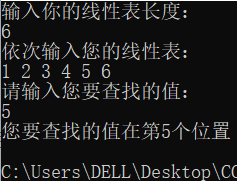
算法7.1顺序查找
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
typedef int KeyType;
typedef int InfoType;
#define MAX 1000
typedef struct {
KeyType key;
InfoType otherinfo;
}ElemType;
typedef struct {
ElemType* R;
int length;
}SSTable;
int Search_Seq(SSTable ST, KeyType key) {
//在顺序表ST中顺序查找其关键字等于key的数据元素。若找到,则函数值为该元素在表中的位置,否则为0
for (int i = ST.length; i >= 1; i--)//从后往前找
if (ST.R[i].key == key) return i;
return 0;
}
void main() {
int i, key;
SSTable t;
t.R = new ElemType[MAX];
cout << "请输入您的线性表长度:\n";
cin >> t.length;
cout << "请输入您要查找的线性表:\n";
for (i = 1; i <= t.length; i++) cin >> t.R[i].key;
cout << "请输入您要查找的数据元素:\n";
cin >> key;
if (Search_Seq(t, key))
cout << "您要查找的" << key << "是线性表中的第" << Search_Seq(t, key)
<< "个元素\n";
else cout << "查找失败!\n";
}

算法7.2设置监视哨的顺序查找
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef int KeyType;
typedef int InfoType;
#define MAX 100
typedef struct{
KeyType key;
InfoType otherinfo;
}ElemType;
typedef struct{
ElemType *R;
int length;
}SSTable;
int Search_Seq(SSTable ST,KeyType key){
//在顺序表ST中顺序查找其关键字等于key的数据元素。若找到,则函数值为该元素在表中的位置,否则为0
int i;
ST.R[0].key=key;//“哨兵”
for(i=ST.length;ST.R[i].key!=key;--i);//从后往前找
return i;
}
void main(){
int i,key;
SSTable t;
t.R=new ElemType[MAX];
cout<<"请输入您的线性表长度:\n";
cin>>t.length;
cout<<"请输入您要查找的线性表:\n";
for(i=1;i<=t.length;i++) cin>>t.R[i].key;
cout<<"请输入您要查找的数据元素:\n";
cin>>key;
if(Search_Seq(t,key))
cout<<"您要查找的"<<key<<"是线性表中的第"<<Search_Seq(t,key)
<<"个元素\n";
else cout<<"查找失败!\n";
}

算法7.3 折半查找
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
typedef int KeyType;
typedef int InfoType;
#define MAX 100
typedef struct {
KeyType key;
InfoType otherinfo;
}ElemType;
typedef struct {
ElemType* R;
int length;
}SSTable;
int Search_Bin(SSTable ST, KeyType key) {
//在有序表ST中折半查找其关键字key的数据元素。若找到,则该函数值为该元素在表中的位置,否则为0
int low = 1, high = ST.length, mid;//置查找区间初值
while (low <= high) {
mid = (low + high) / 2;
if (key == ST.R[mid].key) return mid;//找到待查元素
else if (key < ST.R[mid].key) high = mid - 1;//继续在前一子表进行查找
else low = mid + 1;//继续在后一子表进行查找
}
return 0;//表中不存在元素
}
void main() {
int i, key;
SSTable t;
t.R = new ElemType[MAX];
cout << "请输入您的线性表长度:\n";
cin >> t.length;
cout << "请输入您要查找的线性表:\n";
for (i = 1; i <= t.length; i++) cin >> t.R[i].key;
cout << "请输入您要查找的数据元素:\n";
cin >> key;
if (Search_Bin(t, key))
