知识点如下:
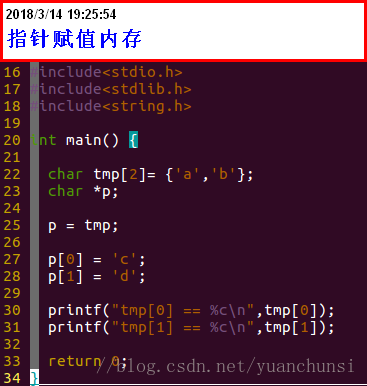
1、pFrameYUV为sws_scale缩放接口的出参,通过指针方式将pFrameYUV数据赋值给bmp
2、播放器函数简介
av_register_all():注册所有组件
avformat_opent_input():打开输入视频文件
avformat_find_stream_info():获取视频文件信息
avcodec_find_decoder():查找解码器
avcodec_open2():打开解码器
av_read_frame():从输入文件读取一帧压缩数据
avcodec_decode_video2():解码一帧压缩数据
avcodec_close():关闭解码器
avformat_close_input():关闭输入视频文件
3、播放器结构体简介
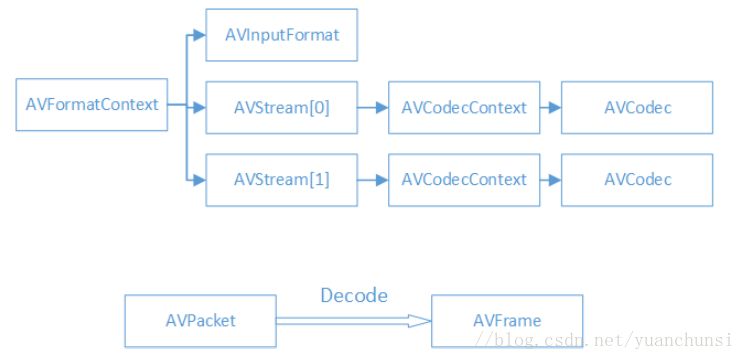
AVFormatContext:封装格式上下文结构体,也是统领全局的结构体,保存了视频文件封装格式相关的信息
iformat:输入视频的AVInputFormat
nb_streams:输入视频的AVStream个数
streams:输入视频的AVstream【】数组
duration:输入视频的时长(微妙)
bit_brate:输入视频的码率
AVInputFormat:各种封装格式(例如FLV,MKV,MP4,AVI)对应一个该结构体
name:封装格式名称
long_name:封装格式的长名称
extensions:封装格式的扩展名
id:封装格式的ID
AVStream:视频文件中每个视频(音频)流对应一个该结构体
id:序号
codec:该流对应的AVCodecContext
time_base:该流的时基
r_frame_rate:该流的帧率
AVCodecContext:编码器上下文结构体,保存视频(音频)编解码相关信息
codec:解编码器的AVCodec
width,height:图像的宽高(只针对视频)
pix_fmt:像素格式(只针对视频)
sample_rate:采样率(只针对音频)
channels:声道数(只针对音频)
sample_fmt:采样格式(只针对音频)
AVCodec:每种视频(音频)编解码器(例如H.264)对应的一个结构体
name:编解码器名称
long_name:解编码器长名称
type:解编码器类型
id:解编码器ID
AVPacket:存储一帧压缩编码数据
pts:显示时间戳
dts:解码时间戳
data:压缩编码数据
size:压缩编码数据大小
stream_index:所属的AVStream
AVFrame:存储一帧解码后像素(采样)数据
data:解码后的图像像素数据(音频采样数据)
linesize:对视频来说是图像中一行像素的大小;对音频说是整个音频帧的大小
width,height:图像的宽高(只针对视频)
key_frame:是否为关键帧(只针对视频)
pict_type:帧类型(只针对视频)如I,P,B帧
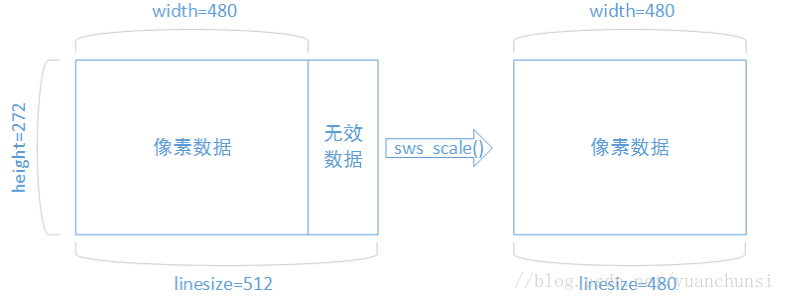
3、解码后数据为什么要sws_scale处理
解码后的YUV格式的视频像素数据保存在AVFrame的data[0],data[1],data[2]中,但是这些像素值不是联系存储的
每一行有效像素之后存储了一些无效的像素,以亮度为Y的数据为例,data[0]中一共包含了linesize[0]*height个数
据。但是出于优化等方面的考虑,linesize[0]实际上并不等于宽度width,而是一共比宽度大一些的值。因此需要用
sws_scale()进行转换去除无效数据,width和linesize[0]取值相等
#include "stdafx.h"
//Refresh
#define SFM_REFRESH_EVENT (SDL_USEREVENT + 1)
int thread_exit = 0;
int sfp_refresh_thread(void *arg){
SDL_Event event;
while(0 == thread_exit){
event.type = SFM_REFRESH_EVENT;
SDL_PushEvent(&event);
SDL_Delay(40);
}
return 0;
}
int _tmain()
{
AVFormatContext *pFormatCtx;//承接编解码整个过程包含媒体格式信息
int i, videoindex;
AVCodecContext *pCodecCtx;//包含编辑器信息
AVCodec *pCodec;//编码器句柄
pFormatCtx = avformat_alloc_context();
char filepath[]="eques2.h264";
av_register_all();
if(avformat_open_input(&pFormatCtx,filepath,NULL,NULL) != 0){
printf("Read file header info for pFormatCtx error\n");
return -1;
}
//此函数的作用:av_dump_format()是一个手工调试的函数,
//能使我们看到pFormatCtx->streams里面有什么内容。
//一般接下来我们使用av_find_stream_info()函数,
//它的作用是为pFormatCtx->streams填充上正确的信息。
av_dump_format(pFormatCtx,0,filepath,0);
if(avformat_find_stream_info(pFormatCtx,NULL)<0){
printf("Read stream info error\n ");
return -1;
}
videoindex = -1;
for(i = 0;i < pFormatCtx->nb_streams;i ++){
if(pFormatCtx->streams[i]->codec->codec_type == AVMEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO){
videoindex = i;
break;
}
