Input Subsystem 底层框架浅析
一、绑定 input_dev 和 input_handler
当我们创建一个input_dev其描述一个输入设备的时候,我们需要把这个输入设备通过接口进行注册,会调用 input_register_device 接口:
int input_register_device(struct input_dev *dev)
{
// 忽略,自己看去,就是那么任性
list_add_tail(&dev->node, &input_dev_list);
list_for_each_entry(handler, &input_handler_list, node)
input_attach_handler(dev, handler);
.................
}
input_register_device做的事情是把input_dev放到input_dev_list的链表尾,然后对input_handler_list进行遍历,
如果对应的input_handler先加入input_handler_list链表,则调用input_attach_handler,
如果是input_dev先加入input_handler_list链表,不用担心,input_register_handler(input_handler)接口也会对input_dev_list进行遍历,同样调用input_attach_handler。
那我们来看看input_register_handler做了什么:
int input_register_handler(struct input_handler *handler)
{
// 给个机会你自己去看
list_add_tail(&handler->node, &input_handler_list);
list_for_each_entry(dev, &input_dev_list, node)
input_attach_handler(dev, handler);
......................
}
把input_handler加入input_attach_handler链表,然后遍历input_dev_list链表,也就是说这个跟平台设备驱动框架一样,各自瞄瞄对方,看来会有激情发生。
// kernel/drivers/input/evdev.c
static const struct input_device_id evdev_ids[] = {
{ .driver_info = 1 }, /* Matches all devices */
{ }, /* Terminating zero entry */
};
static struct input_handler evdev_handler = {
........
.connect = evdev_connect, // 具体实现往下拉吧,不拉你会晕
........
.id_table = evdev_ids,
};
static int __init evdev_init(void)
{
return input_register_handler(&evdev_handler);
}
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// kernel/drivers/input/joydev.c
static struct input_handler joydev_handler = {
........
.match = joydev_match,
.connect = joydev_connect,
........
.id_table = joydev_ids,
};
static int __init joydev_init(void)
{
return input_register_handler(&joydev_handler);
}
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
//kernel/drivers/input/mousedev.c
static struct input_handler mousedev_handler = {
........
.connect = mousedev_connect,
........
.id_table = mousedev_ids,
};
static int __init mousedev_init(void)
{
........
error = input_register_handler(&mousedev_handler);
........
}
看看他们的id_table
// kernel/drivers/input/evdev.c
static const struct input_device_id evdev_ids[] = {
{ .driver_info = 1 }, /* Matches all devices */
{ }, /* Terminating zero entry */
};
// kernel/drivers/input/joydev.c
static const struct input_device_id joydev_ids[] = {
{
.flags = INPUT_DEVICE_ID_MATCH_EVBIT | INPUT_DEVICE_ID_MATCH_ABSBIT,
.evbit = { BIT_MASK(EV_ABS) },
.absbit = { BIT_MASK(ABS_X) },
},
// 太多了,省略省略再省略
{ } /* Terminating entry */
};
接下来看下 input_attach_handler 的内容:
static int input_attach_handler(struct input_dev *dev, struct input_handler *handler)
{
........
id = input_match_device(handler, dev);
if (!id)
return -ENODEV;
error = handler->connect(handler, dev, id);
........
}
看下 input_match_device 函数
static const struct input_device_id *input_match_device(struct input_handler *handler, struct input_dev *dev)
{
const struct input_device_id *id;
for (id = handler->id_table; id->flags || id->driver_info; id++) {
if (id->flags & INPUT_DEVICE_ID_MATCH_BUS)
if (id->bustype != dev->id.bustype)
continue;
if (id->flags & INPUT_DEVICE_ID_MATCH_VENDOR)
if (id->vendor != dev->id.vendor)
continue;
if (id->flags & INPUT_DEVICE_ID_MATCH_PRODUCT)
if (id->product != dev->id.product)
continue;
if (id->flags & INPUT_DEVICE_ID_MATCH_VERSION)
if (id->version != dev->id.version)
continue;
........
if (!handler->match || handler->match(handler, dev))
return id;
}
return NULL;
}
id_table 内容 如下:
static const struct input_device_id evdev_ids[] = {
{ .driver_info = 1 }, /* Matches all devices */
{ }, /* Terminating zero entry */
};
因此对于joydev和mousedev,会根据id成员包括总线类型(bustype),厂家(vendor),产品(product),版本(version)等来决定是否匹配成功。
匹配成功后,input_attach_handler 会调用 connect ,所传参数为 input_dev 、 input_handler、及 input_handler对应的 id.
static struct input_handler evdev_handler = {
...........................
