Java不同数据存储类型使用不同遍历方法效率研究
GitHub代码仓库
数据存储类型
- ArrayList
- HashSet
- HashMap
- LinkedList
遍历方法
- 传统遍历方法
for(int i=0;i<list.size();i++) {
String str = list.get(i);
...
}
- 内置迭代器
for (String str : list) {
...
}
- 显式迭代器
Iterator<String> it = list.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()) {
String str = it.next();
...
}
测试代码模板
- 使用大小为 的数组,遍历 边,平均遍历速度定义为
private static ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
private final static int N = 1000000, M = 1000;
private final static String STR = "abcdefg";
- 首先建立一个固定数组,供给3个遍历方法使用
@BeforeClass
public static void CreateList() {
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
list.add(STR);
}
}
使用JUnit测试单元记录时间
- 传统遍历方法For
@Test
public void FOR() {
for (int k = 0; k < M; k++) {
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
String str = list.get(i);
}
}
}
- 内置迭代器
@Test
public void Inner_Iteration() {
for (int k = 0; k < M; k++) {
for (String str : list) {
String s = str;
}
}
}
- 显式迭代器
@Test
public void Explicit_Iteration() {
for (int k = 0; k < M; k++) {
Iterator<String> it = list.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
String str = it.next();
}
}
}
根据不同的存储类型进行更改
eg. HashMap 要设置key和value
Python数据可视化
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
%matplotlib inline
- 以ArrayList代码为例
- 柱状图
f, ax= plt.subplots()
ArrayList = pd.read_csv("../csv/ArrayList.csv")
sns.barplot(data=ArrayList)
ax.set_title("ArrayList")
- 折线图
f, ax= plt.subplots()
sns.lineplot(data=ArrayList)
ax.set_title("ArrayList")
plt.ylim(0.5, 1.0)
ArrayList
- 整体来说,在ArrayList中for的遍历速度最快,内置迭代器和显式迭代器相当
- 并且ArrayList迭代非常稳定,尤其是for
| Explicit_Iteration | FOR | Inner_Iteration |
|---|---|---|
| 0.775 | 0.585 | 0.757 |
| 0.785 | 0.577 | 0.748 |
| 0.783 | 0.581 | 0.769 |
| 0.775 | 0.583 | 0.77 |
| 0.778 | 0.602 | 0.788 |
| 0.784 | 0.586 | 0.767 |
| 0.775 | 0.581 | 0.807 |
| 0.814 | 0.587 | 0.766 |
| 0.786 | 0.604 | 0.839 |
| 0.815 | 0.593 | 0.775 |


HashMap
- 在HashMap中不能使用For,内置迭代器略优
| Explicit_Iteration | Inner_Iteration |
|---|---|
| 0.608 | 0.507 |
| 0.622 | 0.613 |
| 0.585 | 0.485 |
| 0.587 | 0.533 |
| 0.639 | 0.526 |
| 0.593 | 0.555 |
| 0.534 | 0.431 |
| 0.581 | 0.504 |
| 0.598 | 0.481 |
| 0.64 | 0.504 |


HashSet
- 在HashSet中同样不能使用for, 基本相同,内置迭代器较不稳定
| Explicit_Iteration | Inner_Iteration |
|---|---|
| 2.5 | 2.517 |
| 2.532 | 2.477 |
| 2.684 | 2.523 |
| 2.697 | 3.303 |
| 2.631 | 2.515 |
| 2.956 | 3.016 |
| 3.281 | 3.051 |
| 3.074 | 2.95 |
| 3.206 | 2.935 |
| 2.89 | 2.887 |


