文章目录
1. MapReduce 介绍
MapReduce思想在生活中处处可见。或多或少都曾接触过这种思想。MapReduce的思想核心是“分而治之”,适用于大量复杂的任务处理场景(大规模数据处理场景)。
- Map负责“分”,即把复杂的任务分解为若干个“简单的任务”来并行处理。可以进行拆分的前提是这些小任务可以并行计算,彼此间几乎没有依赖关系。
- Reduce负责“合”,即对map阶段的结果进行全局汇总。
- MapReduce运行在yarn集群
- ResourceManager
- NodeManager
这两个阶段合起来正是MapReduce思想的体现。
还有一个比较形象的语言解释MapReduce:
我们要数图书馆中的所有书。你数1号书架,我数2号书架。这就是“Map”。我们人越多,数书就更快。
现在我们到一起,把所有人的统计数加在一起。这就是“Reduce”。

1.1 MapReduce 设计构思和框架结构
MapReduce是一个分布式运算程序的编程框架,核心功能是将用户编写的业务逻辑代码和自带默认组件整合成一个完整的分布式运算程序,并发运行Hadoop集群上。
既然是做计算的框架,那么表现形式就是有个输入(input),MapReduce操作这个输入(input),通过本身定义好的计算模型,得到一个输出(output)。
Hadoop MapReduce构思:
- 分而治之
- 对相互间不具有计算依赖关系的大数据,实现并行最自然的办法就是采取分而治之的策略。并行计算的第一个重要问题是如何划分计算任务或者计算数据以便对划分的子任务或数据块同时进行计算。不可分拆的计算任务或相互间有依赖关系的数据无法进行并行计算!
- 统一构架,隐藏系统层细节
- 如何提供统一的计算框架,如果没有统一封装底层细节,那么程序员则需要
考虑诸如数据存储、划分、分发、结果收集、错误恢复等诸多细节;为此,
MapReduce设计并提供了统一的计算框架,为程序员隐藏了绝大多数系统
层面的处理细节。 - MapReduce最大的亮点在于通过抽象模型和计算框架把需要做什么(what
need to do)与具体怎么做(how to do)分开了,为程序员提供一个抽象和高
层的编程接口和框架。程序员仅需要关心其应用层的具体计算问题,仅需编
写少量的处理应用本身计算问题的程序代码。如何具体完成这个并行计算任
务所相关的诸多系统层细节被隐藏起来,交给计算框架去处理:从分布代码的
执行,到大到数千小到单个节点集群的自动调度使用。
- 如何提供统一的计算框架,如果没有统一封装底层细节,那么程序员则需要
- 构建抽象模型:Map和Reduce
- MapReduce借鉴了函数式语言中的思想,用Map和Reduce两个函数提供了高层的并行编程抽象模型
- Map: 对一组数据元素进行某种重复式的处理;
- Reduce: 对Map的中间结果进行某种进一步的结果整理。
- Map和Reduce为程序员提供了一个清晰的操作接口抽象描述。MapReduce处理的数据类型是键值对。
- MapReduce中定义了如下的Map和Reduce两个抽象的编程接口,由用户去编程实现:
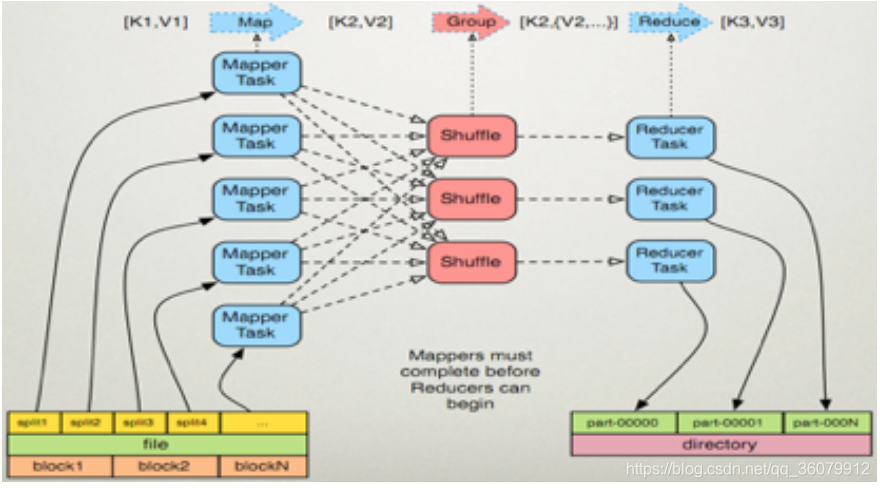
- Map: (k1; v1) → [(k2; v2)]
- Reduce: (k2; [v2]) → [(k3; v3)]
- MapReduce借鉴了函数式语言中的思想,用Map和Reduce两个函数提供了高层的并行编程抽象模型
1.2 MapReduce 框架结构
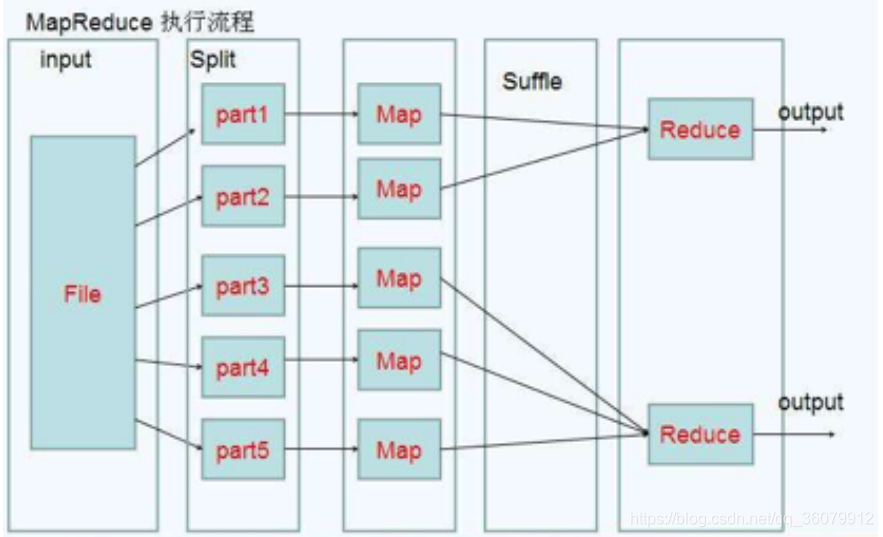
一个完整的mapreduce程序在分布式运行时有三类实例进程:
- MRAppMaster 负责整个程序的过程调度及状态协调
- MapTask 负责map阶段的整个数据处理流程
- ReduceTask 负责reduce阶段的整个数据处理流程


2. MapReduce 编程规范
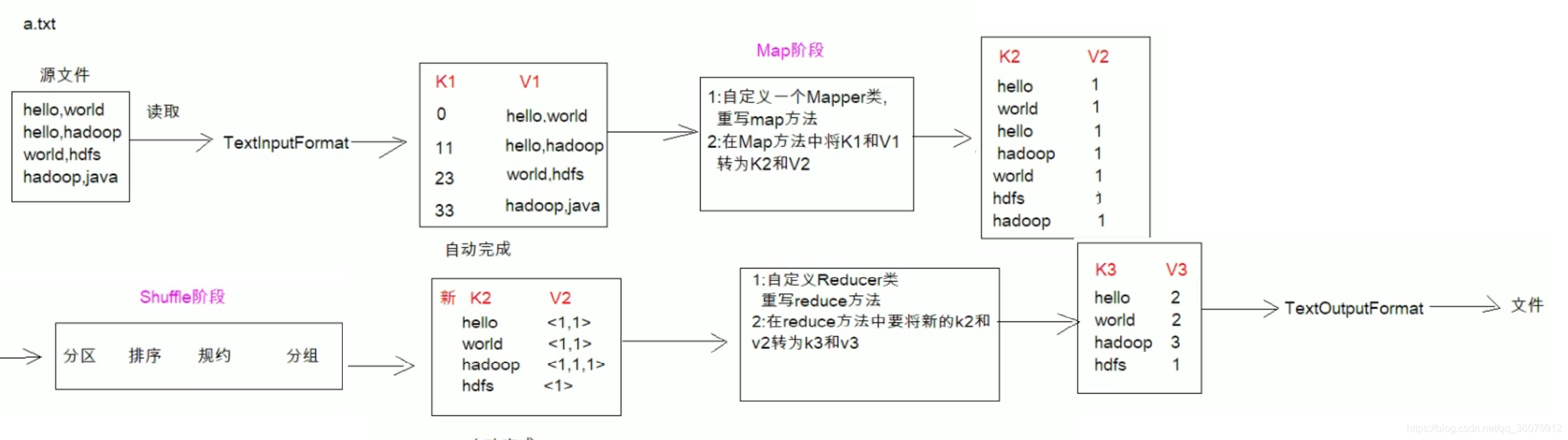
MapReduce 的开发一共有八个步骤, 其中 Map 阶段分为 2 个步骤,Shuffle 阶段 4个步骤,Reduce 阶段分为 2 个步骤
Map 阶段 2 个步骤
- 设置 InputFormat 类, 将数据切分为 Key-Value(K1和V1) 对, 输入到第二步
- 自定义 Map 逻辑, 将第一步的结果转换成另外的 Key-Value(K2和V2) 对, 输出结果
Shuffle 阶段 4 个步骤
- 对输出的 Key-Value 对进行分区
- 对不同分区的数据按照相同的 Key 排序
- (可选) 对分组过的数据初步规约, 降低数据的网络拷贝
