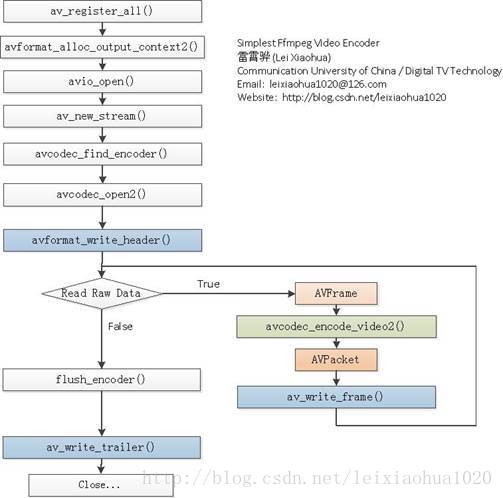
流程
下面附一张使用FFmpeg编码视频的流程图。使用该流程,不仅可以编码H.264的视频,而且可以编码MPEG4/MPEG2/VP8等等各种FFmpeg支持的视频。图中蓝色背景的函数是实际输出数据的函数。浅绿色的函数是视频编码的函数。
简单介绍一下流程中各个函数的意义:
av_register_all():注册FFmpeg所有编解码器。
avformat_alloc_output_context2():初始化输出码流的AVFormatContext。
avio_open():打开输出文件。
av_new_stream():创建输出码流的AVStream。
avcodec_find_encoder():查找编码器。
avcodec_open2():打开编码器。
avformat_write_header():写文件头(对于某些没有文件头的封装格式,不需要此函数。比如说MPEG2TS)。
avcodec_encode_video2():编码一帧视频。即将AVFrame(存储YUV像素数据)编码为AVPacket(存储H.264等格式的码流数据)。
av_write_frame():将编码后的视频码流写入文件。
flush_encoder():输入的像素数据读取完成后调用此函数。用于输出编码器中剩余的AVPacket。
av_write_trailer():写文件尾(对于某些没有文件头的封装格式,不需要此函数。比如说MPEG2TS)。程序源码
/*
*
* 本程序实现了YUV像素数据编码为视频码流(H264)
*
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#define __STDC_CONSTANT_MACROS
extern "C"
{
#include "libavdevice/avdevice.h"
#include "libavutil/imgutils.h"
#include "libavutil/opt.h"
#include "libavcodec/avcodec.h"
#include "libavformat/avformat.h"
#include "libswscale/swscale.h"
};
int flush_encoder(AVFormatContext *fmtCtx,unsigned int streamIndex){
int ret;
int got_frame;
AVPacket enc_pkt;
if (!(fmtCtx->streams[streamIndex]->codec->codec->capabilities & AV_CODEC_CAP_DELAY))
{
return 0;
}
while (1)
{
enc_pkt.data = NULL;
enc_pkt.size = 0;
av_init_packet(&enc_pkt);
ret = avcodec_encode_video2 (fmtCtx->streams[streamIndex]->codec, &enc_pkt,
NULL, &got_frame);
av_frame_free(NULL);
if (ret < 0)
break;
if (!got_frame){
ret=0;
break;
}
printf("Flush Encoder: Succeed to encode 1 frame!\tsize:%5d\n",enc_pkt.size);
/* mux encoded frame */
ret = av_write_frame(fmtCtx, &enc_pkt);
if (ret < 0)
break;
}
return ret;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
AVFormatContext *pFormatCtx = NULL;
AVCodecContext *pCodecCtx = NULL;
AVCodec *pCodec = NULL;
AVOutputFormat *pOutFmt = NULL;
const char *inFilename = "input.yuv";
const char *outFilename = "output.h264";
//1.注册组件:编解码器等
avdevice_register_all();
//2.初始化封装格式上下文
//方法一:
// pFormatCtx = avformat_alloc_context();
// pOutFmt = av_guess_format(NULL, outFilename, NULL);
// pFormatCtx->oformat = pOutFmt;
//方法二:
avformat_alloc_output_context2(&pFormatCtx, NULL, NULL, outFilename);
pOutFmt = pFormatCtx->oformat;
//3.打开输出文件
if (avio_open(&pFormatCtx->pb, outFilename, AVIO_FLAG_WRITE) < 0)
{
printf("can't open output file\n");
return -1;
}
//4.创建输出码流
AVStream *pOutStream = avformat_new_stream(pFormatCtx, NULL);
if (!pOutStream)
{
printf("can't allocate new stream\n");
return -1;
}