cout << "您要查找的" << key << "是线性表中的第" << Search_Bin(t, key)
<< "个元素\n";
else cout << "查找失败!\n";
}
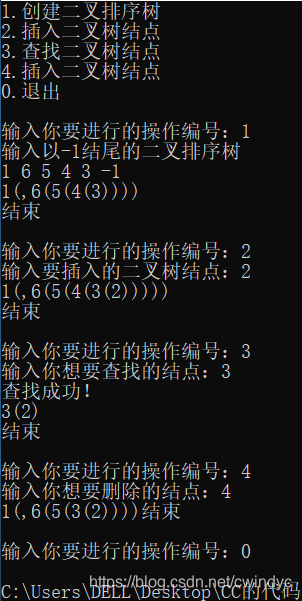
二叉排序树的递归查找、插入、创建、删除
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#define MAXN 1000
#define ENDFLAG -1
#define OK 1
#define ERROR 0
typedef int Status;
typedef int KeyType;
typedef int InfoType;
typedef struct {
KeyType key;
InfoType otherinfo;
}ElemType;
typedef struct BSTNode {
ElemType data;
struct BSTNode* lchild, * rchild;
}BSTNode, * BSTree;
//算法7.4 二叉排序树的递归查找
BSTree SearchBST(BSTree T, KeyType key) {
if ((!T) || key == T->data.key) return T;
else if (key < T->data.key) return SearchBST(T->lchild, key);
else return SearchBST(T->rchild, key);
}
//算法7.5 二叉排序树的插入
void InsertBST(BSTree& T, ElemType e) {
BSTree S;
if (!T) {
S = new BSTNode;
S->data = e;
S->lchild = S->rchild = NULL;
T = S;
}
else if (e.key < T->data.key)
InsertBST(T->lchild, e);
else if (e.key > T->data.key)
InsertBST(T->rchild, e);
}
//算法7.6 二叉排序树的创建
void CreateBST(BSTree& T) {
ElemType e;
T = NULL;
cout << "输入以-1结尾的二叉排序树\n";
cin >> e.key;
while (e.key != ENDFLAG) {
InsertBST(T, e);
cin >> e.key;
}
}
//算法7.7 二叉排序树的删除
void DeleteBST(BSTree& T, KeyType key) {
BSTree p = T, f = NULL, q = NULL, s = NULL;
while (p) {
if (p->data.key == key) break;
f = p;
if (p->data.key > key)p = p->lchild;
else p = p->rchild;
}
if (!p) return;
if ((p->lchild) && (p->rchild)) {
q = p;
s = p->rchild;
while (s->rchild) {
q = s;
s = s->rchild;
}
p->data = s->data;
if (q != p) q->rchild = s->lchild;
else q->lchild = s->lchild;
delete s;
return;
}
else if (!p->rchild) {
q = p;
p = p->lchild;
}
else if (!p->lchild) {
q = p;
p = p->rchild;
}
if (!f) T = p;
else if (q == f->lchild) f->lchild = p;
else f->rchild = p;
delete q;
}
void PrintBST(BSTree T) {
if (T == NULL) return;
else {
cout << T->data.key;
if (T->lchild != NULL || T->rchild != NULL) {
cout << "(";
PrintBST(T->lchild);
if (T->rchild != NULL)
cout << ",";
PrintBST(T->rchild);
cout << ")";
}
}
}
int main() {
BSTree T = NULL;
ElemType e;
int n, key;
cout << "1.创建二叉排序树\n";
cout << "2.插入二叉树结点\n";
cout << "3.查找二叉树结点\n";
cout << "4.插入二叉树结点\n";
cout << "0.退出\n\n";
do {
cout << "输入你要进行的操作编号:";
cin >> n;
if (n == 1) {
CreateBST(T);
PrintBST(T);
cout << "结束\n\n";
}
if (n == 2) {
cout << "输入要插入的二叉树结点:";
cin >> e.key;
InsertBST(T, e);
PrintBST(T);
cout << endl;
cout << "结束\n\n";
}
if (n == 3) {
BSTree t = NULL;