- 对数据进行分组, 相同 Key 的 Value 放入一个集合中
Reduce 阶段 2 个步骤
- 对多个 Map 任务的结果进行排序以及合并, 编写 Reduce 函数实现自己的逻辑, 对输入的 Key-Value 进行处理, 转为新的 Key-Value(K3和V3)输出
- 设置 OutputFormat 处理并保存 Reduce 输出的 Key-Value 数据
3. WordCount案例实现与分析
需求: 在一堆给定的文本文件中统计输出每一个单词出现的总次数
Step 1. 数据格式准备
- 创建一个新的文件
cd /export/servers
vim wordcount.txt
- 向其中放入以下内容并保存
hello,world,hadoop
hive,sqoop,flume,hello
kitty,tom,jerry,world
hadoop
- 上传到 HDFS
hdfs dfs ‐mkdir /wordcount/
hdfs dfs ‐put wordcount.txt /wordcount/
Step 2. Mapper
/*
Mapper的泛型:
KEYIN: k1的类型 行偏移量 LongWritable
VALUEIN:v1的类型 一行的文本数据 Text
KEYOUT:k2的类型 每个单词 Text
VALUEOUT:V2的类型 固定值1 LongWritable
*/
public class WordCountMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable,Text,Text,LongWritable>{
/*
map方法是将k1和v1转为k2和v2
key : 是k1
value: 是 v1
context:表示MapReduce上下文对象
*/
/*
K1 V1
0 hello,world
11 hello,hadoop
---------------------------
K2 V2
hello 1
world 1
hadoop 1
*/
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
Text text = new Text();
//1:对每一行的数据进行字符串拆分
String line = value.toString();
String[] split = line.split(",");
//2:遍历数组,获取每一个单词
for (String word : split) { //word 1
text.set(word);
context.write(text,new LongWritable(1));
}
}
}
Step 3. Reducer
/*
KEYIN: k2 Text 每个单词
VALUEIN:v2 LongWritable 集合中泛型的类型
KEYOUT:k3 Text 每个单词
VALUEOUT:v3 LongWritable 每个单词出现的次数
*/
public class WordCountReducer extends Reducer<Text,LongWritable,Text,LongWritable>{
/*
reduce方法的作用是将K2和V2转为K3和V3
key :K2
values:集合
context:MapReduce的上下文对象
*/
/*
新 K2 V2
hello <1,1>
world <1,1>
hadoop <1,1,1>
-------------------
K3 V3
hello 2
world 2
hadoop 3
*/
@Override
protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<LongWritable> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
long count =0;
//1:遍历values集合
for (LongWritable value : values) {
//2:将集合中的值相加
count += value.get();
}
//3:将k3和v3写入上下文中
context.write(key, new LongWritable(count));
}
}
Step 4. 定义主类, 描述 Job 并提交 Job
public class JobMain extends Configured implements Tool{
@Override
public int run(String[] strings) throws Exception {
//创建一个任务对象
