Article Directory
1. Basic overview
1.1 Protocol type
RIP is a distance vector routing protocol, which belongs to the IGP protocol.
1.2 Scope of application
The RIP protocol is suitable for small and medium-sized networks, and has two types: RIPv1 and RIPv2.
1.3 Port
Use UDP to exchange routing information, the port number is 520.
2. Features
RIP supports split horizon, poison reversal and trigger update.
2.1 Split horizon
Performing split horizon can organize the occurrence of routing loops.
The routing information learned from an interface is no longer sent out from this interface, and the link bandwidth resources occupied by the routing update information can also be reduced.
2.2 Trigger update
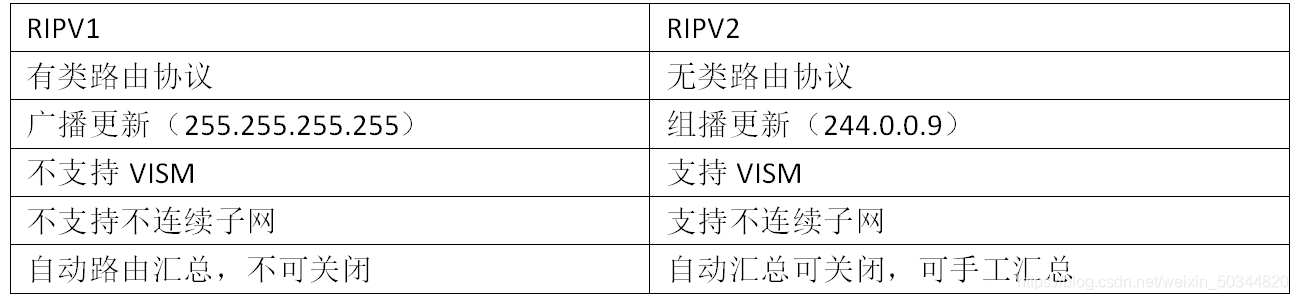
RIPv1 supports broadcast update, the update address is 255.255.255.255
RIPv2 supports multicast update, the update address is 224.0.0.9
3. Comparison of RIPv1 and RIPv2
Four, supplement
4.1 Main class network
The network number obtained by multiplying the IP under the interface and its default subnet mask is called the main network.
4.2 Automatic summary across the main network boundary
If the major network numbers of two adjacent network segments are the same, RIPv1 will not automatically summarize;
if the major network numbers of two adjacent network segments are different, RIPv1 will automatically summarize.