LinkedList
- 注:在链表中可以使用for,但是根据一定的测试,随着数据规模增加,运行时间呈指数型增长,与另两种遍历方法不在一个数量级上,所以不加入统计。
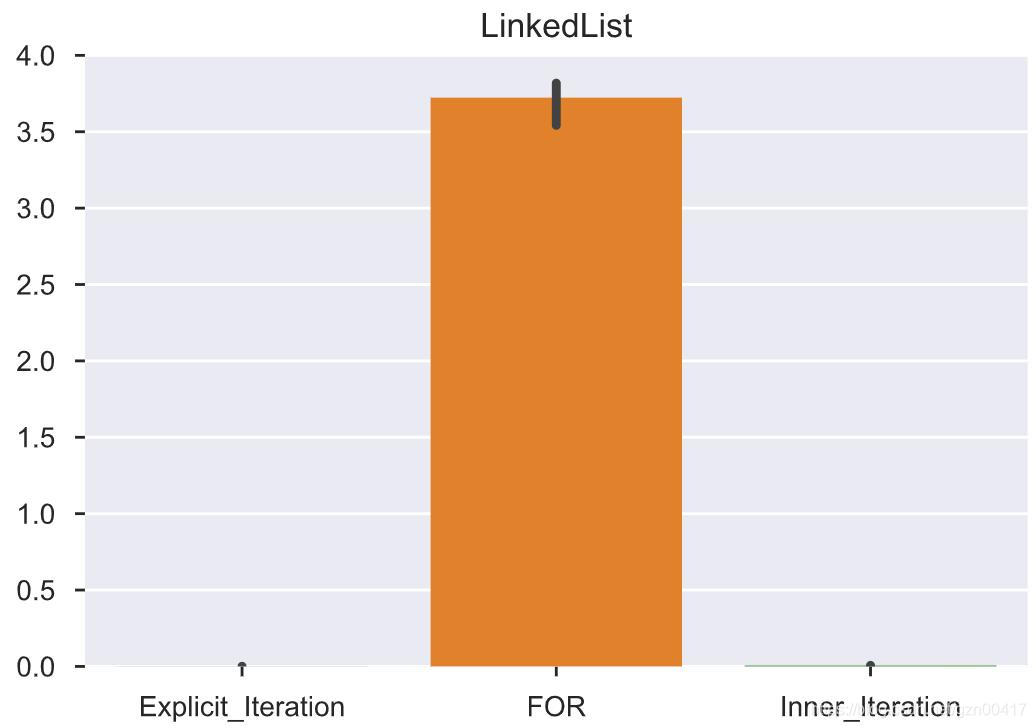
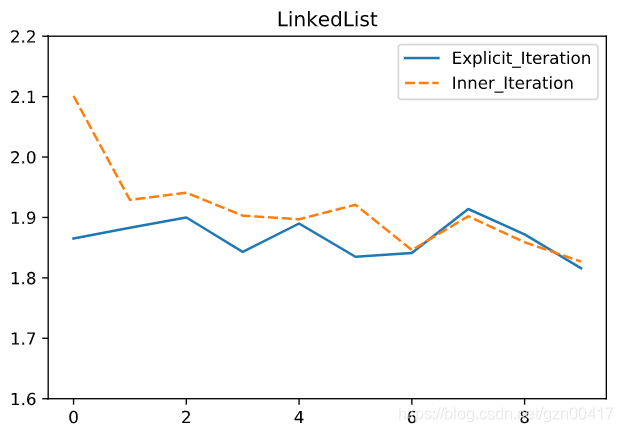
- 在LinkedList中,内置迭代器和显式迭代器效率相当,多个单次试验观察来说显式迭代器略优
| Explicit_Iteration | Inner_Iteration |
|---|---|
| 1.865 | 2.101 |
| 1.883 | 1.929 |
| 1.9 | 1.941 |
| 1.843 | 1.903 |
| 1.89 | 1.897 |
| 1.835 | 1.921 |
| 1.841 | 1.846 |
| 1.914 | 1.902 |
| 1.872 | 1.859 |
| 1.816 | 1.827 |

数据处理和数据清洗
- 将4中存储类型的数据整合起来
- 将数据统一到同样的数据尺度
Base = 0
ArrayList /= 10**(Base-8)
ArrayList['Type'] = 'ArrayList' # 8
HashMap /= 10**(Base-7)
HashMap['Type'] = 'HashMap' # 7
HashSet /= 10**(Base-8)
HashSet['Type'] = 'HashSet' # 8
LinkedList /= 10**(Base-8)
LinkedList['Type'] = 'LinkedList' # 8
- 由于不同数据类型效率差异较大
- 作者选择通过取对数 的方法
- 然后取相反数(时间越少,效率越高)
- 这使数据数量级接近,能容易可视化
data = pd.concat([ArrayList, HashMap, HashSet, LinkedList], ignore_index=True).drop(['FOR'], axis=1)
data[['Explicit_Iteration', 'Inner_Iteration']] = np.log10(data[['Explicit_Iteration', 'Inner_Iteration']])
整体可视化对比
- 将内置迭代器、显式迭代器分别处理后数据对比
- 下图的数据表示效率相对值的数量级
f, ax= plt.subplots()
sns.barplot(x='Type', y='Inner_Iteration', data=data)
ax.set_title("Inner_Iteration")

f, ax= plt.subplots()
sns.barplot(x='Type', y='Explicit_Iteration', data=data)
ax.set_title("Explicit_Iteration")

分析
本质:数组、集合、字典、链表,4种数据结构的差异在遍历方式上的体现
ArrayList
- ArrayList本质上是一个动态数组,数组对于大量随机访问有着高效的响应速度
- 迭代器在ArrayList这种不依赖
__iter__、__next__方法的对象,在使用迭代器时的访存速度远不如有序访存的FOR - 由于数组线性存储,导致ArrayList增加和删除操作效率较低
- 因此ArrayList适用于不定长、不频繁增删的数据存储
HashMap
- Java种的Map主要分为HashMap和TreeMap,属于非Collection接口
- Map需要有键key和值value,内部元素无序,因此无法用For访问
- 使用迭代器时,由于键值的唯一性,单个元素查找速度似乎较快
- 但迭代对象时键值的集合,
keySet()的迭代需要占用时间 - 而且键值是无序的,一定程度上,不满足良好局部性的要求
HashSet
- HashSet继承了Collection种的Set
- HashSet调用了
HashMap.put()方法,将值直接作为键 - 所以HashSet在访问时一定优于HashMap,因为Set不需要对Keys的迭代
- 事实证明,HashSet确实远优于HashMap,但从实用性角度来说却不如HashMap
LinkedList
- LinkedList本质上是一个双向链表
- 链表的特点就是容易增加和删除,但随机访问单个元素效率很低
总结
- 不同的4种数据存储类型中3种迭代方式效率不同
- 内置迭代器和显式迭代器效率相当,for在ArrayList中效率较高、LinkedList很差
- HashSet的迭代效率较高,HashMap迭代效率较低
- 单从迭代器迭代速度来说:HashSet > LinkedList > ArrayList > HashMap
- 总体评价:
- ArrayList:少增删,求稳定
- HashMap:字典功能,效率低
- HashSet:大数据非数字随机元素查找极快
- LinkedList:增删高速,严禁用for