if(videoindex == -1){
return -1;
}
}
pCodecCtx = pFormatCtx->streams[videoindex]->codec;
//函数的参数是一个编码器的ID,返回查找到的编码器
pCodec = avcodec_find_decoder(pCodecCtx->codec_id);
if(NULL == pCodec){
printf("find decoder error\n");
return -1;
}
//打开编码器
if(avcodec_open2(pCodecCtx,pCodec,NULL)< 0) {
printf("could not open codec\n");
return -1;
}
AVFrame *pFrame,*pFrameYUV;//存储解码后的数据结构
AVPacket *packet;//存储压缩编码数据相关信息的结构
pFrame = av_frame_alloc();
pFrameYUV = av_frame_alloc();
//SDL
SDL_Thread *video_tid;
SDL_Thread *Key_tid;
SDL_Event event;
int screen_w,screen_h;
SDL_Surface *screen;
SDL_VideoInfo *vi;
SDL_Overlay *bmp;
SDL_Rect rect;
if(SDL_Init(SDL_INIT_VIDEO | SDL_INIT_AUDIO | SDL_INIT_TIMER)){
printf("Could not init SDL %s\n",SDL_GetError());
return -1;
}
//创建并设置屏幕宽高
screen_w = pCodecCtx->width;
screen_h = pCodecCtx->height;
screen = SDL_SetVideoMode(screen_w,screen_h,0,0);
if(!screen){
printf("SDL: could not set video %s\n",SDL_GetError());
return -1;
}
//创建一个YUV数据覆盖图
bmp = SDL_CreateYUVOverlay(screen_w,screen_h,SDL_YV12_OVERLAY,screen);
//SDL_Rect数据矩阵
rect.x = 0;
rect.y = 0;
rect.w = screen_w;
rect.h = screen_h;
packet= (AVPacket*)av_malloc(sizeof(AVPacket));
//ffmpeg进行图像数据格式的转换以及图片的缩放应用一套函数(sws_getContext,sws_scale,sws_freeContext)
struct SwsContext *img_convert_ctx = sws_getContext(pCodecCtx->width,pCodecCtx->height,pCodecCtx->pix_fmt,
pCodecCtx->width,pCodecCtx->height,PIX_FMT_YUV420P,SWS_BICUBIC,NULL,NULL,NULL);// //视频格式转化为YUV420P格式
//event线程解决屏幕不能拖动问题
video_tid = SDL_CreateThread(sfp_refresh_thread,NULL);
//设置显示窗口的标题和图标
SDL_WM_SetCaption("Simple FFmpeg Player",NULL);
//Event Loop
int ret ,got_picture;
while(1){
//等待线程event时间40毫秒一次,不至于抢占了CPU
SDL_WaitEvent(&event);
if(event.type = SFM_REFRESH_EVENT){
if(0 <= av_read_frame(pFormatCtx,packet)){
//检索到视频
if(packet->stream_index == videoindex){
//解码视频数据,packet和pFrame存储解码前后数据
ret = avcodec_decode_video2(pCodecCtx,pFrame,&got_picture,packet);
if(0 > ret){
printf("Decode Error\n");
return -1;
}
if(got_picture){
//pFrameYUV为sws_scale缩放接口的出参,通过指针方式将pFrameYUV数据赋值给bmp
SDL_LockYUVOverlay(bmp);
pFrameYUV->data[0] = bmp->pixels[0];
pFrameYUV->data[1] = bmp->pixels[2];
pFrameYUV->data[2] = bmp->pixels[1];
pFrameYUV->linesize[0] = bmp->pitches[0];
pFrameYUV->linesize[1] = bmp->pitches[2];
pFrameYUV->linesize[2] = bmp->pitches[1];
sws_scale(img_convert_ctx,(const uint8_t* const*)pFrame->data,pFrame->linesize,0,pCodecCtx->height
,pFrameYUV->data,pFrameYUV->linesize);
SDL_LockYUVOverlay(bmp);
//pFrameYUV数据赋值给bmp,显示视频帧
SDL_DisplayYUVOverlay(bmp,&rect);
}
}
av_free_packet(packet);
}else {
thread_exit = 1;
break;
}
}
}
//释放
SDL_Quit();
sws_freeContext(img_convert_ctx);
av_free(pFrameYUV);
avcodec_close(pCodecCtx);
avformat_close_input(&pFormatCtx);
return 0;
}