//5.查找视频编码器
//获取编码器上下文
// avcodec_parameters_to_context(pCodecCtx, pOutStream->codecpar);
pCodecCtx = pOutStream->codec;
//设置编码器上下文参数
pCodecCtx->codec_id = pOutFmt->video_codec;
pCodecCtx->codec_type = AVMEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO;
pCodecCtx->pix_fmt = AV_PIX_FMT_YUV420P;
//视频的宽度和高度:确保等于输入文件的宽度和高度
pCodecCtx->width = 960;
pCodecCtx->height = 544;
//设置帧率25fps
pCodecCtx->time_base.num = 1;
pCodecCtx->time_base.den = 25;
//设置码率
pCodecCtx->bit_rate = 400000;
//设置GOP
pCodecCtx->gop_size = 250;
//设置量化参数
pCodecCtx->qmin = 10;
pCodecCtx->qmax = 51;
pCodecCtx->max_b_frames = 3;
//6.查找编码器
pCodec = avcodec_find_encoder(pCodecCtx->codec_id);
if (!pCodec)
{
printf("can't find encoder\n");
return -1;
}
printf("pCodec.name = %s\n", pCodec->name);
//若是H264编码器,要设置一些参数
AVDictionary *param = NULL;
if (pCodecCtx->codec_id == AV_CODEC_ID_H264)
{
av_dict_set(¶m, "preset", "slow", 0);
av_dict_set(¶m, "tune", "zerolatency", 0);
}
//7.打开编码器
if (avcodec_open2(pCodecCtx, pCodec, ¶m) < 0)
{
printf("can't open encoder\n");
return -1;
}
//8.写入头文件信息
avformat_write_header(pFormatCtx, NULL);
//9.循环编码YUV文件为H264
//(1)开辟缓冲区
int bufSize = av_image_get_buffer_size(pCodecCtx->pix_fmt, pCodecCtx->width, pCodecCtx->height, 1);
int ySize = pCodecCtx->width * pCodecCtx->height;
uint8_t *outBuffer = (uint8_t *)av_malloc(bufSize);
FILE *inFile = fopen(inFilename, "rb");
if (!inFile)
{
printf("can't find input file\n");
return -1;
}
//(2) 内容空间填充
AVFrame *pFrame = av_frame_alloc();
//设置真的格式、宽度和高度,否则会出现
//1.AVFrame.format is not set
//AVFrame.width or height is not set
pFrame->format = pCodecCtx->pix_fmt;
pFrame->width = pCodecCtx->width;
pFrame->height = pCodecCtx->height;
av_image_fill_arrays(pFrame->data,
pFrame->linesize,
outBuffer,
pCodecCtx->pix_fmt,
pCodecCtx->width,
pCodecCtx->height,
1);
//(3)开辟packet
AVPacket *pPacket = (AVPacket *)av_malloc(bufSize);
int i = 0, frameIndex = 0;
//(4)循环编码
while(1)
{
//从YUV文件里面读取缓冲区
//读取大小:ySize * 3 / 2
if (fread(outBuffer, 1, ySize * 3 / 2, inFile) <= 0)
{
printf("finished to read data\n");
break;
}
else if (feof(inFile))
{
break;
}
//将缓冲区数据转换成AVFrame类型
pFrame->data[0] = outBuffer; //Y值
pFrame->data[1] = outBuffer + ySize; //U值
pFrame->data[2] = outBuffer + ySize * 5 / 4; //V值
pFrame->pts = i * (pOutStream->time_base.den) / (pOutStream->time_base.num * 25);
//10.视频编码处理
//(1)发送一帧视频像素数据
if (avcodec_send_frame(pCodecCtx, pFrame) < 0)
{
printf("failed to encoder\n");
return -1;
}
//(2)接收一帧视频压缩数据格式(像素数据编码而来)