Job job = Job.getInstance(super.getConf(), "mapreduce_wordcount");
//打包放在集群运行时,需要做一个配置
job.setJarByClass(JobMain.class);
//第一步:设置读取文件的类: K1 和V1
job.setInputFormatClass(TextInputFormat.class);
TextInputFormat.addInputPath(job, new Path("hdfs://node01:8020/wordcount"));
//第二步:设置Mapper类
job.setMapperClass(WordCountMapper.class);
//设置Map阶段的输出类型: k2 和V2的类型
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(LongWritable.class);
//第三,四,五,六步采用默认方式(分区,排序,规约,分组)
// //设置我们的规约类
// job.setCombinerClass(MyCombiner.class);
//第七步 :设置文的Reducer类
job.setReducerClass(WordCountReducer.class);
//设置Reduce阶段的输出类型
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(LongWritable.class);
//设置Reduce的个数
//第八步:设置输出类
job.setOutputFormatClass(TextOutputFormat.class);
//设置输出的路径
TextOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path("hdfs://node01:8020/wordcount_out"));
boolean b = job.waitForCompletion(true);
return b?0:1;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
//启动一个任务
int run = ToolRunner.run(configuration, new JobMain(), args);
System.exit(run);
}
}
常见错误
如果遇到如下错误
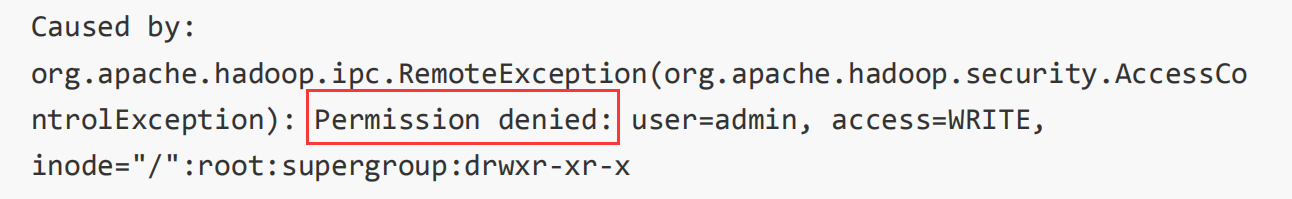
直接将hdfs-site.xml当中的权限关闭即可
<property>
<name>dfs.permissions</name>
<value>false</value>
</property>
最后重启一下 HDFS 集群
小细节
本地运行完成之后,就可以打成jar包放到服务器上面去运行了,实际工作当中,都是将
代码打成jar包,开发main方法作为程序的入口,然后放到集群上面去运行
4. MapReduce 运行模式
本地运行模式
- MapReduce 程序是被提交给 LocalJobRunner 在本地以单进程的形式运行
- 处理的数据及输出结果可以在本地文件系统, 也可以在hdfs上
- 怎样实现本地运行? 写一个程序, 不要带集群的配置文件, 本质是程序的 conf 中是否有 mapreduce.framework.name=local 以及
yarn.resourcemanager.hostname=local 参数 - 本地模式非常便于进行业务逻辑的 Debug , 只要在 Eclipse/idea 中打断点即可
集群运行模式
- 将 MapReduce 程序提交给 Yarn 集群, 分发到很多的节点上并发执行
- 处理的数据和输出结果应该位于 HDFS 文件系统
- 提交集群的实现步骤: 将程序打成JAR包,然后在集群的任意一个节点上用hadoop命令启动
hadoop jar hadoop_hdfs_operate‐1.0‐SNAPSHOT.jar cn.itcast.hdfs.demo1.JobMain
出现下边的这个就是成功了。
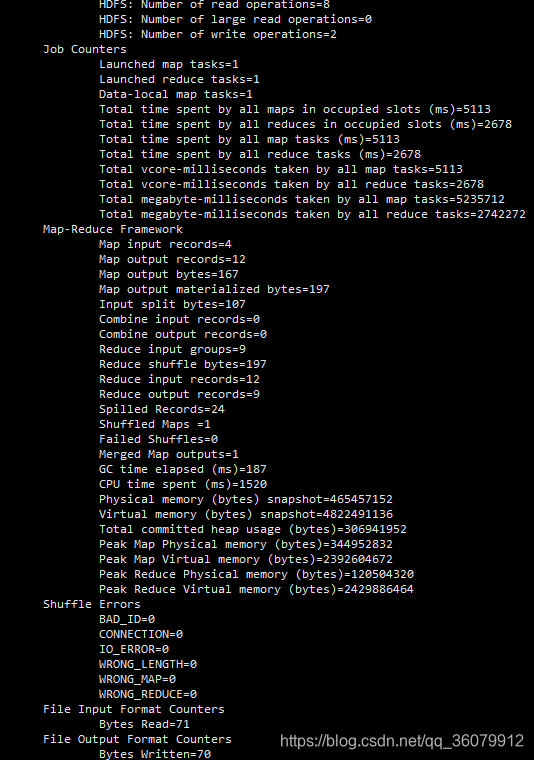
5. MapReduce 分区
在 MapReduce 中, 通过我们指定分区, 会将同一个分区的数据发送到同一个 Reduce 当中进行处理
例如: 为了数据的统计, 可以把一批类似的数据发送到同一个 Reduce 当中, 在同一个Reduce 当中统计相同类型的数据, 就可以实现类似的数据分区和统计等
其实就是相同类型的数据, 有共性的数据, 送到一起去处理
Reduce 当中默认的分区只有一个

