- 姓名:林顺达
- 学号:201821121022
- 班级:计算1811
1. 实验环境介绍
- 操作系统:Ubuntu 18.04.3 LTS
- 平台:双操作系统(Win10+Ubuntu18.04)
2. 常用命令使用(部分)
- 进入特权模式 sudo
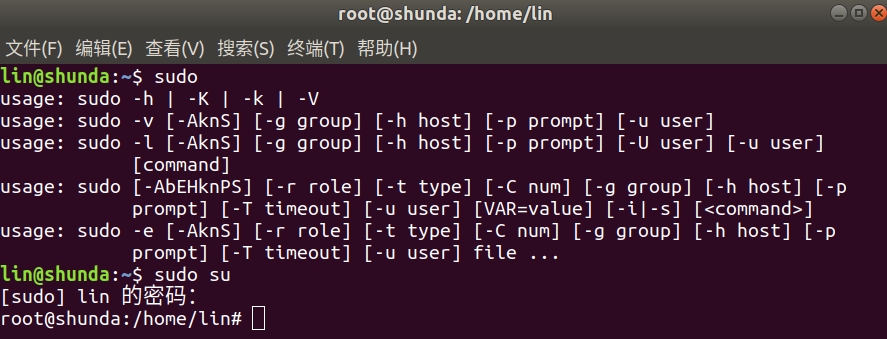
- 更改目录cd/查看目录下文件明细ls/打开目录文件
3. 剖析ps命令
- 运行
man ps,将ps使用方法拷贝过来
NAME ps - report a snapshot of the current processes. SYNOPSIS ps [options] DESCRIPTION ps displays information about a selection of the active processes.
If you want a repetitive update of the selection and the displayed information, use top(1) instead.
执行ps -ef,系统的返回结果(仅部分):
UID PID PPID C STIME TTY TIME CMD root 1 0 0 12:42 ? 00:00:18 /sbin/init splash root 2 0 0 12:42 ? 00:00:00 [kthreadd] root 3 2 0 12:42 ? 00:00:00 [rcu_gp] root 4 2 0 12:42 ? 00:00:00 [rcu_par_gp] root 6 2 0 12:42 ? 00:00:00 [kworker/0:0H-kb] root 9 2 0 12:42 ? 00:00:00 [mm_percpu_wq] root 10 2 0 12:42 ? 00:00:00 [ksoftirqd/0] root 11 2 0 12:42 ? 00:00:08 [rcu_sched] root 12 2 0 12:42 ? 00:00:00 [migration/0] root 13 2 0 12:42 ? 00:00:00 [idle_inject/0] root 14 2 0 12:42 ? 00:00:00 [cpuhp/0] root 15 2 0 12:42 ? 00:00:00 [cpuhp/1] root 16 2 0 12:42 ? 00:00:00 [idle_inject/1] root 17 2 0 12:42 ? 00:00:00 [migration/1] root 18 2 0 12:42 ? 00:00:00 [ksoftirqd/1] root 20 2 0 12:42 ? 00:00:00 [kworker/1:0H-kb]
- 命令 ps -ef 解释
整体作用:查看进程信息
-e:表示列出全部的进程
-f:显示全部的列
- 解释返回结果每个字段的含义
UID:该进程执行的用户ID
PID:进程ID
PPID:该进程的父级进程ID
C:CPU占用率,单位:%
STIME:进程的启动时间
TTY:终端的次要装置号码 (minor device number of tty)
扫描二维码关注公众号,回复:
9577689 查看本文章


TIME:进程的执行时间
CMD:进程的名称或对应的路径
- 执行
ps -aux,系统的返回结果(仅部分)
USER PID %CPU %MEM VSZ RSS TTY STAT START TIME COMMAND root 1 0.2 0.1 225740 9668 ? Ss 12:42 0:20 /sbin/init spla root 2 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 12:42 0:00 [kthreadd] root 3 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? I< 12:42 0:00 [rcu_gp] root 4 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? I< 12:42 0:00 [rcu_par_gp] root 6 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? I< 12:42 0:00 [kworker/0:0H-k root 9 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? I< 12:42 0:00 [mm_percpu_wq] root 10 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 12:42 0:00 [ksoftirqd/0] root 11 0.1 0.0 0 0 ? I 12:42 0:09 [rcu_sched] root 12 