Chapter 2 Project Operating Environment
⚫ What are business environmental factors (P-38) that are not controllable and must be complied with?
Enterprise Environmental Factors (EEFs)—Conditions beyond the control of the project team that will affect, limit, or dictate the project. These factors may increase or limit project management flexibility and may positively or negatively affect project outcomes.

⚫ What are Organizational Process Assets (P-39) for reference, updateable
Organizational Process Assets—Plans, processes, policies, procedures, and knowledge bases that are unique to and used by the performing organization and that affect the management of specific projects. Throughout the project, project team members can make necessary updates and additions to the organizational process assets.
⚫ It includes: 1. Artifacts, practices or knowledge; 2. Lessons learned and historical information; 3. Completed schedule, risk data and earned value data
Processes, Policies and Procedures: Guidelines and Standards, Templates, Vendor Checklist and Contractual Agreement Types, Change Control Procedures, Organizational Requirements for Communication...
Organizational knowledge base: configuration management knowledge base, financial database, metrics database, lessons learned knowledge base, archives of past projects...
⚫ Organizational structure (P-47)—The blue background is the project participating members
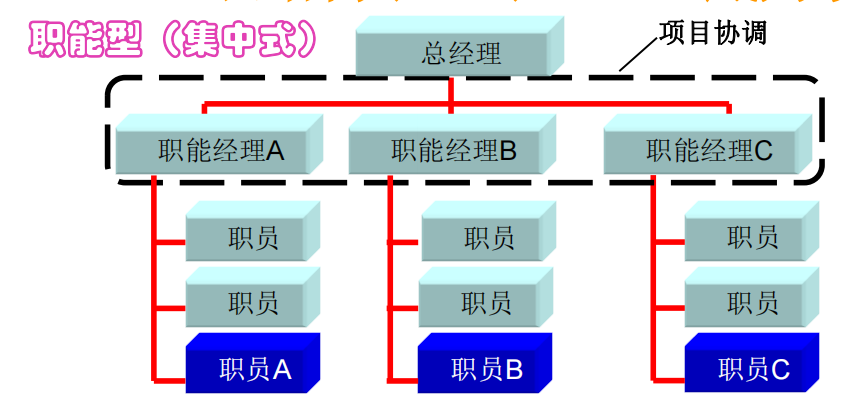
Features:
✓ Part-time Project Manager (Liaison)
✓ Power level: "little" or "none"
✓ Clear career paths and weak horizontal linkages
✓ Power level: "little" or "none"
✓ Clear career paths and weak horizontal linkages
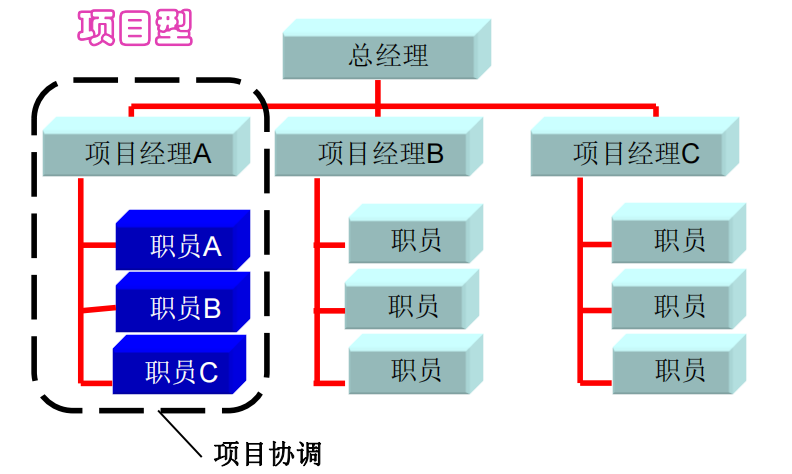
Features:
✓ Full-time project manager
✓ Power level: "large" or even "full"
✓ High degree of project manager control
✓ Duplicate configuration; homeless
⚫ Organizational structure (P-47)—The blue background is the project participating members

