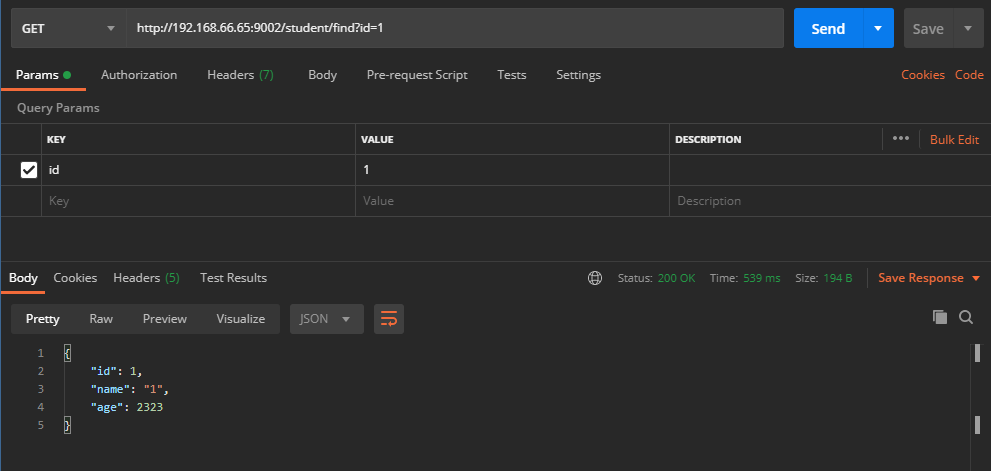
接下来测试一下缓存
@Cacheable
在方法执行前 Spring 先查看缓存中是否有数据,若有,则直接返回缓存数据;若无数据,调用方法将方法返回值放入缓存中;
第一次执行日志:

第二次执行日志:
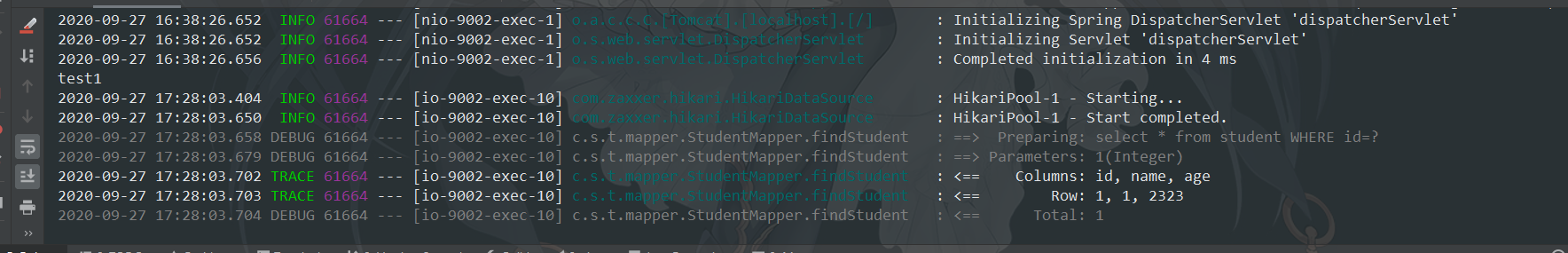
日志没有增加,说明没有查询数据库;
我们添加Debuger,测试下方法有没有执行?

