python opencv 人脸识别
人脸识别个人理解就是分几个步骤,1 找素材,让程序学习得到不同人的不同人脸特点,2,传入图片开始识别
这里先展示一下文件目录
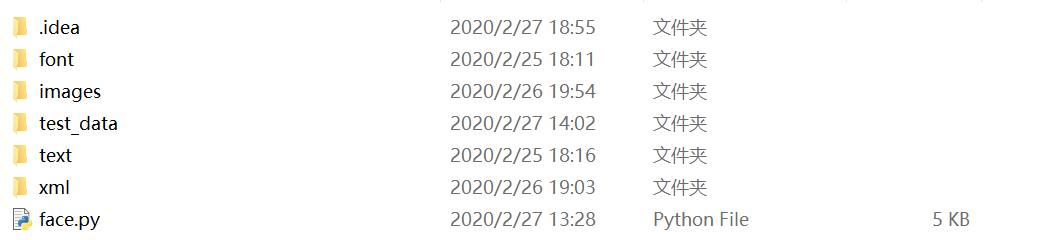
test_data是测试人脸的图片,images里有两个文件夹,每一个文件夹对应着一个人,里面都是那个人的人脸图像

使用opencv开发人脸识别,首先下载对应的包
pip install opencv-python
pip install opencv-contrib-python
然后开始上代码
# # -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import cv2
import os
import numpy as np
# 检测人脸
def detect_face(img):
# 将测试图像转换为灰度图像,因为opencv人脸检测器需要灰度图像
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# 加载OpenCV人脸检测分类器Haar
face_cascade = cv2.CascadeClassifier('./xml/haarcascade_frontalface_default.xml')
# 检测多尺度图像,返回值是一张脸部区域信息的列表(x,y,宽,高)
face = face_cascade.detectMultiScale(gray, scaleFactor=1.2, minNeighbors=5)
# 如果未检测到面部,则返回原始图像
if len(face) > 0:
# 目前假设只有一张脸,xy为左上角坐标,wh为矩形的宽高
(x, y, w, h) = face[0]
# 返回图像的正面部分
return gray[y:y + w, x:x + h], face[0]
else:
return None, None
# 该函数将读取所有的训练图像,从每个图像检测人脸并将返回两个相同大小的列表,分别为脸部信息和标签
def prepare_training_data(data_folder_path):
# 获取数据文件夹中的目录(每个主题的一个目录)
dirs = os.listdir(data_folder_path)
# 两个列表分别保存所有的脸部和标签
faces = []
labels = []
# 浏览每个目录并访问其中的图像
for dir_name in dirs:
# dir_name(str类型)即标签
label = int(dir_name)
# 建立包含当前主题主题图像的目录路径
subject_dir_path = data_folder_path + "/" + dir_name
# 获取给定主题目录内的图像名称
subject_images_names = os.listdir(subject_dir_path)
# 浏览每张图片并检测脸部,然后将脸部信息添加到脸部列表faces[]
for image_name in subject_images_names:
# 建立图像路径
image_path = subject_dir_path + "/" + image_name
# 读取图像
image = cv2.imread(image_path)
# 显示图像0.1s
cv2.imshow("Training on image...", image)
cv2.waitKey(100)
# 检测脸部
face, rect = detect_face(image)
# # 我们忽略未检测到的脸部
if face is not None:
