1. 背景知识
Lipmaa和Bingsheng Zhang 2012年同时期论文《A More Efficient Computationally Sound Non-Interactive Zero-Knowledge Shuffle Argument*》,要点为:
- 非 random-oracle based的shuffle argument。【In a shuffle argument, the prover proves that two tuples of randomized ciphertexts encrypt the same multiset of plaintexts.】
- zero argument。
- 1-sparsity argument。
- 基于zero argument和1-sparsity argument构建的permutation matrix argument。
- 基于的假设有:knowledge BBS cryptosystem、DLIN assumption以及power symmetric discrete logarithm(PSDL) assumption.【The PSDL assumption is much more standard(-looking) than the SPA and PPA assumptions from [GL07].】
Shuffle argument的历史情况:
- Groth and Ishai [GI08] 的communication复杂度为 。
- Groth [Gro09] 的communication复杂度为 。
- Bayer and Groth [BG12] 的communication复杂度为 。
1.1 Permutation matrix
Permutation matrix为每行每列仅有一个‘1’值的Boolean matrix。
A matrix is a permutation matrix iff its every column sums to 1 and its every row has exactly one non-zero element.
论文研究情况:
- 论文[FS01]等中,Prover对permutation matrix进行commit,同时提供一份有效的permutation matrix argument。
- 论文Terelius and Wikstr¨om [TW10]中,基于“A matrix is a permutation matrix iff its every column sums to 1 and its every row has exactly one non-zero element.“事实,构建了interactive permutation matrix. 使用了Schwartz-Zippel lemma。
- 本论文基于的事实为:a matrix is a permutation matrix exactly if every column sums to 1 and every row has at most one non-zero element. 且不采用Schwartz-Zippel lemma,故而不需要基于random oracle model来实现NIZK。
1.2 一些说明

1.3 Trapdoor commitment

2. Zero argument
Zero argument,即prover can open the given commitment to the zero tuple,可理解为Groth[10]中的restriction argument的特例化,即prover知道knowledge of the discrete logarithm.

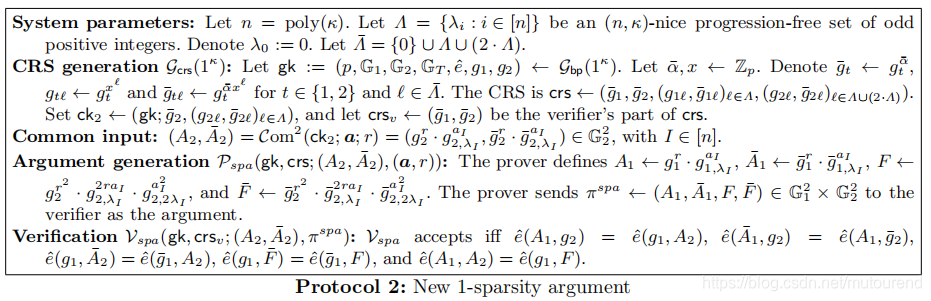
3. 1-sparsity argument
A vector is -sparse, if it has at most non-zero coefficients. 可认为,zero argument为0-sparsity argument.
1-sparsity argument,即prover can open the given commitment to
,其中最多只有一个
为非零值。
可转换为证明:
, for every