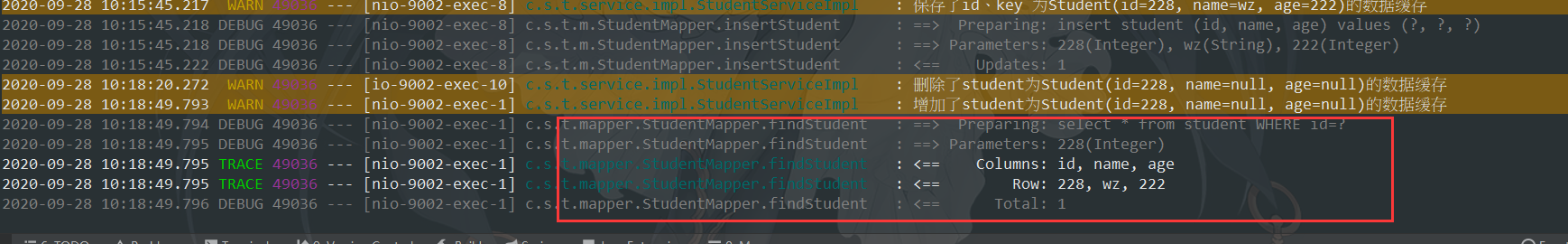
结果findStudent方法并没有执行,说明数据全部取自缓存。
其他方法测试:
@CacheEvict
将一条或多条数据从缓存中删除
添加实现类方法
@Override
@CacheEvict(value = "cacheData")
public void deleteStudent(Student student) {
log.warn("删除了student为{}的数据缓存", student);
}
添加控制器路由
@GetMapping("delete")
public void deleteStudent(Student student){
studentService.deleteStudent(student);
}
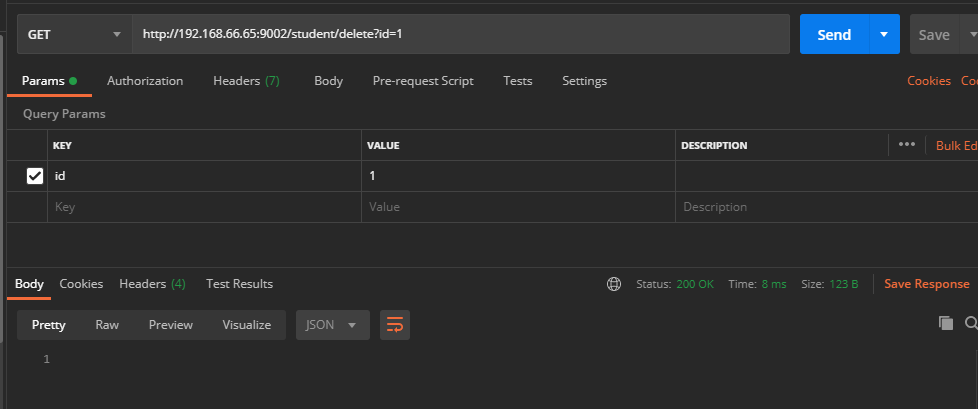

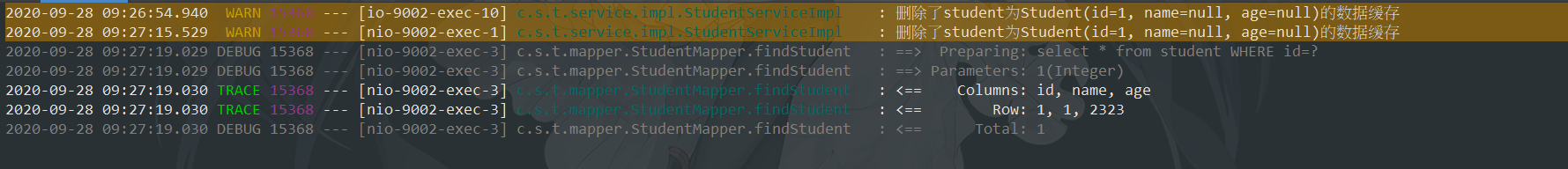
删除缓存后,再次查询会查询Sql库;
@CachePut
缓存新增的或更新的数据到缓存
新增数据
/**
* @CachePut 缓存新增的或更新的数据到缓存
* 其中缓存名称为 student 数据的 key 是 student 的 id
* @param student
*/
@Override
@CachePut(value = "cacheData", key = "#student.id")
public void saveStudent(Student student) {
log.warn("保存了id、key 为{}的数据缓存", student);
studentMapper.insertStudent(student);
}
@GetMapping("add")
public void addStudent(Student student){
studentService.saveStudent(student);
}
先插入一条数据到数据库
这条数据会被立马缓存起来
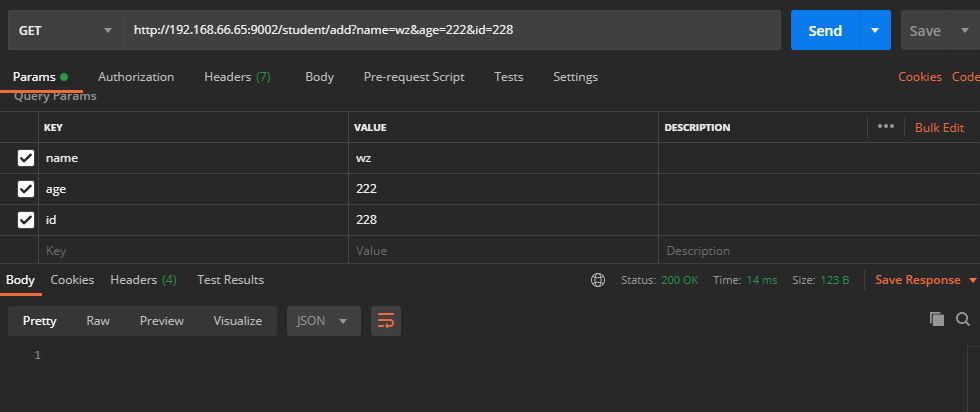

测试缓存数据,看到并没有查询数据库
无sql执行,说明从缓存里面成功拿到了数据
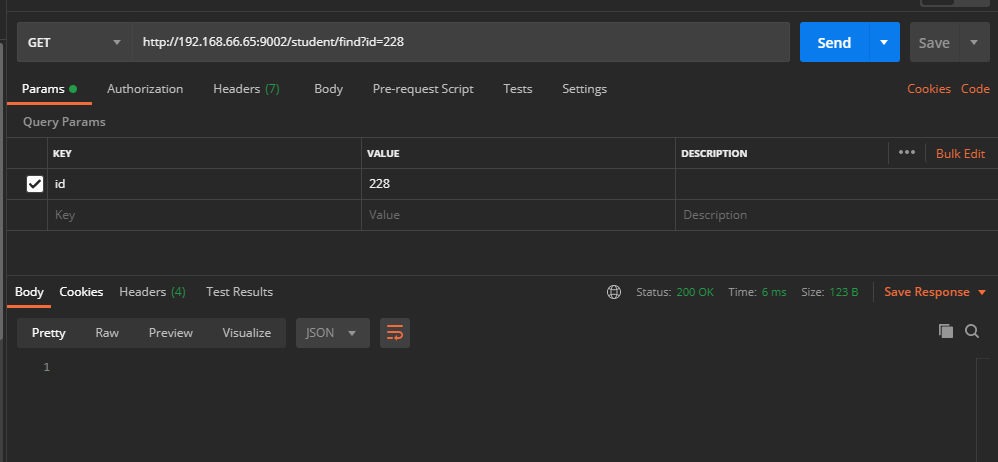
然后删除缓存,重新获取,正确的结果应该是有Sql查询;
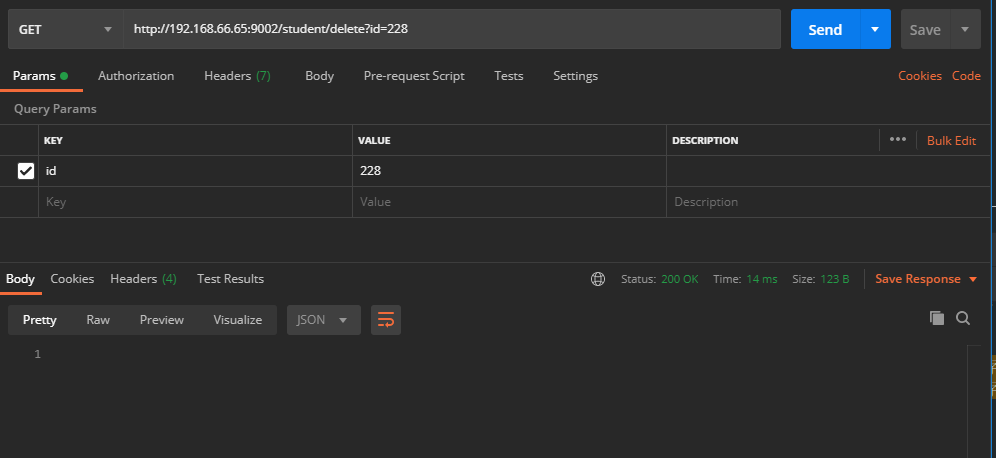
postman访问 http://192.168.66.65:9002/student/delete?id=228 删除了id=288的缓存
postman访问 http://192.168.66.65:9002/student/find?id=228 重新查询数据库获取数据


这个流程走下来,三个缓存方法,各自对应的功能都被验证成功。
缺点:
缓存数据并不持久,如果当前的服务关闭重启了,所有的缓存数据都会丢失了。
3.3、RedisCacheManage
在实际项目中,大多使用是Redis数据库,把所有的缓存数据存储在Redis中。
并且可以设置缓存的存活时间,超过一定时间后,自动获取最新数据。
缓存的方法同上, 不再赘述。
配置文件
server:
port: 9002
spring:
redis:
# Redis服务器地址
host: 127.0.0.1
# Redis服务器连接端口
port: 6379
# Redis服务器连接密码(默认为空)
password:
# 连接超时时间(毫秒)
timeout: 0
jedis:
pool:
# 连接池最大连接数(使用负值表示没有限制)
max-active: 8
# 连接池最大阻塞等待时间(使用负值表示没有限制)
max-wait: -1
