Purpose:
• Understand how routing protocols work;
• Master how to configure the RIP routing protocol on the router.
Rip protocol introduction:
RIP (Routing Information Protocol, Routing Information Protocol) is an interior gateway protocol (IGP), which is a dynamic routing protocol used for the transmission of routing information within an autonomous system (AS). The RIP protocol is based on the distance vector algorithm (Bellham-Ford) (DistanceVectorAlgorithms), using "hops" (ie metric) to measure the routing distance to the destination address
RIP uses request and response packets to exchange information.
(1) When the router starts, the RIP protocol sends a request message on the interface, waits for the request and response of the adjacent router, and responds, and uses the distance vector algorithm to update the route when the response is received.
(2) The router sends a response periodically, and regularly notifies the local routing information to the neighboring routers.
(3) When the routing information of a router changes, it will actively send a response to the neighbor router (using trigger update).
Each router will maintain a routing table. Each item in the routing table is the distance from itself to other routers. The distance is the number of hops. Every time a router passes through, the number of hops is increased by 1. RIP stipulates that a route can store up to 15 routers, so the distance (metric) can only be within 0-16, and 16 means that the infinite length is unreachable, so RIP is only suitable for small networks, and OSPF is mostly used in large networks.
A router will only exchange its own routing table with neighboring routers, and the routing table usually includes: destination network, distance, and next-hop router. They will be exchanged every 30s, and then judge whether to update their own routing table according to the received routing table. If the exchange information is not received within 180s, then it is determined that the adjacent router is unreachable, and it is listed in the routing table. Set the distance to 16.
After n times of routing table exchange, each router knows the shortest distance and next hop to any router in the current AS. This process is called convergence.
Three timers:
Update timer: The router will send update information every 30s. In order to prevent all routers from sending at the same time, an offset of 5s is added, and the value is between [25, 35].
过期定时器:在180s没有收到该路由项的任何信息,就将其设为不可达。
刷新定时器:一条记录失效后不会立即删除,而是等待指定时间后删除。
收到其他路由器发来的RIP报文后,执行以下步骤:
若路由表中没有对应的目的网络表项,就直接将此表项填入到路由表中。
将所有路由项都先加一,若路由表中存在对应的目的网络表项,同时下一跳相同,直接将路由表中的更新(网络可能会改变,应该使用最新的)。下一跳不相同,就会和路由器中的距离进行比较,若大于路由表中的则不做处理,若小于就执行更新。
若180s还没有收到邻居路由器的路由表,就将这个邻居路由表的距离设为16,不可达。
每隔30s就会循环这个步骤。若使用触发更新,既当跳数发送变化时,路由器就会发送response更新信息,这样可以加快收敛速度。
实验拓扑图及配置:

实验拓扑图如上所示,有两个PC和三个路由器组成。路由器的两个网段是10.1.1.0和20.2.2.0。
两个PC的基础配置如下:


第一个的ip为192.168.1.1 第二个的ip为192.168.2.1。
接下来进行rip的配置。对于第一个路由器,我们把10.0.0.0加进network,还有PC的的网段192.168.1.0.具体如下:

这里我们把做端地址设置为子网掩码,右端地址因为有两个口,所以两个地址就够了这里我们设置为10.1.1.1 30.
同理我们进行第二个路由器设置:

这里不同的是加入network的是10.0.0.0和20.0.0.0。其余地址设置仿照第一个路由器的设置进行。
同理第三个路由器:
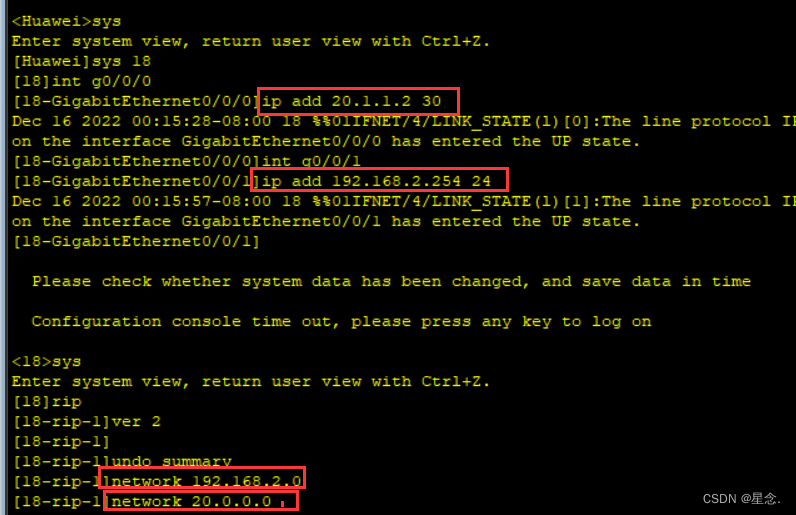
第三个路由器连接另一台电脑和第二个路由器,所以network加入的是192.168.2.0和20.0.0.0两个网段。
以上配置完成,我们进行查看路由表,以第三个路由器为例:

这里明显可以看到 当目的地址是192.168.1.0网段的时候有两跳,使用的是rip协议,当访问的是10.1.1.0/30网段的时候,有一条.
接下来进行ping 操作。结果如下:
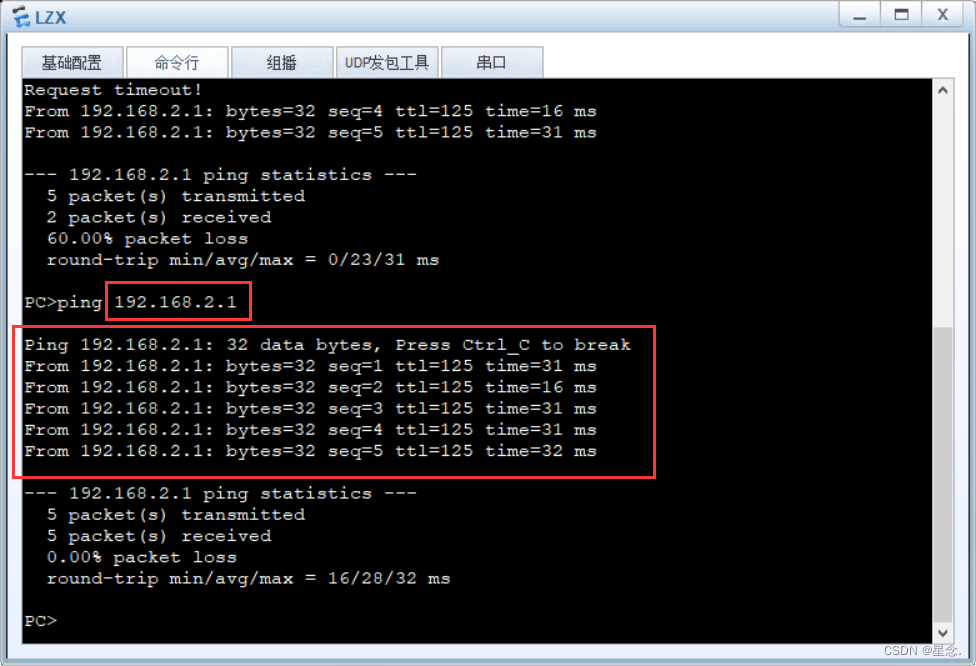
这里可以看到实验成功。
抓包分析:
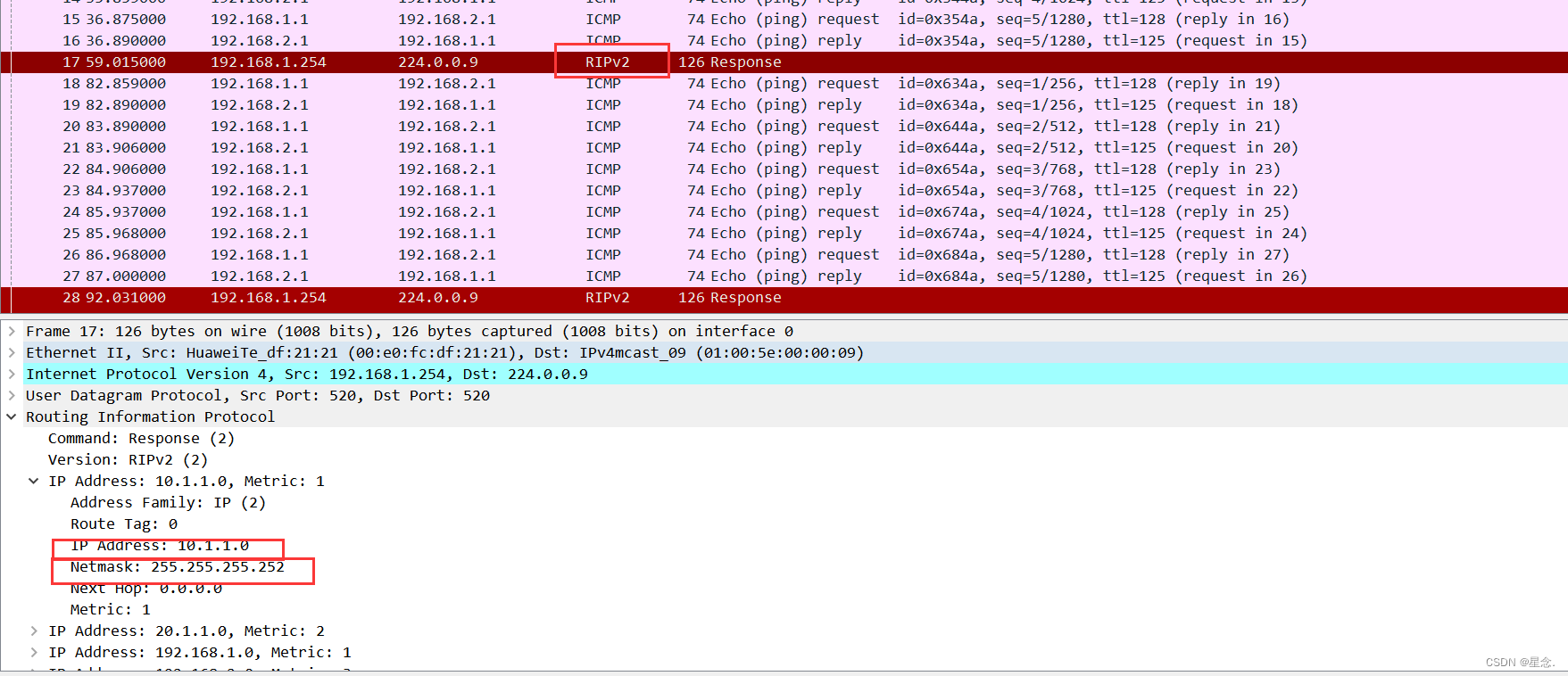
Here you can see that the rip protocol is used when accessing. The experiment was successful!