一、简介
遗传算法可以用来求解该问题。遗传算法是一种进化算法,由于其启发式算法的属性,并不能保证得到最优解。求解效果与初始种群选取,编码方法,选择方法,交叉变异规则有关。
二、源代码
function GaTSPChen
% mainly amended by Chen Zhen, 2012~2016
CityNum = 30; % 城市数目,可以选 10, 30, 50, 75
[dislist, Clist] = tsp(CityNum); % dislist 为城市之间相互的距离,Clist 为各城市的坐标
inn = 30; % 初始种群大小
gnMax = 500; % 最大代数
crossProb = 0.8; % 交叉概率
muteProb = 0.8; % 变异概率
% 随机产生初始种群
population = zeros(inn, CityNum); % population 为初始种群,包括多条染色体
for i = 1 : inn
population(i,:) = randperm(CityNum);
end
[~, cumulativeProbs] = calPopulationValue(population, dislist); % 计算种群每条染色体的累计概率
generationNum = 1;
generationMeanValue = zeros(generationNum, 1); % 每一代的平均距离
generationMaxValue = zeros(generationNum, 1); % 每一代的最短距离
bestRoute = zeros(inn, CityNum); % 最佳路径
newPopulation = zeros(inn, CityNum); % 新的种群
while generationNum < gnMax + 1
for j = 1 : 2 : inn
selectedChromos = select(cumulativeProbs); % 选择操作,选出两条需要交叉编译的染色体,即父亲母亲
crossedChromos = cross(population, selectedChromos, crossProb); % 交叉操作,返回交叉后的染色体
newPopulation(j, :) = mut(crossedChromos(1, :),muteProb); % 对交叉后的染色体进行变异操作
newPopulation(j + 1, :) = mut(crossedChromos(2, :), muteProb); % 对交叉后的染色体进行变异操作
end
population = newPopulation; %产生了新的种群
[populationValue, cumulativeProbs] = calPopulationValue(population, dislist); % 计算新种群的适应度
% 记录当前代最好和平均的适应度
[fmax, nmax] = max(populationValue); % 因为计算适应度时取距离的倒数,这里面取最大的倒数,即最短的距离
generationMeanValue(generationNum) = 1 / mean(populationValue);
generationMaxValue(generationNum) = 1 / fmax;
bestChromo = population(nmax, :); % 前代最佳染色体,即对应的路径
bestRoute(generationNum, :) = bestChromo; % 记录每一代的最佳染色体
drawTSP(Clist, bestChromo, generationMaxValue(generationNum), generationNum, 0);
generationNum = generationNum + 1;
end
[bestValue,index] = min(generationMaxValue);
drawTSP(Clist, bestRoute(index, :), bestValue, index,1);
figure(2);
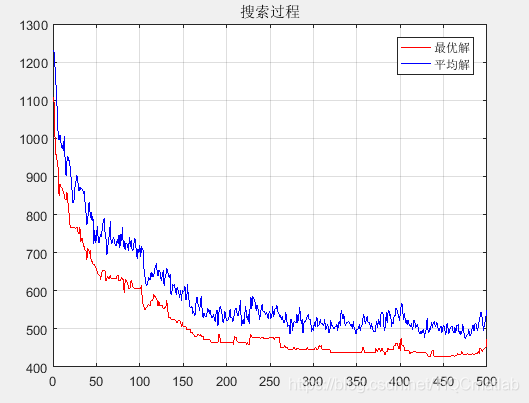
plot(generationMaxValue, 'r');
hold on;
plot(generationMeanValue, 'b');
grid;
title('搜索过程');
legend('最优解', '平均解');
fprintf('遗传算法得到的最短距离: %.2f\n', bestValue);
fprintf('遗传算法得到的最短路线');
disp(bestRoute(index, :));
end
%------------------------------------------------
% 计算所有染色体的适应度
function [chromoValues, cumulativeProbs] = calPopulationValue(s, dislist)
inn = size(s, 1); % 读取种群大小
chromoValues = zeros(inn, 1);
for i = 1 : inn
chromoValues(i) = CalDist(dislist, s(i, :)); % 计算每条染色体的适应度
end
chromoValues = 1./chromoValues'; % 因为让距离越小,选取的概率越高,所以取距离倒数
% 根据个体的适应度计算其被选择的概率
fsum = 0;
for i = 1 : inn
% 乘以15次方的原因是让好的个体被选取的概率更大(因为适应度取距离的倒数,若不乘次方,则个体相互之间的适应度差别不大),换成一个较大的数也行
fsum = fsum + chromoValues(i)^15;
end
% 计算单个概率
probs = zeros(inn, 1);
for i = 1: inn
probs(i) = chromoValues(i)^15 / fsum;
end
% 计算累积概率
cumulativeProbs = zeros(inn,1);