# 连接池中的最大空闲连接
max-idle: 8
# 连接池中的最小空闲连接
min-idle: 0
# Redis数据库索引(默认为0)
database: 0
# 缓存数据
# cache:
## type: simple
# type: redis
# cache-names: cacheData
# redis:
# time-to-live: 600000
# use-key-prefix: false
# cache-null-values: off
# key-prefix: test
<!-- redisson 分布锁 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.redisson</groupId>
<artifactId>redisson</artifactId>
<version>3.13.3</version>
</dependency>
修改配置文件 cacheConfig
package com.scaffold.test.config;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnProperty;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.EnableCaching;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
/**
* 缓存配置文件
* 配置文件读取是否启用此配置
* @author alex
*/
@Configuration
@EnableCaching
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "caching", name = "enabled", havingValue = "true")
public class CacheConfig {
// @Bean
// public CacheManager cacheManager() {
// return new ConcurrentMapCacheManager("cacheData");
// }
}
RedisConf添加
CacheManage配置
package com.scaffold.test.config;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonAutoDetect;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.PropertyAccessor;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import org.redisson.Redisson;
import org.redisson.api.RedissonClient;
import org.redisson.codec.JsonJacksonCodec;
import org.redisson.config.Config;
import org.springframework.cache.CacheManager;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheConfiguration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheManager;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.RedisSerializationContext;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.RedisSerializer;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import java.time.Duration;
