JZOJ7月17日提高组T1 亲戚
题目
Description
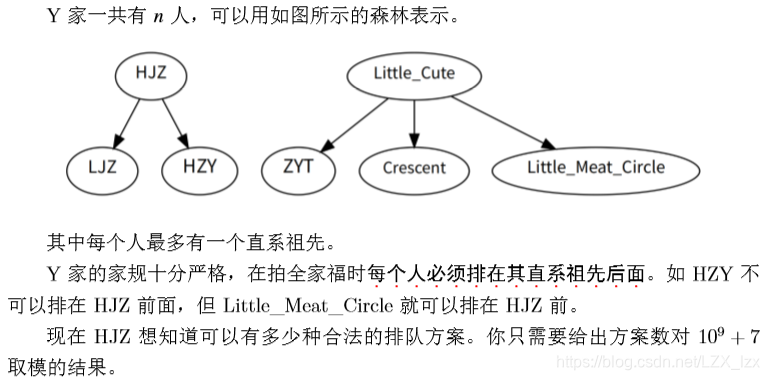
Input

Output
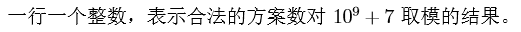
Sample Input
4
0 1 1 0
Sample Output
8
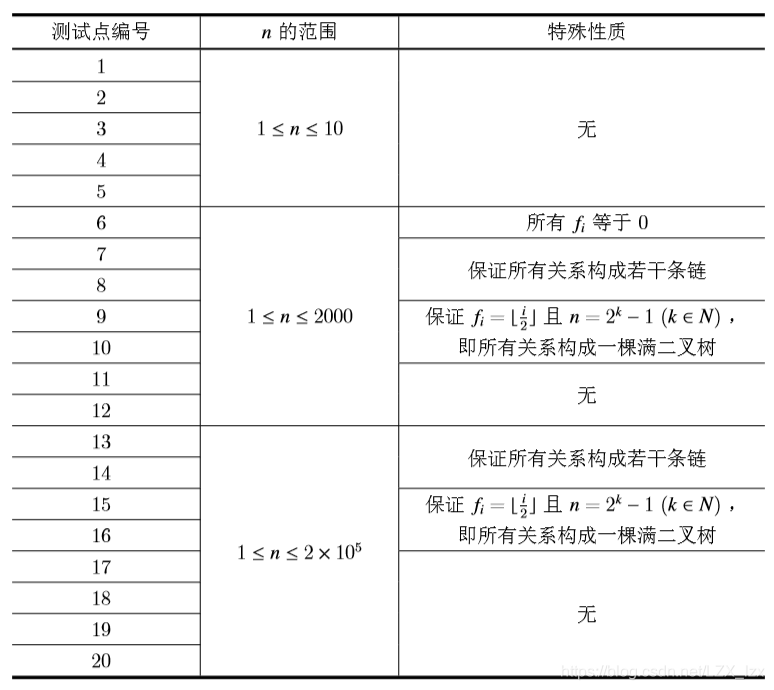
Data Constraint
题解
分析
题意:排序,其中每个节点必须在它的父亲之后
方法1
设一个虚拟根(如0)
使数据变成一棵树
先思考倒数第2层
那么这时候,不考虑当前节点
子节点的排序方法可以这样算:
当一个子节点进来时
判断是否为第一个子节点
如果不是,那么这个子节点就可以插入在已经进来的所有子节点的左右两侧
如图:
接下来思考剩下层
对于倒数第3层
这时以当前节点为根的树就不止一个节点了
那么这时候,就要用到组合数
设已经进入的儿子节点贡献的节点个数为
,将要进来的节点个数为
,那么有公式:
对于组合数,可以通过逆元来计算
我们知道:
PS:先预处理出阶乘
计算
,如果暴力计算C++没有类型存的下(如果暴力模数可能会导致答案出错)
那么这时逆元就可以用起来了
求逆元有很多种方法
例如:费马小定理
以下是费马小定理如何求逆元:
我们知道,当
时,称
是
在模
下的逆元(反过来也行)
同时又有费马小定理:当
是质数时,有
,而且显而易见
所以
可以转换为
结合
和
,可以发现
在模
的意义下时,
就是
的逆元
而
通常用快速幂来求
注意,费马小定理推逆元仅当P是质数时才适用!!!
求出组合数后,依次传递
最后输出
结合代码理解
方法2
对于答案,其实有公式:
其中
表示以i为根节点的子树的点的个数
为什么呢?
证明过程:
Code(方法1)
#include<cstdio>
#define mod 1000000007
using namespace std;
int n,i,x,tot,num[200005];
long long f[200005],jc[200005];
struct node
{
int to,head,next;
}a[200005];
long long ksm(long long x,long long y)
{
long long s;
s=1;
while (y>0)
{
if (y&1) s=s*x%mod;
y>>=1;
x=x*x%mod;
}
return s;
}
long long Cc(int x,int y)
{
long long Ksm=ksm(jc[y]*jc[x-y]%mod,mod-2)%mod;
long long ccc=jc[x]*Ksm%mod;
return ccc%mod;
}
void dfs(int now)
{
int i,x;
long long c;
for (i=a[now].head;i!=0;i=a[i].next)
{
x=a[i].to;
dfs(x);
if (num[now]!=0)
{
c=Cc(num[now]+num[x],num[x]);
f[now]=f[now]*c%mod;
}
num[now]+=num[x];
f[now]=f[now]*f[x]%mod;
}
num[now]++;
}
int main()
{
freopen("input.in","r",stdin);
scanf("%d",&n);
f[0]=1;
for (i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&x);
tot++;
a[tot].to=i;
a[tot].next=a[x].head;
a[x].head=tot;
f[i]=1;
}
jc[0]=1;
for (i=1;i<=n;i++)
jc[i]=jc[i-1]*(long long)i%mod;
dfs(0);
printf("%lld\n",f[0]);
return 0;
}
抱歉只有方法1的Code,毕竟方法2的代码量很小,可以自己试着理解码出来