if (avcodec_receive_packet(pCodecCtx, pPacket) >= 0)
{
//编码成功
//11.将视频写入到输出文件
pPacket->stream_index = pOutStream->index;
if (av_write_frame(pFormatCtx, pPacket) < 0)
{
printf("failed to write frame\n");
return -1;
}
printf("succeed to write frame: %d\tsize:%d\n", frameIndex++, pPacket->size);
}
av_packet_unref(pPacket);
}
//写入剩余帧数据->可能没有
flush_encoder(pFormatCtx, 0);
//写入文件尾部信息
av_write_trailer(pFormatCtx);
//释放内存
avcodec_close(pCodecCtx);
av_free(pFrame);
av_free(outBuffer);
av_packet_free(&pPacket);
avio_close(pFormatCtx->pb);
avformat_free_context(pFormatCtx);
fclose(inFile);
return 0;
}
代码分析
1、注册组件
av_register_all();
2、初始化化封装格式上下文
AVFormatContext* avformat_context = avformat_alloc_context();
获取视频压缩格式类型(h254、h265、mpeg2等)
AVOutputFormat *avoutput_format = av_guess_format(NULL, coutFilePath, NULL);
3、打开输出文件
avio_open(&avformat_context->pb, coutFilePath, AVIO_FLAG_WRITE)
参数一:输出流
参数二:输出文件
参数三:权限->输出到文件中
4、创建输出码流
AVStream* av_video_stream = avformat_new_stream(avformat_context, NULL);
注意:这里只是开辟了一块内存空间,还不知道他是什么类型
5、查找视频编码器(重点)
5.1、获取上下文
AVCodecContext *avcodec_context = av_video_stream->codec;
上下文种类:视频解码器、视频编码器、音频解码器、音频编码器
5.2、设置为视频编码器上下文
1、设置视频编码器ID
avcodec_context->codec_id = avoutput_format->video_codec;
2、设置编码器类型
avcodec_context->codec_type = AVMEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO;
3、设置读取像素格式
//注意:这个类型是根据你解码的时候指定的解码的视频像素数据格式类型
avcodec_context->pix_fmt = AV_PIX_FMT_YUV420P;
4、设置视频宽高
avcodec_context->width = 640;
avcodec_context->height = 352;
这里的尺寸是通过一定工具查看的,不同的视频不一样。
5、设置帧率(重点)
avcodec_context->time_base.num = 1;
avcodec_context->time_base.den = 25;
这两个参数表示帧率为25.000fps
帧率越大越流畅。视频卡顿说明掉帧了。
6、设置码率(重点)
码率:也叫比特率,单位bps。也就是每秒传送的比特数,码率越高传送速度越快。
视频码率:单位为kbps,千位每秒
视频码率的计算方式:视频文件大小/视频时间
注意:一个视频的总文件包括视频文件和音频文件,上面公式中,是指视频文件的大小。
e.g 一个视频,视频文件的大小是1.34MB,时长是24s,那么他的视频帧率为:1.34 * 1024 * 8 / 24 / 1000 = 468 Kbps
每个文件的码率不一样,都要经过计算得到
avcodec_context->bit_rate = 468000;
从上面的分析可以看出:码率越大,视频越大
7、设置GOP(重点)
GOP:画面组,一组连续画面(一个完整的画面)
MPEG格式的画面类型有3种:
I帧:内部编码帧,原始帧,也叫关键帧。视频的第一帧都是I帧,可独立编码。
P帧:向前预测帧。编码需要依赖前一帧。
B帧:前后预测帧,也叫双向预测帧。编码需要依赖本帧与前一帧和后一帧的对比。B帧压缩率高,但对性能要求高
701545128389_.pic.jpg
avcodec_context->gop_size = 250;
这里设置250,表示每250帧插入一个I帧。I帧约少,视频越小。但过分的少,会导致视频编码失败,所以要适量。
8、设置量化参数(难点,我们一般设置默认值)
avcodec_context->qmin = 10;
avcodec_context->qmax = 51;
量化系数越小,视频越是清晰。一般情况下都是默认值,最小量化系数默认值是10,最大量化系数默认值是51。
9、设置B帧最大值
avcodec_context->max_b_frames = 0;
我们设置为0,表示不需要B帧
5.3、查找编码器h264
查找编码器h264:找不到???深坑
原因:编译库没有依赖x264库(默认情况下FFmpeg没有编译进行h264库)
如何编译x264库?