.connect= evdev_connect,
...........................
};
因此调用到了kernel/drivers/input/evdev.c的evdev_connect函数:
static const struct file_operations evdev_fops= {
.....................
.read = evdev_read,
.write = evdev_write,
.poll = evdev_poll,
.open = evdev_open,
.....................
.fasync = evdev_fasync,
.flush = evdev_flush,
.llseek = no_llseek,
};
static int evdev_connect(struct input_handler *handler, struct input_dev *dev, const struct input_device_id *id)
{
// 忽略各种装逼代码
.....................
dev_set_name(&evdev->dev, "event%d", dev_no);
.....................
cdev_init(&evdev->cdev, &evdev_fops);
cdev_add(&evdev->cdev, evdev->dev.devt, 1);
device_add(&evdev->dev);
}
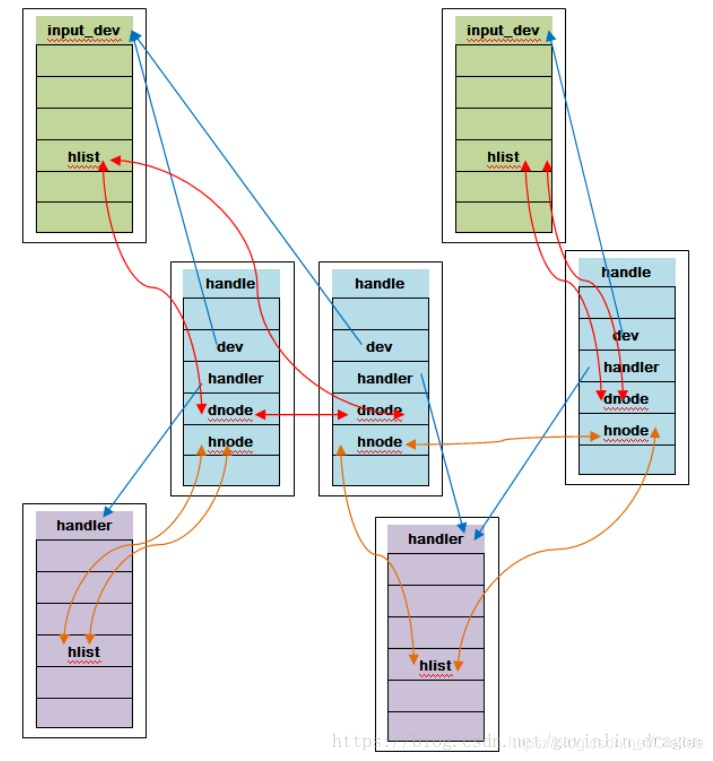
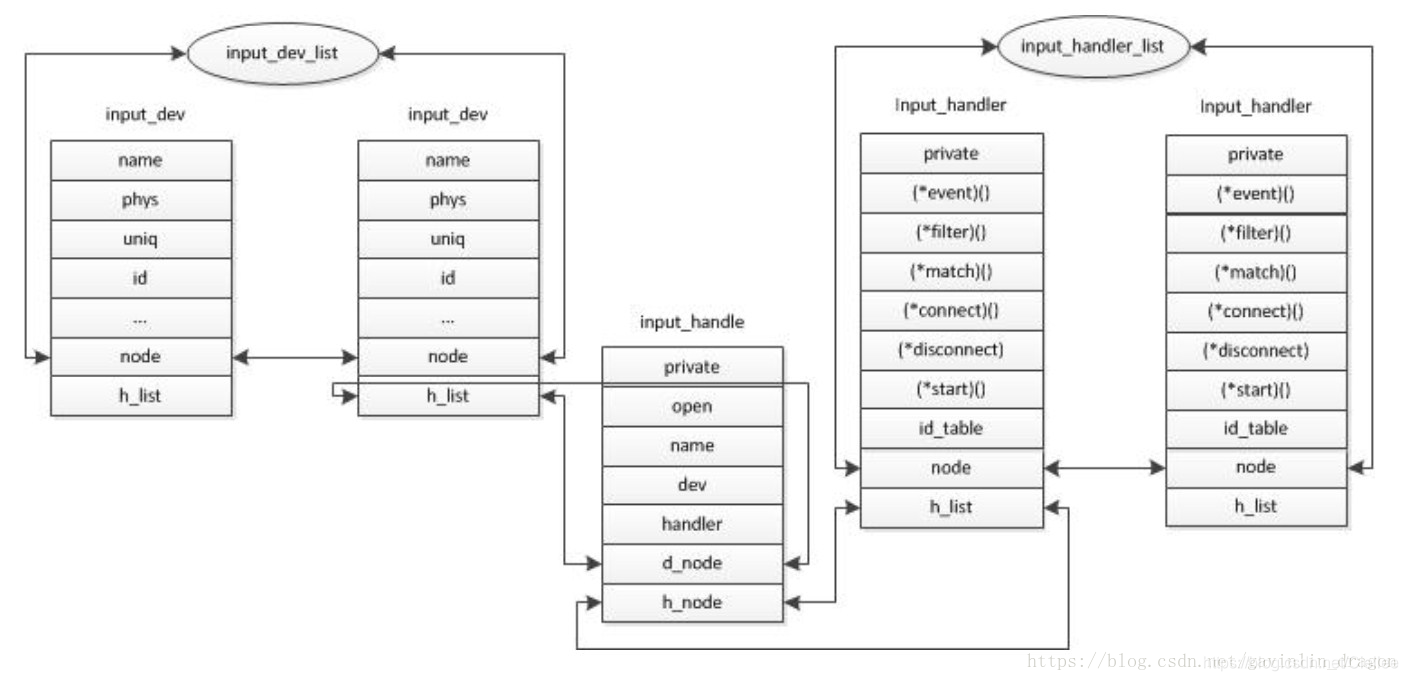
input_dev, input_handler和input_handle之间的关系:
再看evdev_connect函数
static int evdev_connect(struct input_handler *handler, struct input_dev *dev, const struct input_device_id *id)
{
.....................
evdev->handle.dev = input_get_device(dev);
evdev->handle.name = dev_name(&evdev->dev);
evdev->handle.handler = handler;
evdev->handle.private = evdev;
.....................
input_register_handle(&evdev->handle);
.....................
}
可以看到,input_dev 被赋值给 evdev->handle.dev,而 input_handler 被赋值给 evdev->handle.handler = handler,
那 input_register_handle 又做了啥呢?
int input_register_handle(struct input_handle *handle)
{
struct input_handler *handler = handle->handler;