cumulativeProbs(1) = probs(1);
for i = 2 : inn
cumulativeProbs(i) = cumulativeProbs(i - 1) + probs(i);
end
cumulativeProbs = cumulativeProbs';
end
%--------------------------------------------------
%“选择”操作,返回所选择染色体在种群中对应的位置
% cumulatedPro 所有染色体的累计概率
function selectedChromoNums = select(cumulatedPro)
selectedChromoNums = zeros(2, 1);
% 从种群中选择两个个体,最好不要两次选择同一个个体
for i = 1 : 2
r = rand; % 产生一个随机数
prand = cumulatedPro - r;
j = 1;
while prand(j) < 0
j = j + 1;
end
selectedChromoNums(i) = j; % 选中个体的序号
if i == 2 && j == selectedChromoNums(i - 1) % 若相同就再选一次
r = rand; % 产生一个随机数
prand = cumulatedPro - r;
j = 1;
while prand(j) < 0
j = j + 1;
end
end
end
end
%------------------------------------------------
% “交叉”操作
function crossedChromos = cross(population, selectedChromoNums, crossProb)
length = size(population, 2); % 染色体的长度
crossProbc = crossMuteOrNot(crossProb); %根据交叉概率决定是否进行交叉操作,1则是,0则否
crossedChromos(1,:) = population(selectedChromoNums(1), :);
crossedChromos(2,:) = population(selectedChromoNums(2), :);
if crossProbc == 1
c1 = round(rand * (length - 2)) + 1; %在[1,bn - 1]范围内随机产生一个交叉位 c1
c2 = round(rand * (length - 2)) + 1; %在[1,bn - 1]范围内随机产生一个交叉位 c2
chb1 = min(c1, c2);
chb2 = max(c1,c2);
middle = crossedChromos(1,chb1+1:chb2); % 两条染色体 chb1 到 chb2 之间互换位置
crossedChromos(1,chb1 + 1 : chb2)= crossedChromos(2, chb1 + 1 : chb2);
crossedChromos(2,chb1 + 1 : chb2)= middle;
for i = 1 : chb1 % 看交叉后,染色体上是否有相同编码的情况(路径上重复出现两个城市)。若有,则该编码不参与交叉
while find(crossedChromos(1,chb1 + 1: chb2) == crossedChromos(1, i))
location = find(crossedChromos(1,chb1 + 1: chb2) == crossedChromos(1, i));
y = crossedChromos(2,chb1 + location);
crossedChromos(1, i) = y;
end
while find(crossedChromos(2,chb1 + 1 : chb2) == crossedChromos(2, i))
location = find(crossedChromos(2, chb1 + 1 : chb2) == crossedChromos(2, i));
y = crossedChromos(1, chb1 + location);
crossedChromos(2, i) = y;
end
end
for i = chb2 + 1 : length
while find(crossedChromos(1, 1 : chb2) == crossedChromos(1, i))
location = logical(crossedChromos(1, 1 : chb2) == crossedChromos(1, i));
y = crossedChromos(2, location);
crossedChromos(1, i) = y;
end
while find(crossedChromos(2, 1 : chb2) == crossedChromos(2, i))
location = logical(crossedChromos(2, 1 : chb2) == crossedChromos(2, i));
y = crossedChromos(1, location);
crossedChromos(2, i) = y;
end
end
end
end
%--------------------------------------------------
%“变异”操作
% choromo 为一条染色体
function snnew = mut(chromo,muteProb)
length = size(chromo, 2); % 染色体的的长度
snnew = chromo;
muteProbm = crossMuteOrNot(muteProb); % 根据变异概率决定是否进行变异操作,1则是,0则否
if muteProbm == 1
c1 = round(rand*(length - 2)) + 1; % 在 [1, bn - 1]范围内随机产生一个变异位
c2 = round(rand*(length - 2)) + 1; % 在 [1, bn - 1]范围内随机产生一个变异位