# 将脸添加到脸部列表并添加相应的标签
faces.append(face)
labels.append(label)
cv2.waitKey(1)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
# 最终返回值为人脸和标签列表
return faces, labels
# 调用prepare_training_data()函数
faces, labels = prepare_training_data("images")
# 创建LBPH识别器并开始训练,当然也可以选择Eigen或者Fisher识别器
face_recognizer = cv2.face.LBPHFaceRecognizer_create()
face_recognizer.train(faces, np.array(labels))
# 根据指定的坐标和宽高在图片上绘制矩形
def draw_rectangle(img, rect):
(x, y, w, h) = rect
cv2.rectangle(img, (x, y), (x + w, y + h), (128, 128, 0), 2)
# 根据给定的(x,y)坐标标识出人名
def draw_text(img, text, x, y):
cv2.putText(img, text, (x, y), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_COMPLEX, 1, (128, 128, 0), 2)
# 建立标签和人名的映射表
subjects = ["yangmi", "liuyifei"]
def predict(test_img):
# 生成图片的副本,这样就可以保留原始图片
img = test_img.copy()
# 检测人脸
face, rect = detect_face(img)
print(face)
print(rect)
# 预测人脸
label = face_recognizer.predict(face)
print(label)
# 判断是否识别成功
if label:
# 获取由人脸识别器返回的相应的标签名称
label_text = subjects[label[0]]
# 在检测到的脸部周围绘制一个矩形
draw_rectangle(img, rect)
# 标出预测的名字
draw_text(img, label_text, rect[0], rect[1] - 5)
# 返回预测图像
return img
# else:
# print(img)
# # 在检测到的脸部周围绘制一个矩形
# draw_rectangle(img, rect)
# # 标出预测的名字
# draw_text(img, "unkonwn", rect[0], rect[1] - 5)
# # 返回预测图像
# return img
test_img1 = cv2.imread("test_data/5.jpg")
test_img2 = cv2.imread("test_data/6.jpg")
predicted_img1 = predict(test_img1)
predicted_img2 = predict(test_img2)
cv2.imshow(subjects[0], predicted_img1)
cv2.imshow(subjects[1], predicted_img2)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
最后结果为
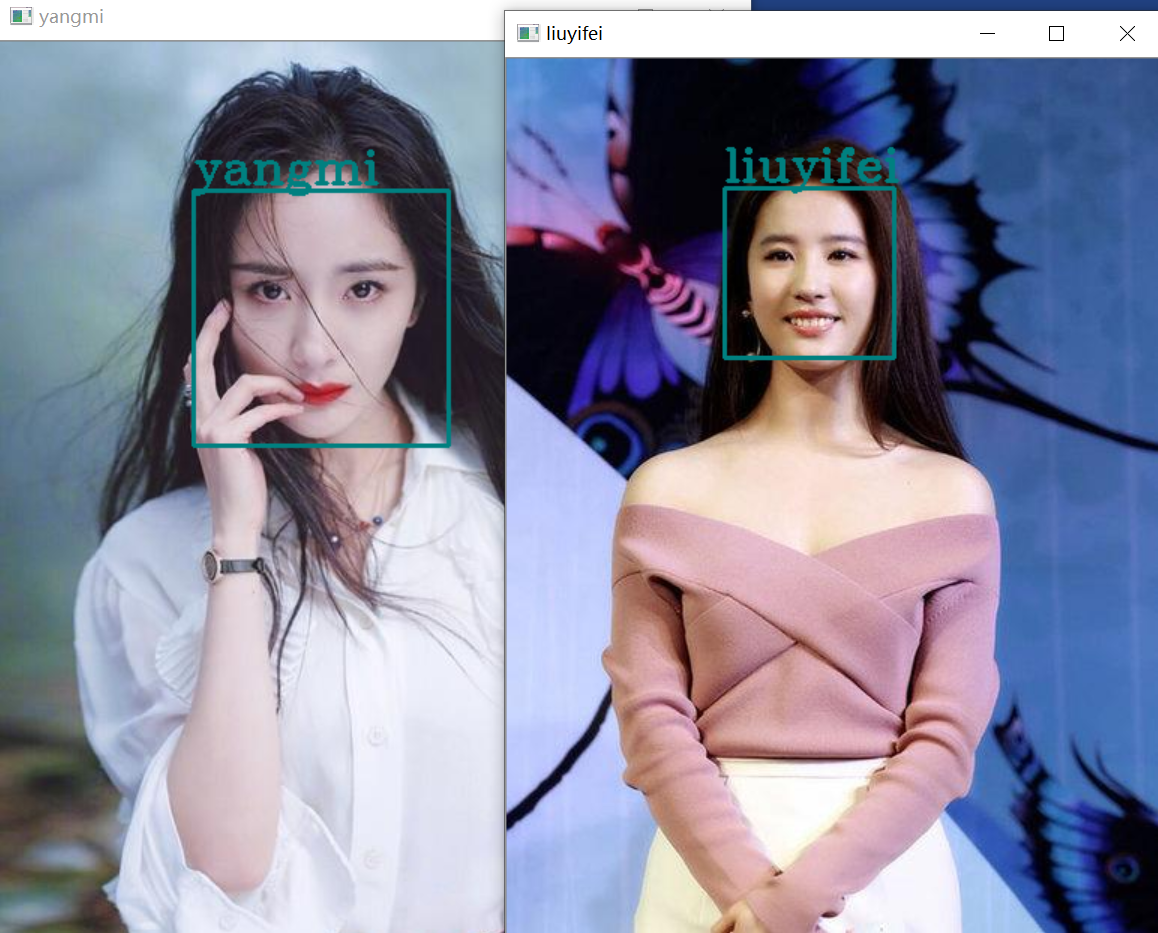
这个是识别率很低很低