Step 1. 定义 Mapper
这个 Mapper 程序不做任何逻辑, 也不对 Key-Value 做任何改变, 只是接收数据, 然后往下发送
public class MyMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable,Text,Text,NullWritable>
{
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
context.write(value,NullWritable.get());
}
}
Step 2. 定义 Reducer 逻辑
这个 Reducer 也不做任何处理, 将数据原封不动的输出即可
public class MyReducer extends Reducer<Text,NullWritable,Text,NullWritable> {
@Override
protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<NullWritable> values,Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
context.write(key,NullWritable.get());
}
}
Step 3. 自定义 Partitioner
主要的逻辑就在这里, 这也是这个案例的意义, 通过 Partitioner 将数据分发给不同的Reducer:
public class PartitonerOwn extends Partitioner<Text,LongWritable> {
@Override
public int getPartition(Text text, LongWritable longWritable, int i){
if(text.toString().length() >=5 ){
return 0;
} else {
return 1;
}
}
}
Step 4. Main 入口
public class PartitionMain extends Configured implements Tool {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
int run = ToolRunner.run(new Configuration(), new
PartitionMain(), args);
System.exit(run);
}
@Override
public int run(String[] args) throws Exception {
Job job = Job.getInstance(super.getConf(),
PartitionMain.class.getSimpleName());
job.setJarByClass(PartitionMain.class);
job.setInputFormatClass(TextInputFormat.class);
job.setOutputFormatClass(TextOutputFormat.class);
TextInputFormat.addInputPath(job,new
Path("hdfs://192.168.52.250:8020/partitioner"));
TextOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job,new
Path("hdfs://192.168.52.250:8020/outpartition"));
job.setMapperClass(MyMapper.class);
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class);
job.setReducerClass(MyReducer.class);
/**
* 设置我们的分区类,以及我们的reducetask的个数,注意reduceTask的个数
*一定要与我们的分区数保持一致
*/
job.setPartitionerClass(MyPartitioner.class);
job.setNumReduceTasks(2);
boolean b = job.waitForCompletion(true);
return b?0:1;
}
}
6. MapReduce 排序和序列化
- 序列化 (Serialization) 是指把结构化对象转化为字节流
