数据结构
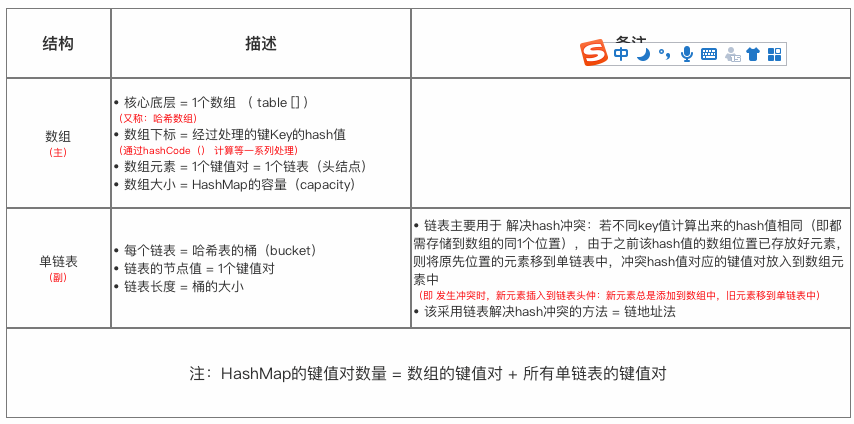
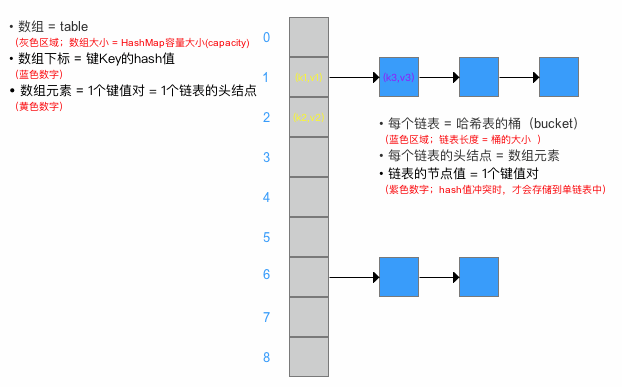
HashMap 采用的数据结构 = 数组(主) + 单链表(副)
HashMap的主结构类似于一个数组,添加值时通过key确定储存位置.,每个位置是一个Entry的数据结构,该结构可组成链表,当发生冲突时,相同hash值的键值对会组成链表.
这种数组+链表的组合形式大部分情况下都能有不错的性能效果,Java6、7就是这样设计的.然而,在极端情况下,一组(比如经过精心设计的)键值对都发生了冲突,这时的哈希结构就会退化成一个链表,使HashMap性能急剧下降。
put 方法
/** * Associates the specified value with the specified key in this map. * If the map previously contained a mapping for the key, the old * value is replaced. * * @param key key with which the specified value is to be associated * @param value value to be associated with the specified key * @return the previous value associated with <tt>key</tt>, or * <tt>null</tt> if there was no mapping for <tt>key</tt>. * (A <tt>null</tt> return can also indicate that the map * previously associated <tt>null</tt> with <tt>key</tt>.) */ public V put(K key, V value) { //如果为数组为空,则进行初始化操作。 if (table == EMPTY_TABLE) { inflateTable(threshold); } if (key == null) //如果key为空,则将值value方到数组0位置上,如果0位置有值则替换 return putForNullKey(value); //计算key的hash值 int hash = hash(key); //根据hash值和存储数据的数组长度计算位置索引 int i = indexFor(hash, table.length); //查找对应位置是否有值,如果有值则使用新值替换 for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) { Object k; if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) { V oldValue = e.value; e.value = value; //HashMap 空实现,可忽略 e.recordAccess(this); return oldValue; } } //记录修改次数加1 modCount++; //增加key-value映射到数组中 addEntry(hash, key, value, i); return null; }
初始化数组方法inflateTable
/** * Inflates the table. */ private void inflateTable(int toSize) { // Find a power of 2 >= toSize //查找大于toSize的最小2的幂数,例如传入的toSize=23,那么capacity为2^6=32 int capacity = roundUpToPowerOf2(toSize); //根据容量和负载因子计算扩展阈值,当容量达到此阀值时,HashMap进行扩容。 threshold = (int) Math.min(capacity * loadFactor, MAXIMUM_CAPACITY + 1); //初始化EntiEntry<K,V>[] 数组存储大小 table = new Entry[capacity]; //初始化HashSeed initHashSeedAsNeeded(capacity); }
transfer方法
void transfer(Entry[] newTable, boolean rehash) { int newCapacity = newTable.length; for (Entry<K,V> e : table) { while(null != e) { Entry<K,V> next = e.next; if (rehash) { e.hash = null == e.key ? 0 : hash(e.key); } int i = indexFor(e.hash, newCapacity); e.next = newTable[i]; newTable[i] = e; e = next; } } }
这段代码是HashMap的扩容操作,重新定位每个桶的下标,并采用头插法将元素迁移到新数组中。头插法会将链表的顺序翻转,这也是形成死循环的关键点。理解了头插法后再继续往下看是如何造成死循环以及数据丢失的。
https://blog.csdn.net/carson_ho/article/details/79373026
https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1489931