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 12:42 0:00 [migration/0] root 13 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 12:42 0:00 [idle_inject/0] root 14 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 12:42 0:00 [cpuhp/0] root 15 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 12:42 0:00 [cpuhp/1] root 16 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 12:42 0:00 [idle_inject/1] root 17 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 12:42 0:00 [migration/1] root 18 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 12:42 0:00 [ksoftirqd/1] root 20 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? I< 12:42 0:00 [kworker/1:0H-k root 21 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 12:42 0:00 [cpuhp/2] root 22 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 12:42 0:00 [idle_inject/2] root 23 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 12:42 0:00 [migration/2] root 24 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 12:42 0:00 [ksoftirqd/2] root 26 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? I< 12:42 0:00 [kworker/2:0H-k root 27 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 12:42 0:00 [cpuhp/3] root 28 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 12:42 0:00 [idle_inject/3] root 29 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 12:42 0:00 [migration/3] root 30 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 12:42 0:00 [ksoftirqd/3]
- 命令 ps -aux 解释
整体作用:查看进程信息
a:显示现行终端机下的所有程序,包括其他用户的程序
u:以用户为主的格式来显示程序状况
x:显示所有程序,不以终端机来区分
- 解释返回结果每个字段的含义
USER: 进程拥有者
PID:进程ID
%CPU:占用的 CPU 使用率
%MEM:占用的记忆体使用率
VSZ:占用的虚拟记忆体大小
RSS:占用的记忆体大小
TTY:终端的次要装置号码 (minor device number of tty)
STAT:该行程的状态,linux的进程有5种状态:
– D 不可中断 uninterruptible sleep (usually IO)
– R 运行 runnable (on run queue)
– S 中断 sleeping
– T 停止 traced or stopped
– Z 僵死 a defunct (”zombie”) process–注: 其它状态还包括W(无驻留页), <(高优先级进程), N(低优内存锁页)
START:行程开始时间
TIME:执行的时间
COMMAND:所执行的指令
4. 通过该实验产生新的疑问及解答
- 疑问: 如何使用命令查找文件
- 解答:使用 sudo -name "*file*" ('file'替换成文件名)
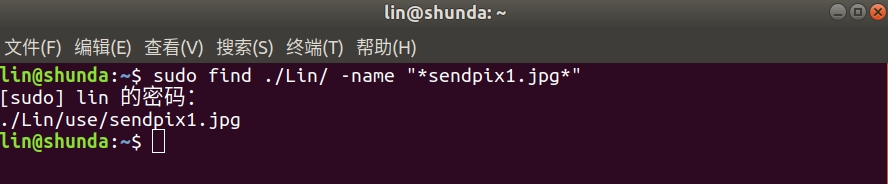
- 实践:查找一张图片
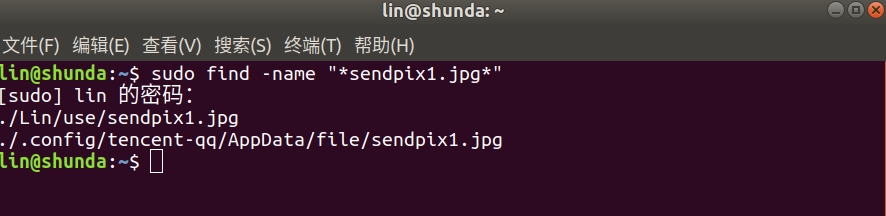
查找全部范围:(查询到两个同名但存储位置不同的文件)
查找指定范围:(此时只查询到制定目录下唯一文件)