⚫ Organizational structure (P-47) ---- some other types
Organic or simple organization—an informal organization originally described by British theorists Tom Burns and George Stalker. An organic organization is a very flexible organization that adapts well to change. It is structured with little specialization of work, few layers of management, decentralized decision-making, and little oversight.
Virtual organization----a temporary organization that temporarily gathers people together to take advantage of specific opportunities and disbands after the goal is completed. virtual organization structure, also known as network organization
Multi-divisional organization (Multi-divisional) - a center, multiple departments or divisions, these divisions are semi-autonomous, and the center issues financial indicators to them. For example, departments are divided according to regions, each department has repeated functions and is not centralized.
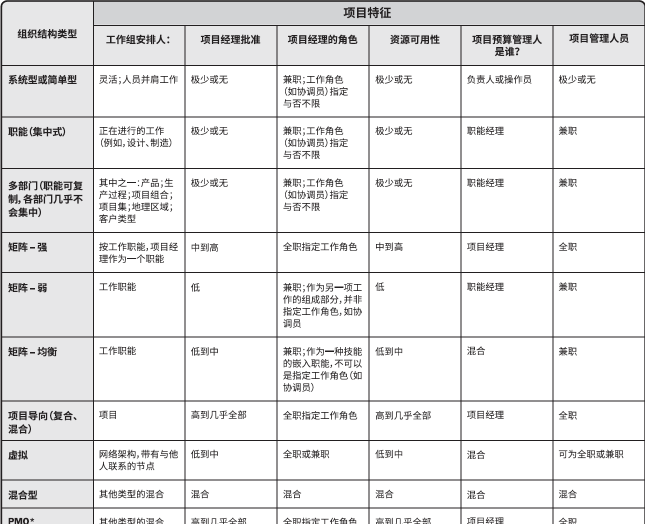
⚫ What is PMO—Project Management Office (P-48)
Project Management Office (PMO) - is an organizational structure that standardizes project-related governance processes and facilitates the sharing of resources, methodologies, tools, and techniques. The projects supported and managed by the PMO are not necessarily related to each other.
Types of PMO ("support finger"):
➢ Support type: support, is a consultant, a project resource bank, and has a low degree of control over the project.
➢ Controlling type: support + require obedience, and moderately control the project.
➢ Command type: direct management and control, with a high degree of control over the project.
⚫ How PMO supports project managers (P-49)
➢ Manage “shared resources”, identify and develop “best practices” and “standards” (administrative function)
➢ Supervise the degree of compliance with the "Standard" through the "Project Audit" (Supervisory function)
➢ Develop and manage policies, procedures, templates, provide guidance and training (directed training function)
➢ Coordinating "cross-project" communication (coordinating function)
Chapter 3 The Project Manager's Role
⚫ What is a project manager (P-52)
Project Manager - An individual appointed by the executing organization to lead a team to achieve project objectives
➢ Project manager: focus on the achievement of project goals
➢ Functional manager: focus on the management and supervision of a certain functional area or business unit
➢ Operations Manager: Focus on the efficiency of business operations
⚫ The project manager does not need to take on every role in the project, but should have project management knowledge, technical knowledge, understanding and relevant experience.
⚫ The project manager provides leadership, planning and coordination functions to the project team through communication. The project manager's communication is divided into real-time communication (meetings, oral communication, etc.) and non-real-time communication (written communication, document planning, etc.).
⚫ Project manager's scope of influence (P-52~P-56)
project
➢ Lead the project team to achieve project goals and expectations of stakeholders;
➢ use available resources to balance competing constraints;
➢ Serve as a communicator between project sponsors, team members and other interested parties, including providing guidance and demonstrating a vision for project success
organize
➢ Actively interact with other project managers;
➢ Act as a strong advocate, working with project sponsors on internal political and strategic issues;
➢ Improve their overall project management capabilities and skills within the organization
industry
➢ Always pay attention to the latest development trend of the industry;
➢ Consider whether this information is relevant or usable for current projects.
Discipline
➢ Continuous knowledge transfer and integration
cross field
➢ Instruct and educate other professionals on project management methods
➢ Serve as an informal advocacy ambassador Chapter 3 project manager role
⚫ Project Manager Competence (P-56)

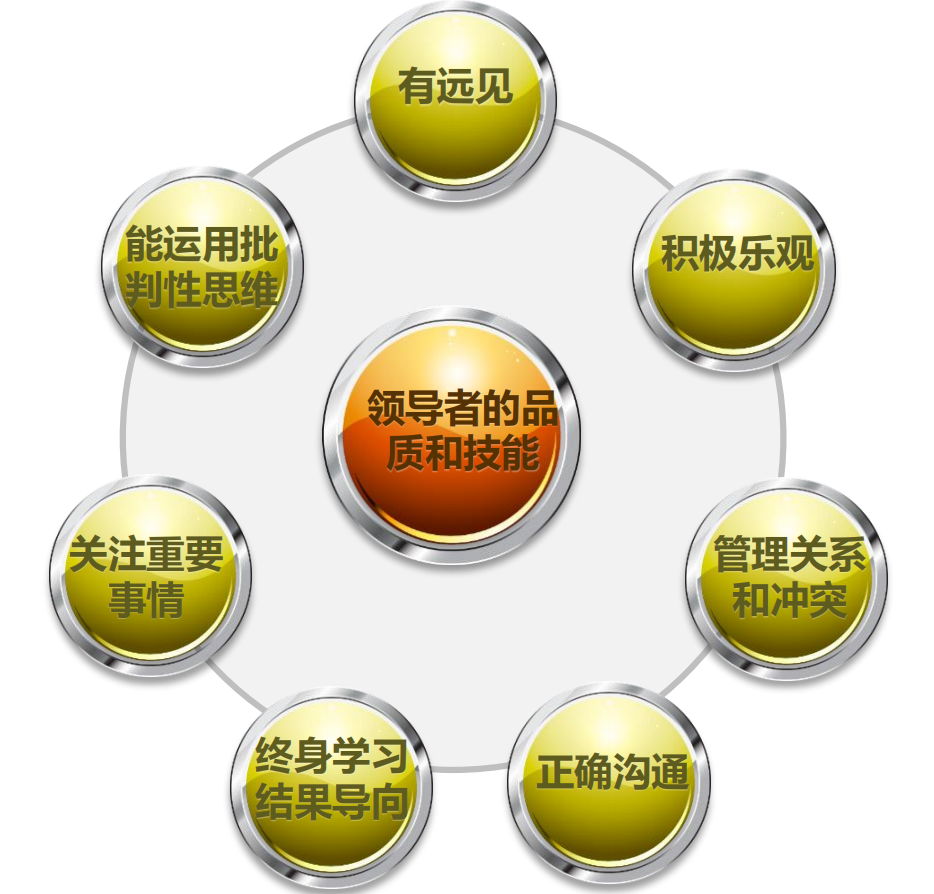
⚫ Leadership Skills----Qualities and Skills of Leaders (P-61)
⚫Leadership skills----Understanding several powers of project managers (Power) (P-63)