@Configuration
public class RedisConfig {
@Resource
private RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate;
/**
* 单机模式
*/
@Bean
RedissonClient RedissonSingle() {
Config config = new Config();
config.setCodec(new JsonJacksonCodec())
.useSingleServer()
.setAddress("redis://localhost:6379");
return Redisson.create(config);
}
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<String, Object> setRedisTemplate() {
// 使用 Jackson2JsonRedisSerialize 替换默认序列化
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer jackson2JsonRedisSerializer = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer(Object.class);
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
objectMapper.setVisibility(PropertyAccessor.ALL, JsonAutoDetect.Visibility.ANY);
objectMapper.enableDefaultTyping(ObjectMapper.DefaultTyping.NON_FINAL);
jackson2JsonRedisSerializer.setObjectMapper(objectMapper);
// 字符串序列化
RedisSerializer stringSerializer = new StringRedisSerializer();
redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(stringSerializer);
// value 使用 Jackson2JsonRedisSerialize 序列化
redisTemplate.setValueSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer);
redisTemplate.setHashKeySerializer(stringSerializer);
redisTemplate.setHashValueSerializer(stringSerializer);
return redisTemplate;
}
private Duration timeToLive = Duration.ofSeconds(600);
@Bean
public CacheManager cacheManager(RedisConnectionFactory factory) {
// RedisSerializer<String> redisSerializer = new StringRedisSerializer();