1、下载x264的库
2、编译x264的.a静态库,也可以便以动态库,根据需要而定
3、重新编译ffmpeg库,使ffmpeg依赖2中生成的x264库
4、替换代码中之前生成的ffmpeg库
6、打开视频编码器
对于h264解码器,要多设置参数如下
AVDictionary *param = 0;
if (avcodec_context->codec_id == AV_CODEC_ID_H264) {
// 查看h264.c源码
av_dict_set(¶m, "preset", "slow", 0);
av_dict_set(¶m, "tune", "zerolatency", 0);
}
打开视频编码器
if (avcodec_open2(avcodec_context, avcodec, ¶m) < 0) {
NSLog(@"打开编码器失败");
return;
}
7、写入头文件信息
avformat_write_header(avformat_context, NULL);
8、循环编码视频像素数据为视频压缩数据(YUV-->h264)-- 视频编码处理
1、申请缓冲区
av_frame_alloc()
av_image_fill_arrays
(AVPacket *)av_malloc(buffer_size)
2、将缓冲区数据填充到AVFrame中
3、avcodec_send_frame
4、avcodec_receive_packet
9、将编码后的视频压缩数据写入文件中
av_packet->stream_index = av_video_stream->index;
result = av_write_frame(avformat_context, av_packet);
10、写入剩余帧数据(可能没有)
int flush_encoder(AVFormatContext *fmt_ctx, unsigned int stream_index) {
int ret;
int got_frame;
AVPacket enc_pkt;
if (!(fmt_ctx->streams[stream_index]->codec->codec->capabilities &
CODEC_CAP_DELAY))
return 0;
while (1) {
enc_pkt.data = NULL;
enc_pkt.size = 0;
av_init_packet(&enc_pkt);
ret = avcodec_encode_video2(fmt_ctx->streams[stream_index]->codec, &enc_pkt,
NULL, &got_frame);
av_frame_free(NULL);
if (ret < 0)
break;
if (!got_frame) {
ret = 0;
break;
}
NSLog(@"Flush Encoder: Succeed to encode 1 frame!\tsize:%5d\n", enc_pkt.size);
/* mux encoded frame */
ret = av_write_frame(fmt_ctx, &enc_pkt);
if (ret < 0)
break;
}
return ret;
}
11、写入文件尾部信息
av_write_trailer(avformat_context);
12、释放内存,关闭编码器等等
avcodec_close(avcodec_context);
av_free(av_frame);
av_free(out_buffer);
av_packet_free(&av_packet);
avio_close(avformat_context->pb);
avformat_free_context(avformat_context);
fclose(in_file);
问题总结
出错问题1:AVFrame.format is not set
这是因为没有设置帧的格式
解决办法:
pFrame->format = pCodecCtx->pix_fmt;出错问题2:AVFrame.width or height is not set
这是因为没有设置帧的宽度和高度
解决办法:
pFrame->width = pCodecCtx->width;
pFrame->height = pCodecCtx->height;参考
参考:
https://blog.csdn.net/leixiaohua1020/article/details/25430425