- 反序列化 (Deserialization) 是序列化的逆过程. 把字节流转为结构化对象. 当要在进程间传递对象或持久化对象的时候, 就需要序列化对象成字节流, 反之当要将接收到或从磁盘读取的字节流转换为对象, 就要进行反序列化
- Java 的序列化 (Serializable) 是一个重量级序列化框架, 一个对象被序列化后, 会附带很多额外的信息 (各种校验信息, header, 继承体系等), 不便于在网络中高效传输. 所以, Hadoop 自己开发了一套序列化机制(Writable), 精简高效. 不用像 Java 对象类一样传输多层的父子关系, 需要哪个属性就传输哪个属性值, 大大的减少网络传输的开销
- Writable 是 Hadoop 的序列化格式, Hadoop 定义了这样一个 Writable 接口. 一个类要支持可序列化只需实现这个接口即可
- 另外 Writable 有一个子接口是 WritableComparable, WritableComparable 是既可实现序列化, 也可以对key进行比较, 我们这里可以通过自定义 Key 实现
WritableComparable 来实现我们的排序功能
数据格式如下

要求: - 第一列按照字典顺序进行排列
- 第一列相同的时候, 第二列按照升序进行排列
解决思路: - 将 Map 端输出的 <key,value> 中的 key 和 value 组合成一个新的 key(newKey),value值不变
- 这里就变成 <(key,value),value> , 在针对 newKey 排序的时候, 如果 key 相同, 就再对value进行排序
Step 1. 自定义类型和比较器
public class PairWritable implements WritableComparable<PairWritable> {
// 组合key,第一部分是我们第一列,第二部分是我们第二列
private String first;
private int second;
public PairWritable() {
}
public PairWritable(String first, int second) {
this.set(first, second);
}
/**
* 方便设置字段
*/
public void set(String first, int second) {
this.first = first;
this.second = second;
}
/**
* 反序列化
*/
@Override
public void readFields(DataInput input) throws IOException {
this.first = input.readUTF();
this.second = input.readInt();
}
/**
* 序列化
*/
@Override
public void write(DataOutput output) throws IOException {
output.writeUTF(first);
output.writeInt(second);
}
/*
* 重写比较器
*/
public int compareTo(PairWritable o) {
//每次比较都是调用该方法的对象与传递的参数进行比较,说白了就是第一行与第二行比较完了之后的结果与第三行比较,
//得出来的结果再去与第四行比较,依次类推
System.out.println(o.toString());
System.out.println(this.toString());
int comp = this.first.compareTo(o.first);
if (comp != 0) {
return comp;
} else { // 若第一个字段相等,则比较第二个字段
return Integer.valueOf(this.second).compareTo(
Integer.valueOf(o.getSecond()));
}
}
public int getSecond() {
return second;
}
public void setSecond(int second) {
this.second = second;
}
public String getFirst() {
return first;
}
public void setFirst(String first) {
this.first = first;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "PairWritable{" +
"first='" + first + '\'' +
", second=" + second +
