0. 字节流与二进制文件
我的代码
package javalearning;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class Student {
private int id;
private String name;
private int age;
private double grade;
public Student(){
}
public Student(int id, String name, int age, double grade) {
this.id = id;
this.setName(name);
this.setAge(age);
this.setGrade(grade);
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
if (name.length()>10){
throw new IllegalArgumentException("name's length should <=10 "+name.length());
}
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
if (age<=0){
throw new IllegalArgumentException("age should >0 "+age);
}
this.age = age;
}
public double getGrade() {
return grade;
}
public void setGrade(double grade) {
if (grade<0 || grade >100){
throw new IllegalArgumentException("grade should be in [0,100] "+grade);
}
this.grade = grade;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ", age=" + age + ", grade=" + grade + "]";
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String fileName="d:\\testStream\\0\\student.data";
try(DataOutputStream dos=new DataOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(fileName)))
{
Student stu1=new Student(1,"zhang",13,80);
dos.writeInt(stu1.getId());
dos.writeUTF(stu1.getName());
dos.writeInt(stu1.getAge());
dos.writeDouble(stu1.getGrade());
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
try(DataInputStream dis=new DataInputStream(new FileInputStream(fileName)))
{
int id=dis.readInt();
String name=dis.readUTF();
int age=dis.readInt();
double grade=dis.readDouble();
Student stu=new Student(id,name,age,grade);
System.out.println(stu);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}我的总结
一、 使用DataOutputStream与FileOutputStream将Student对象写入二进制文件student.data
- 二进制文件与文本文件的区别
- 二进制文件可以存储int/double/char..等基本数据类型,文本文件只能存储char型变量。因此文本文件在读取或存储过程中常需要用到类型转换(类似parseInt)
2.try...catch...finally注意事项
- catch多个异常时要注意异常写的先后顺序,总体来说越大的(父类)异常要放越后面。可以直接使用eclipse的提示功能直接自己生成异常,方便又不会出错。
3.使用try..with...resouces关闭资源
- 是jdk8新的语法,可以直接在try(........)的括号中定义最后要关闭的资源,在运行结束后会自动关闭,不需要传统地在finally中关闭资源。用法详见上面代码块。
1. 字符流与文本文件
我的代码
任务1
String fileName="d:\\testStream\\1\\Students.txt";
List<Student> studentList = new ArrayList<>();
try(
FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream(fileName);
InputStreamReader isr=new InputStreamReader(fis, "UTF-8");
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(isr))
{
String line=null;
while((line=br.readLine())!=null)
{
String[] msg=line.split("\\s+");
int id=Integer.parseInt(msg[0]);
String name=msg[1];
int age=Integer.parseInt(msg[2]);
double grade=Double.parseDouble(msg[3]);
Student stu=new Student(id,name,age,grade);
studentList.add(stu);
}
}
catch (FileNotFoundException e)
{
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
catch (IOException e)
{
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(studentList);任务2
public static List<Student> readStudents(String fileName)
{
List<Student> studentList = new ArrayList<>();
try(
FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream(fileName);
InputStreamReader isr=new InputStreamReader(fis, "UTF-8");
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(isr))
{
String line=null;
while((line=br.readLine())!=null)
{
String[] msg=line.split("\\s+");
int id=Integer.parseInt(msg[0]);
String name=msg[1];
int age=Integer.parseInt(msg[2]);
double grade=Double.parseDouble(msg[3]);
Student stu=new Student(id,name,age,grade);
studentList.add(stu);
}
}
catch (FileNotFoundException e)
{
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
catch (IOException e)
{
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
return studentList;
}
任务3
String fileName="d:\\testStream\\1\\Students.txt";
try(
FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream(fileName,true);
OutputStreamWriter osw=new OutputStreamWriter(fos,"UTF-8");
PrintWriter pw=new PrintWriter(osw))
{
pw.println();
pw.print("4 一一 13 80");
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}任务4
String fileName1="d:\\testStream\\1\\Students.dat";
try(
FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream(fileName1);
ObjectOutputStream oos=new ObjectOutputStream(fos))
{
Student ts=new Student(5,"asd",14,60);
oos.writeObject(ts);
}
catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
try(
FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream(fileName1);
ObjectInputStream ois=new ObjectInputStream(fis))
{
Student newStudent =(Student)ois.readObject();
System.out.println(newStudent);
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}我的总结
- 在任务1、2、3中,程序生成的txt文件是指定的UTF-8编码。后续如果人为地通过系统自带的文本文档打开Students.txt并进行保存,该文本会变成UTF-8-BOM编码。这样程序再次运行时就会报错,因为指定的UTF-8跟文件实际上的UTF-8-BOM是不一样的,这个问题困扰了我一段时间,目前我的解决方法是两个:不人为保存,或者需要人为保存时用notepad++。
- 任务3中一开始PrintWriter会直接覆盖原文件,通过查阅资料,在构造FileOutputStream时多传一个true就可以了。
- 任务4中,一开始是让对象流写在txt中,后面发现会发生乱码。通过查阅资料知道writeObject()的作用是让实例以文件的形式保存在磁盘上,而这个文件是用二进制的形式写的,所以就让对象流的处理文件是bat格式,就没错了。
2.缓冲流
我的代码
package javalearning;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String fileName="d:\\testStream\\2\\test.txt";
try (PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(fileName);)
{
Random random=new Random();
random.setSeed(100);
double sum=0,aver;
for (int i = 0; i < 1000_0000; i++) {
int r=random.nextInt(10);
sum+=r;
pw.println(r);
}
aver=sum/1000_0000;
System.out.format("%.5f", aver);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
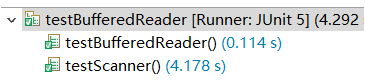
}JUNIT测试部分
package javalearning;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
class testBufferedReader {
String fileName="d:\\testStream\\2\\test.txt";
@Test
void testScanner() {
try ( FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(fileName);
Scanner sc=new Scanner(fis))
{
while(sc.hasNextInt())
{
sc.nextInt();
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e1) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e1.printStackTrace();
}finally
{
System.out.println("sc end");
}
}
@Test
void testBufferedReader() {
try ( FileReader fr = new FileReader(fileName);
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(fr))
{
String line=null;
while((line=br.readLine())!=null)
{
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e1) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e1.printStackTrace();
}finally
{
System.out.println("br end");
}
}
}
我的总结
- 生成随机数平时用的少,每次需要用时都得先找点资料,要尽量记住常见的用法。
- 在将随机数写入文件时,如果用的是print而不是println,文本大小会是println的三分一(1000_0000字节和3000_0000字节),原因暂时不理解,没有写回车的话junit跑出来的结果Scanner和BufferedReader的时间是差不多的,而写了回车时间差距就很大。
- JUNIT中要测试的方法前要加上@Test