struct input_dev *dev = handle->dev;
.....................
if (handler->filter)
list_add_rcu(&handle->d_node, &dev->h_list);
else
list_add_tail_rcu(&handle->d_node, &dev->h_list); // 把handle的d_node插入input_dev的h_list的尾部
.....................
list_add_tail_rcu(&handle->h_node, &handler->h_list); // 把handle的h_node插入input_handler的h_list的尾部
if (handler->start)
handler->start(handle);
}
原来 input_register_handler 的目的是通过 input_handle 把input_dev 和 input_handler 贯穿起来。
每个dev或handler匹配后都会对应一个handle,所以其实对于input_dev与input_handler是一个多对多的关系,一个dev可以对应多个handler,一个handler也可以对应多个dev。
我们在驱动里上报的接口有如下几种:
static inline void input_report_key(struct input_dev *dev, unsigned int code, int value)
static inline void input_report_rel(struct input_dev *dev, unsigned int code, int value)
static inline void input_report_abs(struct input_dev *dev, unsigned int code, int value)
static inline void input_report_ff_status(struct input_dev *dev, unsigned int code, int value)
static inline void input_report_switch(struct input_dev *dev, unsigned int code, int value)
static inline void input_sync(struct input_dev *dev)
而且他们都是调用共同的接口:
input_event(struct input_dev *dev, unsigned int type, unsigned int code, int value)
在 input_event 函数中:
void input_event(struct input_dev *dev, unsigned int type, unsigned int code, int value)
{
...............
input_handle_event(dev, type, code, value);
...............