chb1 = min(c1, c2);
chb2 = max(c1, c2);
x = chromo(chb1 + 1 : chb2);
snnew(chb1 + 1 : chb2) = fliplr(x); % 变异,则将两个变异位置的染色体倒转
end
end
% 根据变异或交叉概率,返回一个 0 或 1 的数
function crossProbc = crossMuteOrNot(crossMuteProb)
test(1: 100) = 0;
l = round(100 * crossMuteProb);
test(1 : l) = 1;
n = round(rand * 99) + 1;
crossProbc = test(n);
end
%------------------------------------------------
% 计算一条染色体的适应度
% dislist 为所有城市相互之间的距离矩阵
% chromo 为一条染色体,即一条路径
function chromoValue = CalDist(dislist, chromo)
DistanV = 0;
n = size(chromo, 2); % 染色体的长度
for i = 1 : (n - 1)
DistanV = DistanV + dislist(chromo(i), chromo(i + 1));
end
DistanV = DistanV + dislist(chromo(n), chromo(1));
chromoValue = DistanV;
end
%------------------------------------------------
% 画图
% Clist 为城市坐标
% route 为一条路径
function drawTSP(Clist, route, generationValue, generationNum,isBestGeneration)
CityNum = size(Clist, 1);
for i = 1 : CityNum - 1
plot([Clist(route(i), 1),Clist(route(i + 1), 1)], [Clist(route(i),2),Clist(route(i+1),2)],'ms-','LineWidth',2,'MarkerEdgeColor','k','MarkerFaceColor','g');
text(Clist(route(i), 1),Clist(route(i), 2), [' ', int2str(route(i))]);
text(Clist(route(i+1), 1),Clist(route(i + 1), 2), [' ', int2str(route(i+1))]);
hold on;
end
plot([Clist(route(CityNum), 1), Clist(route(1), 1)], [Clist(route(CityNum), 2), Clist(route(1), 2)],'ms-','LineWidth',2,'MarkerEdgeColor','k','MarkerFaceColor','g');
title([num2str(CityNum),'城市TSP']);
if isBestGeneration == 0 && CityNum ~= 10
text(5, 5, ['第 ',int2str(generationNum),' 代',' 最短距离为 ', num2str(generationValue)]);
else
text(5, 5, ['最终搜索结果:最短距离 ',num2str(generationValue),', 在第 ',num2str(generationNum),' 代达到']);
end
if CityNum == 10 % 因为文字显示位置不一样,所以将城市数目为 10 时单独编写
if isBestGeneration == 0
text(0, 0, ['第 ',int2str(generationNum),' 代',' 最短距离为 ', num2str(generationValue)]);
else
text(0, 0, ['最终搜索结果:最短距离 ',num2str(generationValue),', 在第 ', num2str(generationNum),' 代达到']);
end
end
hold off;
pause(0.005);
end
%------------------------------------------------
三、运行结果

四、备注
完整代码或者代写添加QQ912100926
往期回顾>>>>>>
【路径规划】粒子群优化算法之三维无人机路径规划【Matlab 012期】
【路径规划】遗传算法之多物流中心的开放式车辆路径规划【Matlab 013期】
【路径规划】粒子群算法之机器人栅格路径规划【Matlab 014期】
【路径规划】蚁群算法之求解最短路径【Matlab 015期】
【路径规划】免疫算法之物流中心选址【Matlab 016期】
【路径规划】人工蜂群之无人机三维路径规划【Matlab 017期】
【路径规划】遗传算法之基于栅格地图机器人路径规划【Matlab 018期】
【路径规划】蚁群算法之多无人机攻击调度【Matlab 019期】
【路径规划】遗传算法之基于栅格地图的机器人最优路径规划【Matlab 020期】
【路径规划】遗传算法之考虑分配次序的多无人机协同目标分配建模【Matlab 021期】
【路径规划】蚁群算法之多中心vrp问题【Matlab 022期】
【路径规划】蚁群算法之求解带时间窗的多中心VRP【Matlab 023期】
【路径规划】遗传算法之多中心VRP求解【Matlab 024期】
【路径规划】模拟退火之求解VRP问题【Matlab 025期】
【路径规划】A星之栅格路径规划【Matlab 026期】
【路径规划】基于一种带交叉因子的双向寻优粒子群栅格地图路径规划【Matlab 027期】
【路径规划】【TSP】蚁群算法之求解TSP问题含GUI【Matlab 028期】
【路径规划】蚁群算法之栅格地图路径规划【Matlab 029期】