⚫Leadership skills--understand several leadership styles of project managers (P-65)

⚫ Perform Integration (P-66)
-
The dual role of the project manager in integration
-
Work with sponsors to understand strategic objectives and ensure project goals and outcomes are aligned with portfolio, program, and business areas
-
Responsible for directing the team to focus on what really matters and work together
Three Levels of Integration Occur
-
process level
-
Cognitive level
-
background level
Differences and typical examples of enterprise environmental factors and organizational process assets
The power of the project manager in each organizational structure, the matrix type is used by default in the exam to coordinate cross-departmental projects
Three types of PMO: Supportive, Controlling, and Directive
Definition of project manager
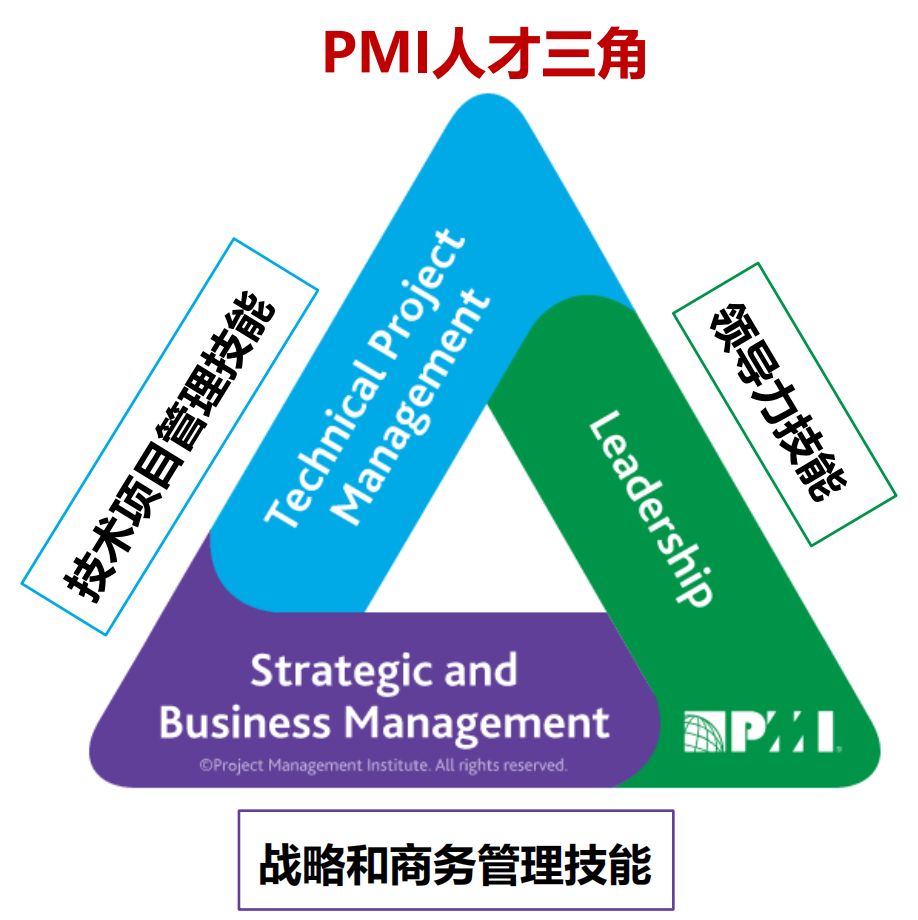
PMI Talent Triangle
Several Powers and Several Leadership Styles of Project Managers
Notes for each chapter [1-13 chapters] Private message me to share with you for free