// 解决从redis数据缓存value使用Jackson2JsonRedisSerialize序列化
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer jackson2JsonRedisSerializer = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer(Object.class);
//解决查询缓存转换异常的问题
ObjectMapper om = new ObjectMapper();
om.setVisibility(PropertyAccessor.ALL, JsonAutoDetect.Visibility.ANY);
om.enableDefaultTyping(ObjectMapper.DefaultTyping.NON_FINAL);
jackson2JsonRedisSerializer.setObjectMapper(om);
// 配置序列化(解决乱码的问题)
RedisCacheConfiguration config = RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig()
// 设置缓存的存活时间
.entryTtl(timeToLive)
// 设置缓存名字的前缀
.prefixCacheNameWith("test")
// 禁止缓存名字的前缀
.disableKeyPrefix()
// 序列化value数据
.serializeValuesWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer))
// 禁止缓存 Null 数据
.disableCachingNullValues();
RedisCacheManager cacheManager = RedisCacheManager.builder(factory).cacheDefaults(config).build();
return cacheManager;
}
}
一般情况,可以在配置中,修改配置,我们这里增加配置文件全权控制的原因是,需要格式化存储的数据,否则看到的不是JSON格式的数据。
以上配置等同于以下配置:
spring:
cache:
type: redis
cache-names: cacheData
redis:
time-to-live: 600000
use-key-prefix: false
cache-null-values: off
key-prefix: test
其余代码同 3.2.2,切换缓存方式,只需要更改配置即可。
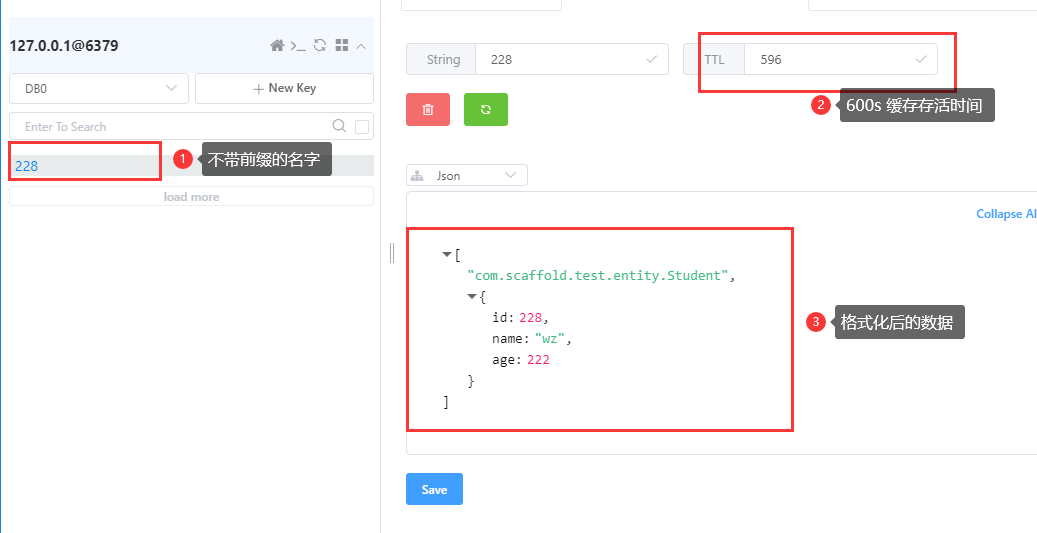
接下来让我们测试一下Redis存储缓存数据。
postman访问 http://192.168.66.65:9002/student/find?id=228
在600s的时间范围内,即使重启项目,依然能否获取到缓存数据。
.prefixCacheNameWith(“test”)

移除序列化的代码
.serializeValuesWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer))
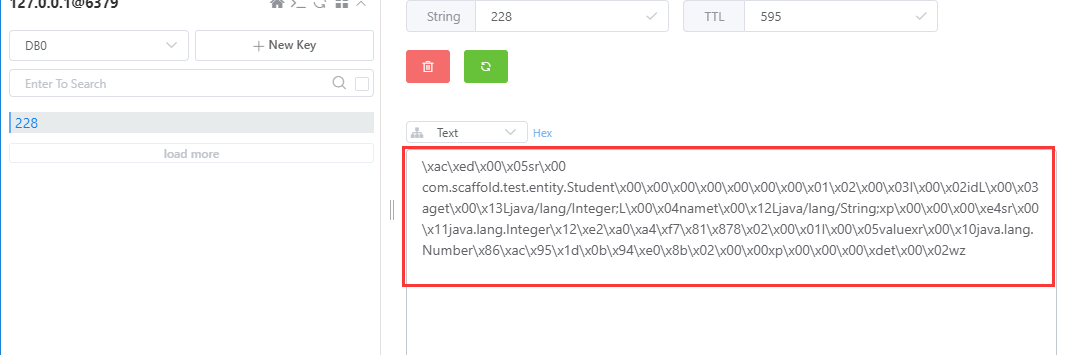
删除缓存
postman 访问 http://192.168.66.65:9002/student/delete?id=228
删除redis中的缓存数据
删除成功
4、总结
以上就是简单的数据缓存案例,Springboot集成Redis缓存是比较常用的。其他缓存方法这里不再说明。