cout << "输入你想要查找的结点:";
cin >> key;
t = SearchBST(T, key);
if (t) {
cout << "查找成功!\n";
PrintBST(t);
cout << endl;
}
else cout << "查找失败!\n";
cout << "结束\n\n";
}
if (n == 4) {
cout << "输入你想要删除的结点:";
cin >> key;
DeleteBST(T, key);
PrintBST(T);
cout << "结束\n\n";
}
if (n == 0) return 0;
} while (n);
return 0;
}
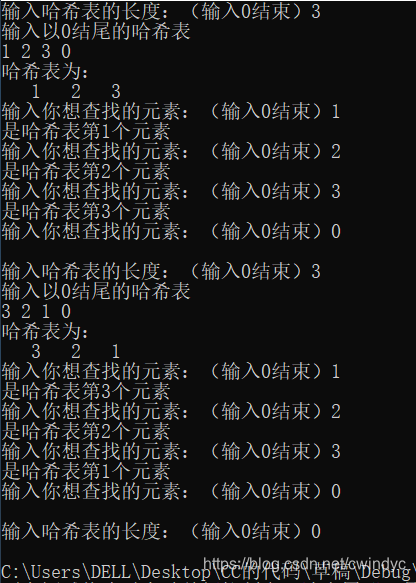
算法7.10 散列表的查找
#include<iostream>
#include<iomanip>
using namespace std;
#define MAXN 1005
typedef int Status;
typedef int KeyType;
typedef int InfoType;
//- - - - -开放地址法散列表的储存表示- - - - -
typedef struct {
KeyType key;
InfoType otherinfo;
}HashTable[MAXN];
int H_p(int length) {
for (int i = length; i > 2; i--) {
int flag = 1;
for (int j = 2; j <= sqrt(length); j++)
if (i % j == 0) flag = 0;
if (flag) return i;
}
return 2;
}
int H(int length, KeyType key) {
return key % H_p(length);
}
//- - - - -算法7.10 散列表的查找- - - - -
int SearchHash(HashTable HT, KeyType key, int length) {
int H0 = H(length, key), Hi, i;
if (HT[H0].key == 0) return -1;
else if (HT[H0].key == key) return H0;
else {
for (i = 1; i < length; ++i) {
Hi = (H0 + i) % length;
if (HT[Hi].key == 0) return -1;
else if (HT[Hi].key == key) return Hi;
}
return -1;
}
}
void CreateHash(HashTable& HT, int length) {
KeyType key = 0;
memset(&HT, 0, sizeof(HT));
int H0 = H(length, key), Hi, i;
cout << "输入以0结尾的哈希表\n";
do {
cin >> key;
if (key == 0) break;
if (HT[H0].key == 0) HT[H0].key = key;
else if (HT[H0].key == key) {
cout << "元素" << HT[H0].key << "重复!\n";
}
else {
int flag = 1;
for (i = 1; i < length; ++i) {
Hi = (H0 + i) % length;
if (HT[Hi].key == 0) {
HT[Hi].key = key;
flag = 0;
break;
}
else if (HT[Hi].key == key) {
cout << "数字" << HT[Hi].key << "重复!\n";
flag = 0;
break;
}
}
if (flag) cout << "哈希表已满!\n";
}
} while (key);
}
void PrintHash(HashTable HT, int length) {
cout << "哈希表为:\n";
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++)
cout << setw(4) << HT[i].key;
cout << endl;
}
void main() {
int length, place;
HashTable HT;
KeyType key;
do {
cout << "输入哈希表的长度:(输入0结束)";
cin >> length;
if (length == 0) break;
CreateHash(HT, length);
PrintHash(HT, length);
do {
cout << "输入你想查找的元素:(输入0结束)";
cin >> key;
if (key == 0) break;
place = SearchHash(HT, key, length) + 1;
if (place) cout << "是哈希表第" << place << "个元素\n";
else cout << "不存在要查找的元素!\n";
} while (key);
cout << endl;
} while (length);
}
(前面三个算法可以合并一下,有兴趣就操作一下。新手怼着书抄的,如果有不严谨的地方,请指点!)