一,从现有的数据创建数组
1,使用arange创建
import numpy as np
temp1 = np.arange(12,dtype=np.float32)
temp2 = np.arange(3,12,dtype=np.float32)
temp3 = temp1.reshape(3,4)
print(temp1,temp1.dtype)
print(temp3,temp3.dtype)
# -----------output-----------------
[ 0. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11.] float32
[[ 0. 1. 2. 3.]
[ 4. 5. 6. 7.]
[ 8. 9. 10. 11.]] float32
2,使用array创建
import numpy as np
temp1 = np.array([[1,2,3,4],[3,4,5,6],[7,8,9,0]],dtype=float)
temp2 = np.array([[1,2,3,4],[3,4,5,6],[7,8,9,0]],dtype='float32')
temp3 = np.array([[1,2,3,4],[3,4,5,6],[7,8,9,0]],dtype=np.float32)
temp4 = np.array([[1,2,3,4],[3,4,5,6],[7,8,9,0]],dtype='i4')
temp5 = np.array([[1,1,0,0],[1,1,0,0],[1,1,0,0]],dtype=bool)
temp6 = np.array(range(1,6))
print(temp1.dtype)
print(temp2.dtype)
print(temp3.dtype)
print(temp4.dtype)
print(temp5.dtype)
print(temp6,temp6.dtype)
# -----------output-----------------
float64
float32
float32
int32
bool
[1 2 3 4 5] int32
3,使用asarray创建
temp1 = np.array([[1,2,3,4],[3,4,5,6],[7,8,9,0]],dtype=np.float32)
temp3 = np.asarray(temp1 )
print(temp3)
4,使用copy创建
temp1 = np.array([[1,2,3,4],[3,4,5,6],[7,8,9,0]],dtype=np.float32)
temp3 = temp1.copy()
print(temp3)
5,array和asarray的区别
array和asarray都可以将结构数据转化为ndarray,但是主要区别就是当数据源是ndarray时,array仍然会copy出一个副本,占用新的内存,但asarray不会。
temp = np.array([[1,2,3,4],[3,4,5,6],[7,8,9,0]],dtype=np.float32)
temp1 = np.array(temp) # 创建了一个新的数组
temp2 = np.asarray(temp) # 还是引用原来的数组
print(temp1,temp2)
二,创建固定范围的数组
1,创建一个全0的数组
import numpy as np
# temp = np.arange(30).reshape(5,6)
temp = np.zeros((2,3))
print(temp)
# -----------output-----------------
[[0. 0. 0.]
[0. 0. 0.]]
2,创建一个全1的数组
import numpy as np
# temp = np.arange(30).reshape(5,6)
temp = np.ones((2,3))
print(temp)
# -----------output-----------------
[[1. 1. 1.]
[1. 1. 1.]]
3,创建一个对角线为1的正方形数组:
np.eye(number)
import numpy as np
print(np.eye(4))
# -----------output-----------------
[[1. 0. 0. 0.]
[0. 1. 0. 0.]
[0. 0. 1. 0.]
[0. 0. 0. 1.]]
4,使用linspace创建数组
常用于创建等差数列
np.linspace (start, stop, num, endpoint, retstep, dtype)
生成等间隔的序列
start 序列的起始值
stop 序列的终止值,如果endpoint为true,该值包含于序列中
num 要生成的等间隔样例数量,默认为50
endpoint 序列中是否包含stop值,默认为ture
retstep 如果为true,返回样例,以及连续数字之间的步长
dtype 输出ndarray的数据类型
import numpy as np
temp = np.linspace(0,100,11,True,True)
print(temp)
# -----------output-----------------
(array([ 0., 10., 20., 30., 40., 50., 60., 70., 80., 90., 100.]), 10.0)
5,类似的还有:
numpy.arange(start, stop, step, dtype)
numpy.logspace(start, stop, num, endpoint, base, dtype)
常用于创建等比数列
三,创建随机的数组
1,numpy生成均匀分布随机数
import numpy as np
# 给定随机种子
np.random.seed(10)
# 创建维度为(3,1)的0~1的随机数列
t1 = np.random.rand(3,1)
# 创建维度为(2,2)的(0~100)的小数随机数列
t2 = np.random.uniform(0,100,(2,2))
# 创建维度为(2,2)的(0~100)的整数随机数列
t3 = np.random.randint(0,20,(2,2))
for i in [t1,t2,t3]:
print(i)
# -----------output-----------------
[[0.77132064]
[0.02075195]
[0.63364823]]
[[74.88038825 49.85070123]
[22.47966455 19.80628648]]
[[ 8 9]
[ 0 10]]
2,numpy生成正态分布随机数
import numpy as np
# 给定均值、标准差、维度的正态分布
t1 = np.random.normal(0,1,(2,2))
# 标准正太分布。定均值为0、标准差为1的正太分布
t2 = np.random.standard_normal(size=(2,2))
for i in [t1,t2]:
print(i)
# -----------output-----------------
[[-0.290396 1.32423901]
[ 0.59322204 -2.37736497]]
[[-1.31577873 0.99945344]
[ 1.55544037 0.8770521 ]]

3,什么是正太分布
率密度函数为正态分布的期望值μ决定了其位置,其标准差σ决定了分布的幅度。
当μ = 0,σ = 1时的正态分布是标准正态分布。
方差用来衡量数据的离散程度: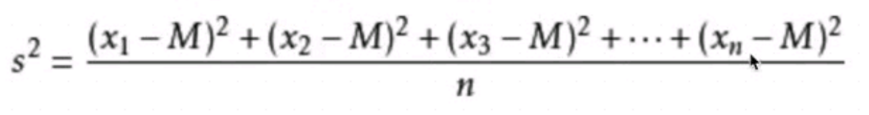
标准差用数据公式代替表示为:
