Risk is a board game in which several opposing players attempt to conquer the world. The gameboard
consists of a world map broken up into hypothetical countries. During a player’s turn, armies stationed
in one country are only allowed to attack only countries with which they share a common border. Upon
conquest of that country, the armies may move into the newly conquered country.
During the course of play, a player often engages in a sequence of conquests with the goal of
transferring a large mass of armies from some starting country to a destination country. Typically,
one chooses the intervening countries so as to minimize the total number of countries that need to
be conquered. Given a description of the gameboard with 20 countries each with between 1 and 19
connections to other countries, your task is to write a function that takes a starting country and a
destination country and computes the minimum number of countries that must be conquered to reach
the destination. You do not need to output the sequence of countries, just the number of countries to be
conquered including the destination. For example, if starting and destination countries are neighbors,
then your program should return one.
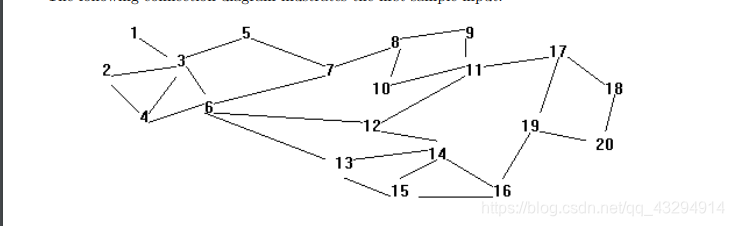
The following connection diagram illustrates the first sample input.
Input
Input to your program will consist of a series of country configuration test sets. Each test set will
consist of a board description on lines 1 through 19. The representation avoids listing every national
boundary twice by only listing the fact that country I borders country J when I < J. Thus, the I-th
line, where I is less than 20, contains an integer X indicating how many “higher-numbered” countries
share borders with country I, then X distinct integers J greater than I and not exceeding 20, each
describing a boundary between countries I and J. Line 20 of the test set contains a single integer
(1 ≤ N ≤ 100) indicating the number of country pairs that follow. The next N lines each contain
exactly two integers (1 ≤ A, B ≤ 20; A ̸= B) indicating the starting and ending countries for a possible
conquest.
There can be multiple test sets in the input file; your program should continue reading and processing
until reaching the end of file. There will be at least one path between any two given countries in every
country configuration.
Output
For each input set, your program should print the following message ‘Test Set #T’ where T is the
number of the test set starting with 1 (left-justified starting in column 11).
The next NT lines each will contain the result for the corresponding test in the test set — that is,
the minimum number of countries to conquer. The test result line should contain the start country
code A right-justified in columns 1 and 2; the string ‘ to ’ in columns 3 to 6; the destination country
code B right-justified in columns 7 and 8; the string ‘: ’ in columns 9 and 10; and a single integer
indicating the minimum number of moves required to traverse from country A to country B in the test
set left-justified starting in column 11. Following all result lines of each input set, your program should
print a single blank line.
Sample Input
1 3
2 3 4
3 4 5 6
1 6
1 7
2 12 13
1 8
2 9 10
1 11
1 11
2 12 17
1 14
2 14 15
2 15 16
1 16
1 19
2 18 19
1 20
1 20
5
1 20
2 9
19 5
18 19
16 20
4 2 3 5 6
1 4
3 4 10 5
5 10 11 12 19 18
2 6 7
2 7 8
2 9 10
1 9
1 10
2 11 14
3 12 13 14
3 18 17 13
4 14 15 16 17
0
0
0
2 18 20
1 19
1 20
6
1 20
8 20
15 16
11 4
7 13
2 16
Sample Output
Test Set #1
1 to 20: 7
2 to 9: 5
19 to 5: 6
18 to 19: 2
16 to 20: 2
Test Set #2
1 to 20: 4
8 to 20: 5
15 to 16: 2
11 to 4: 1
7 to 13: 3
2 to 16: 4
UVa的题的特点:做题10分钟,读题半小时
就当复习六级了
裸的flyod多源最短路,flyod不会的看这里
这个题难在输入输出格式
注意换行,PE了好几次(不开心
flyod模板
放一坨代码在这里
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int M = 20;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const int N = 1e3 + 5;
int d[N][N];
int n;
void init()
{
for (int i = 1; i <= M; i++)
for (int j = 1; j <= M; j++)
{
if (i == j)
d[i][j] = 0;
else
d[i][j] = INF;
}
}
void floyd()
{
for (int k = 1; k <= M; k++)
for (int i = 1; i <= M; i++)
for (int j = 1; j <= M; j++)
d[i][j] = min(d[i][j], d[i][k] + d[k][j]);
}
int main()
{
int cnt = 0;
while (cin >> n)
{
init();
int a, b = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
scanf("%d", &a);
d[a][b] = 1;
d[b][a] = 1;
}
for (b = 2; b <= M - 1; b++)
{
scanf("%d", &n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
scanf("%d", &a);
d[a][b] = 1;
d[b][a] = 1;
}
}
floyd();
printf("Test Set #%d\n", ++cnt);
cin>>n;
int l, r;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
cin >> l >> r;
printf("%2d to %2d: %d\n",l,r,d[l][r]);
}
puts("");
}
return 0;
}