}
static void input_handle_event(struct input_dev *dev, unsigned int type, unsigned int code, int value)
{
...............
disposition = input_get_disposition(dev, type, code, &value);
if (disposition & INPUT_PASS_TO_HANDLERS) {
struct input_value *v;
if (disposition & INPUT_SLOT) { // 如果使用B协议
v = &dev->vals[dev->num_vals++]; // dev->vals地址赋给v,直接把driver上报的数据封装到dev->vals
v->type = EV_ABS;
v->code = ABS_MT_SLOT;
v->value = dev->mt->slot;
}
v = &dev->vals[dev->num_vals++];
v->type = type;
v->code = code;
v->value = value;
}
input_pass_values(dev, dev->vals, dev->num_vals);
...............
}
在传给 input_pass_values 之前,我们把驱运输传过来的上报数据封装成 struct input_value 结构体,而且 num_vals 会累加,那么就知道了我们现在总共传了多少数据。
input.h里定义的input_value值如下:
// kernel/include/linux/input.h
struct input_value {
__u16 type;
__u16 code;
__s32 value;
};
static void input_pass_values(struct input_dev *dev, struct input_value *vals, unsigned int count)
{
...............
handle = rcu_dereference(dev->grab);
if (handle) {
count = input_to_handler(handle, vals, count);
} else {
list_for_each_entry_rcu(handle, &dev->h_list, d_node)
if (handle->open)
count = input_to_handler(handle, vals, count);
}
...............
}
怎么需要进这么多道门,其实已经到了关键地方,
我们通过操作grab获取handle,前面分析了那么多,把input_handle,input_dev和input_handler联系起来,终于用上场了,
我们通过dev找到了对应的handle,也就找到了对应的handler,然后我们把handle传给input_to_handler:
static unsigned int input_to_handler(struct input_handle *handle, struct input_value *vals, unsigned int count)
{
struct input_handler *handler = handle->handler;
...............
if (handler->events)
handler->events(handle, vals, count);
else if (handler->event)
for (v = vals; v != end; v++)
handler->event(handle, v->type, v->code, v->value);
...............
}
这里的handler就是evdev.c里面的evdev_handler,如果handler->events存在则调用evdev_events,如果不存在但是handler->event存在,则调用evdev_event:
static struct input_handler evdev_handler = {
.event = evdev_event,
.events = evdev_events,
......................
};
// kernel/drivers/input/evdev.c
static void evdev_events(struct input_handle *handle, const struct input_value *vals, unsigned int count)
{
struct evdev *evdev = handle->private;
struct evdev_client *client;
.........................
client = rcu_dereference(evdev->grab);
if (client)
evdev_pass_values(client, vals, count, time_mono, time_real);
else
list_for_each_entry_rcu(client, &evdev->client_list, node)
evdev_pass_values(client, vals, count, time_mono, time_real);
.........................
}
static void evdev_pass_values(struct evdev_client *client, const struct input_value *vals, unsigned int count, ktime_t mono, ktime_t real)
{
struct evdev *evdev = client->evdev;
struct input_event event;
.......................
for (v = vals; v != vals + count; v++) {
// count是从input_handle_event传下来的,目的是为了计算现在是第几次传的数据,
// v != vals + count就是针对这次传数据定的条件,避免漏了数据
event.type = v->type;
event.code = v->code;
event.value = v->value;
__pass_event(client, &event);
if (v->type == EV_SYN && v->code == SYN_REPORT)
wakeup = true;
}
.......................
