为什么需要互斥量
在多任务操作系统中,同时运行的多个任务可能都需要使用同一种资源。这个过程有点类似于,公司部门里,我在使用着打印机打印东西的同时(还没有打印完),别人刚好也在此刻使用打印机打印东西,如果不做任何处理的话,打印出来的东西肯定是错乱的。
#include <iostream> // std::cout
#include <thread> // std::thread, std::this_thread::sleep_for
using namespace std;
// 打印机
void printer(const char *str)
{
while(*str != '\0')
{
cout << *str;
str++;
this_thread::sleep_for (chrono::seconds(1));
}
cout << endl;
}
// 线程一
void func1()
{
const char *str = "hello";
printer(str);
}
// 线程二
void func2()
{
const char *str = "world";
printer(str);
}
int main(void)
{
thread t1(func1);
thread t2(func2);
t1.join();
t2.join();
return 0;
}
运行结果如下:

独占互斥量std::mutex
互斥量的基本接口很相似,一般用法是通过lock()方法来阻塞线程,直到获得互斥量的所有权为止。在线程获得互斥量并完成任务之后,就必须使用unlock()来解除对互斥量的占用,lock()和unlock()必须成对出现。try_lock()尝试锁定互斥量,如果成功则返回true, 如果失败则返回false,它是非阻塞的。
#include <iostream> // std::cout
#include <thread> // std::thread, std::this_thread::sleep_for
#include <mutex> // std::mutex
using namespace std;
mutex g_lock; //全局互斥锁对象,#include <mutex>
// 打印机
void printer(const char *str)
{
g_lock.lock(); //上锁
while (*str != '\0')
{
cout << *str;
str++;
this_thread::sleep_for(chrono::seconds(1));
}
cout << endl;
g_lock.unlock(); //解锁
}
// 线程一
void func1()
{
const char *str = "hello";
printer(str);
}
// 线程二
void func2()
{
const char *str = "world";
printer(str);
}
int main(void)
{
thread t1(func1);
thread t2(func2);
t1.join();
t2.join();
return 0;
}
运行结果如下:

使用std::lock_guard可以简化lock/unlock的写法,同时也更安全,因为lock_guard在构造时会自动锁定互斥量,而在退出作用域后进行析构时就会自动解锁,从而避免忘了unlock操作。(看自己喜欢那一种,效果都是一样的)
#include <iostream> // std::cout
#include <thread> // std::thread, std::this_thread::sleep_for
#include <mutex> // std::mutex
using namespace std;
mutex g_lock; //全局互斥锁对象,#include <mutex>
// 打印机
void printer(const char *str)
{
lock_guard<std::mutex> locker(g_lock);
while(*str != '\0')
{
cout << *str;
str++;
this_thread::sleep_for (chrono::seconds(1));
}
cout << endl;
}
// 线程一
void func1()
{
const char *str = "hello";
printer(str);
}
// 线程二
void func2()
{
const char *str = "world";
printer(str);
}
int main(void)
{
thread t1(func1);
thread t2(func2);
t1.join();
t2.join();
return 0;
}
运行效果跟上面的一样:

原子操作
所谓的原子操作,取的就是“原子是最小的、不可分割的最小个体”的意义,它表示在多个线程访问同一个全局资源的时候,能够确保所有其他的线程都不在同一时间内访问相同的资源。也就是他确保了在同一时刻只有唯一的线程对这个资源进行访问。这有点类似互斥对象对共享资源的访问的保护,但是原子操作更加接近底层,因而效率更高。
#include <iostream> // std::cout
#include <thread> // std::thread, std::this_thread::sleep_for
using namespace std;
//全局的结果数据
long total = 0;
//点击函数
void func()
{
for(int i = 0; i < 1000000; ++i)
{
// 对全局数据进行无锁访问
total += 1;
}
}
int main()
{
clock_t start = clock(); // 计时开始
//线程
thread t1(func);
thread t2(func);
t1.join();
t2.join();
clock_t end = clock(); // 计时结束
cout << "total = " << total << endl;
cout << "time = " << end-start << " ms\n";
return 0;
}
注意:此接口在windows平台测试,如果在linux平台测试,时间需要除以1000。
运行结果如下:
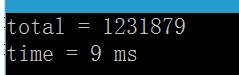
由于线程间对数据的竞争而导致每次运行的结果都不一样。因此,为了防止数据竞争问题,我们需要对total进行原子操作。
通过互斥锁进行原子操作:
#include <iostream> // std::cout
#include <thread> // std::thread, std::this_thread::sleep_for
#include <mutex>
using namespace std;
//全局的结果数据
long total = 0;
mutex g_lock;
//点击函数
void func()
{
for(int i = 0; i < 1000000; ++i)
{
g_lock.lock(); //加锁
total += 1;
g_lock.unlock(); //解锁
}
}
int main()
{
clock_t start = clock(); // 计时开始
//线程
thread t1(func);
thread t2(func);
t1.join();
t2.join();
clock_t end = clock(); // 计时结束
cout << "total = " << total << endl;
cout << "time = " << end-start << " ms\n";
return 0;
}
每次运行的结果都一样,只是耗时长点:
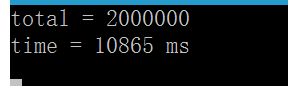
在新标准C++11,引入了原子操作的概念。如果我们在多个线程中对这些类型的共享资源进行操作,编译器将保证这些操作都是原子性的,也就是说,确保任意时刻只有一个线程对这个资源进行访问,编译器将保证多个线程访问这个共享资源的正确性。从而避免了锁的使用,提高了效率。
#include <iostream> // std::cout
#include <thread> // std::thread, std::this_thread::sleep_for
#include <mutex>
#include <atomic>
using namespace std;
//原子数据类型
atomic<long> total = { 0 }; //需要头文件 #include <atomic>
//点击函数
void func()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 1000000; ++i)
{
total += 1;
}
}
int main()
{
clock_t start = clock(); // 计时开始
//线程
thread t1(func);
thread t2(func);
t1.join();
t2.join();
clock_t end = clock(); // 计时结束
cout << "total = " << total << endl;
cout << "time = " << end - start << " ms\n";
return 0;
}
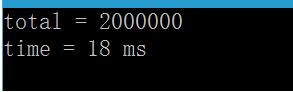
原子操作的实现跟普通数据类型类似,但是它能够在保证结果正确的前提下,提供比mutex等锁机制更好的性能。