根据Lip[12]可知,the discrete logartihm of the non-interactive argument为:
,其中
为secret key。
- 多项式中,对于honest prover来说,每个constraint均只有1个monomial。在论文Lip[12]中,其constraints的数量为线性的:for any , ,而在本论文1-sparsity argument中,其constraints数量为quadratic的:for any two different coefficients and , 。
- 多项式中,Lip[12]论文中的monomials为quasilinear的( ),而在1-sparsity argument中为linear的。1-sparsity argument与Lip[12]中的argument相比,其CRS length和prover’s computational complexity均更低。
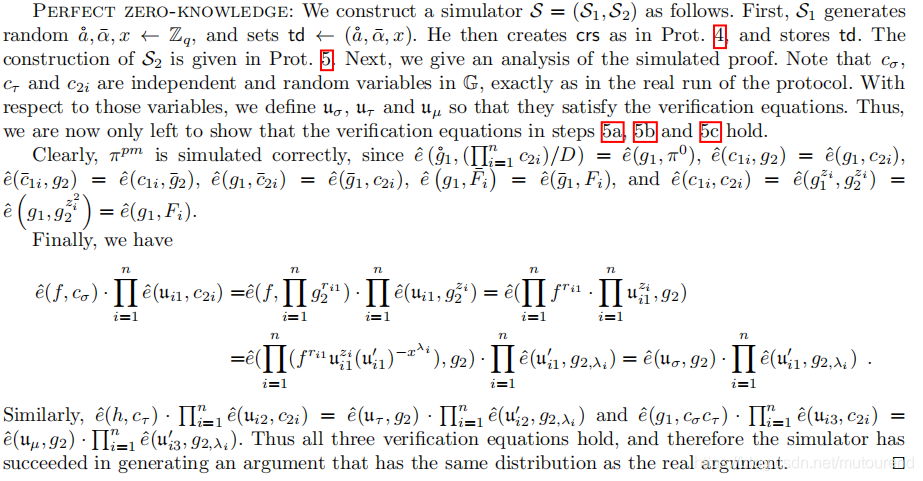
以上1-sparity argument为非perfectly zero-knwoledge的,原因为:


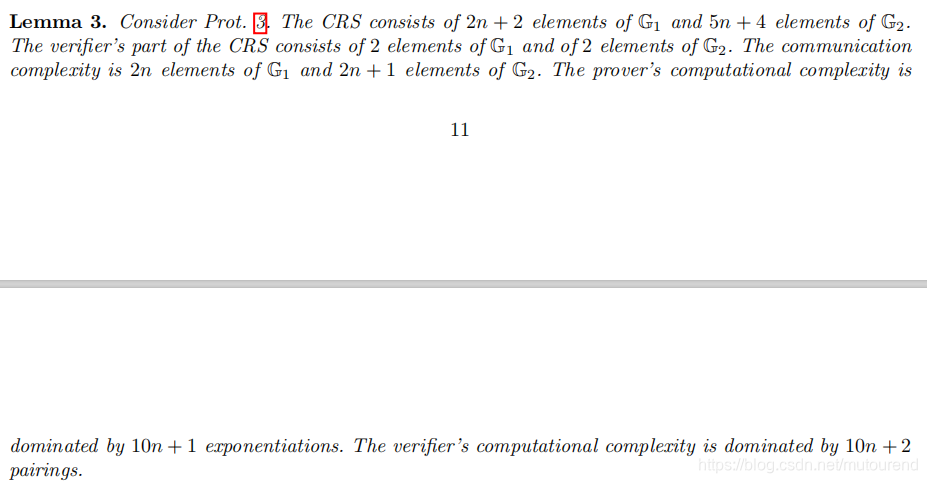
4. Permutation matrix argument
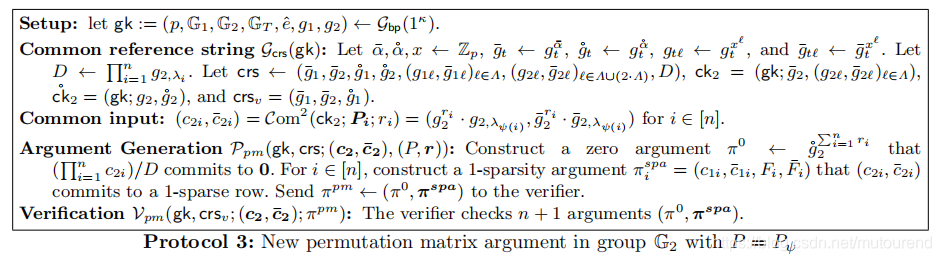
其中的
即为permutation matrix
的第
行。
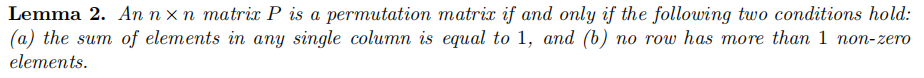
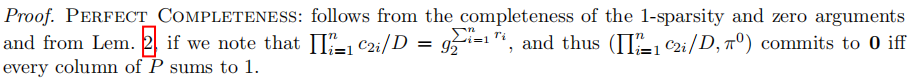
5. Knowledge BBS cryptosystem

6. New shuffle argument

该new shuffle argument具有perfect zero-knowledge。