}
我们从input_handle_event传下来的的input_value数据赋给event,然后通过__pass_event(client, &event);传给client的buffer。
static void __pass_event(struct evdev_client *client, const struct input_event *event)
{
client->buffer[client->head++] = *event;
client->head &= client->bufsize - 1;
.......................
if (event->type == && event->code == SYN_REPORT) {
client->packet_head = client->head;
.......................
kill_fasync(&client->fasync, SIGIO, POLL_IN);
}
}
__pass_event 作用是把我们要传的event数据传给client->buffer,而client就是代表这个输入设备,
后面判断传下来的type是EV_SYN 并且code 是SYN_REPORT,也就是调用了input_sync(input_dev)这个接口。
我们可以看看input_sync接口,它是一个内联函数:
static inline void input_sync(struct input_dev *dev)
{
input_event(dev, EV_SYN, SYN_REPORT, 0);
}
判断到需要sync后会通过异步通知 kill_fasync 的方式通知native层。
evdev_events里 client = rcu_dereference(evdev->grab);,这个是怎么来的,
其实需要追究到我们native层的eventhub.cpp中对我们所有的/dev/input/eventx进行的open操作,当
open的时候,最终通过fops调用到evdev_open:
static int evdev_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file)
{
struct evdev *evdev = container_of(inode->i_cdev, struct evdev, cdev);
struct evdev_client *client;
............
client = kzalloc(size, GFP_KERNEL | __GFP_NOWARN);
............
client->evdev = evdev;
evdev_attach_client(evdev, client);
............
file->private_data = client;
............
}
等等,我只看到创建client,并把client放到file->private_data作为私有数据,但是看不到evdev 究竟是从哪里来的,这个我们要追溯到evdev_connect,看看做了什么事情:
static int evdev_connect(struct input_handler *handler, struct input_dev *dev, const struct input_device_id *id)
{
struct evdev *evdev;
........
evdev = kzalloc(sizeof(struct evdev), GFP_KERNEL);
........
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&evdev->client_list);
.........
evdev->exist = true;
.........
evdev->handle.private = evdev;
evdev->dev.devt = MKDEV(INPUT_MAJOR, minor);
evdev->dev.class = &input_class;
evdev->dev.parent = &dev->dev;
evdev->dev.release = evdev_free;
device_initialize(&evdev->dev)
cdev_init(&evdev->cdev, &evdev_fops);
cdev_add(&evdev->cdev, evdev->dev.devt, 1);
.........
}
在evdev_connect已经把evdev给创建好,并初始化好evdev->client_list,而且创建好字符设备,
因此open该字符设备的时候通过 container_of(inode->i_cdev, struct evdev, cdev); 可以获取evdev。
在evdev_open创建client后,通过调用 evdev_attach_client(evdev, client);把client插入到client_list链表尾,证明这个设备已经打开了:
static void evdev_attach_client(struct evdev *evdev,struct evdev_client *client)
{
.........
list_add_tail_rcu(&client->node, &evdev->client_list);
.........
}
eventhub在确定open成功后会进行read操作,而read操作会调用:
static ssize_t evdev_read(struct file *file, char __user *buffer, size_t count, loff_t *ppos)
{
struct evdev_client *client = file->private_data;
struct evdev *evdev = client->evdev;
struct input_event event;
........
for (;;) {
while (read + input_event_size() <= count && evdev_fetch_next_event(client, &event)) {
if (input_event_to_user(buffer + read, &event))
return -EFAULT;
read += input_event_size();
}
........
}
........
}
client是从 evdev_open后把新建的client赋给 file->private_data作为私有数据,
而evdev则存在client->evdev里,因此所有想要的数据都可以获得,
而且前面有说过,我们上报的数据被封装成input_vals后直接传给client->buffer,因此我们可以从client->buffer里获取数据,获取数据后通过input_event_to_user(buffer + read, &event)往eventhub里传,下面是实现把client里的数据传给event:
static int evdev_fetch_next_event(struct evdev_client *client, struct input_event *event)
{
int have_event;
........
have_event = client->packet_head != client->tail;
if (have_event) {
*event = client->buffer[client->tail++];
client->tail &= client->bufsize - 1;
........
}
........
return have_event;
}
到这里为止,我们上报数据完成,等到我们调用input_sync()接口后,
会调用 __pass_event的kill_fasync(&client->fasync, SIGIO, POLL_IN);,
eventhub收到异步信号后会进行对应的同步,具体过程需要input子系统native层的分析。
————————————————
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/gavinlin_dragon/article/details/80603206