'}';
}
}
Step 2. Mapper
public class SortMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable,Text,PairWritable,IntWritable> {
private PairWritable mapOutKey = new PairWritable();
private IntWritable mapOutValue = new IntWritable();
@Override
public void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String lineValue = value.toString();
String[] strs = lineValue.split("\t");
//设置组合key和value ==> <(key,value),value>
mapOutKey.set(strs[0], Integer.valueOf(strs[1]));
mapOutValue.set(Integer.valueOf(strs[1]));
context.write(mapOutKey, mapOutValue);
}
}
Step 3. Reducer
public class SortReducer extends Reducer<PairWritable,IntWritable,Text,IntWritable> {
private Text outPutKey = new Text();
@Override
public void reduce(PairWritable key, Iterable<IntWritable> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
//迭代输出
for(IntWritable value : values) {
outPutKey.set(key.getFirst());
context.write(outPutKey, value);
}
}
}
Step 4. Main 入口
public class SecondarySort extends Configured implements Tool {
@Override
public int run(String[] args) throws Exception {
Configuration conf = super.getConf();
conf.set("mapreduce.framework.name","local");
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf,
SecondarySort.class.getSimpleName());
job.setJarByClass(SecondarySort.class);
job.setInputFormatClass(TextInputFormat.class);
TextInputFormat.addInputPath(job,new Path("file:///L:\\大数据离线阶段备课教案以及资料文档——by老王\\4、大数据离线第四天\\排序\\input"));
TextOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job,new Path("file:///L:\\大数据离线阶段备课教案以及资料文档——by老王\\4、大数据离线第四天\\排序\\output"));
job.setMapperClass(SortMapper.class);
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(PairWritable.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);
job.setReducerClass(SortReducer.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);
boolean b = job.waitForCompletion(true);
return b?0:1;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Configuration entries = new Configuration();
ToolRunner.run(entries,new SecondarySort(),args);
}
}