一、二分查找
思想:从中间开始查找。
时间复杂度:O(logN)。
eg.查英文字典。
eg.猜0-100大小数从50开始猜。
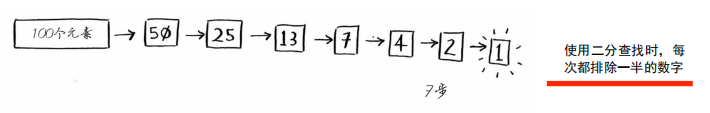
二分查找是一种算法,其输入一个有序的元素列表。如果要查找的元素包含在列表中,二分查找返回其位置,否则返回null(或者-1)。
1 import math 2 3 def binary_search(my_list,item): 4 low = 0 #跟踪的范围 5 high = len(my_list) - 1 6 7 while(low <= high): 8 mid_value = (low + high) / 2 9 mid = math.floor(mid_value) #floor为向下取整 10 guess = my_list[mid] 11 12 if guess == item: 13 return mid 14 if guess > item: #猜大了,high减1 15 high = mid - 1 16 if guess < item: #猜小了,low加1 17 low = mid + 1 18 return None 19 20 my_list = [1,3,5,7,9] 21 print(binary_search(my_list,3)) 22 print(binary_search(my_list,-1))
>>>1 >>>None
向上取整(ceil)与向下取整(floor)会有啥区别?
mid = (high - low) / 2 + low 与 mid = (low + high) / 2有啥区别?
用二分查找的列表需要升序(降序)排列?仅当列表是有序的时候,二分查找才管用。
详解二分查找:https://www.cnblogs.com/kyoner/p/11080078.html
你真的会写二分查找么:https://www.cnblogs.com/luoxn28/p/5767571.html
二、选择排序
时间复杂度:O(n2)。

继续,找出播放次数第二多的乐队:
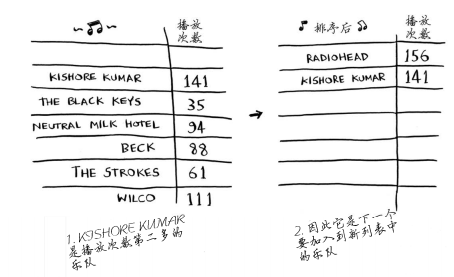
最后得到一个有序列表:

1 def findSmallest(arr): #找数组中的最小元素 2 smallest = arr[0] 3 smallest_index = 0 4 for i in range(1,len(arr)): 5 if arr[i] < smallest: 6 smallest = arr[i] 7 smallest_index = i 8 return smallest_index #返回索引值 9 10 def selectSort(arr): #对数组进行排序 11 newArr = [] 12 for i in range(0,len(arr)): 13 smallest = findSmallest(arr) 14 newArr.append(arr.pop(smallest)) 15 return newArr 16 17 print(selectSort([5,3,7,5,8,9,0]))
>>>[0, 3, 5, 5, 7, 8, 9]
pop()弹出指定索引处的元素,原列表改变:
1 a = [54,6,5,7,8,5,6] 2 b = a.pop(0) 3 print(b) 4 print(a)
>>>54 >>>[6, 5, 7, 8, 5, 6]
选择排序与冒泡排序的区别?
选择排序算法:https://www.cnblogs.com/2019wxw/p/11234072.html
冒泡排序与选择排序的内容,区别:https://www.cnblogs.com/Good-good-stady-day-day-up/p/9055698.html
三、调用栈
在函数之中调用了其他函数,就像栈一样,函数被调用则压入栈中,函数执行完毕再从栈中弹出。
1 def greet(name): 2 print('hello,' + name + '!') 3 greet2(name) #函数之内调用的第一个函数 4 print('getting ready to say bye...') 5 bye() #函数之内调用的第二个函数 6 7 def greet2(name): 8 print('how are you,' + name + '?') 9 10 def bye(): 11 print('ok bye!') 12 13 greet('lily')
>>>hello,lily! >>>how are you,lily? >>>getting ready to say bye... >>>ok bye!



现在你又回到了函数greet。由于没有别的事情要做,你就从函数greet返回。
这个栈用于存储多个函数的变量,被称为调用栈。
四、递归调用栈
递归函数也使用调用栈。
1 def fact(x): 2 if x == 1: 3 return 1 4 else: 5 return x * fact(x-1) 6 7 fact(3)
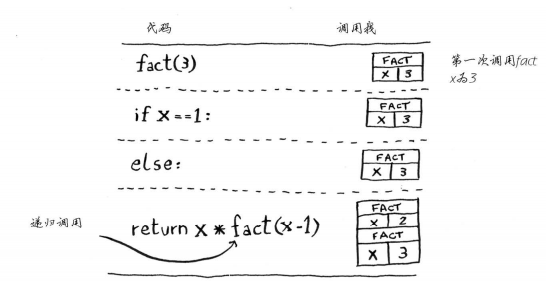
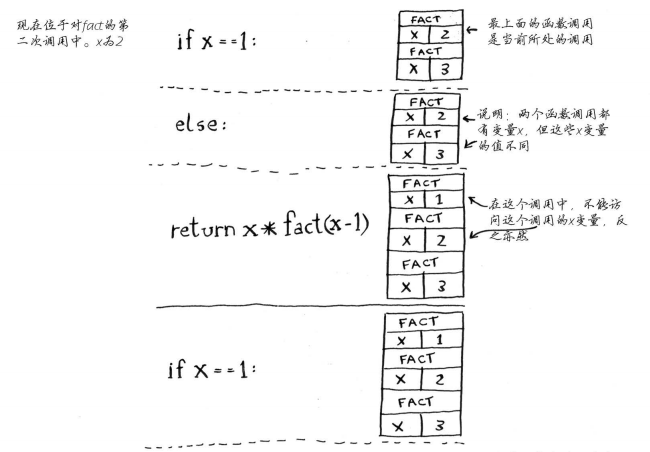

调用栈可能很长,这将占用大量的内存。