POJ 3449 Geometric Shapes
Description
While creating a customer logo, ACM uses graphical utilities to draw a picture that can later be cut into special fluorescent materials. To ensure proper processing, the shapes in the picture cannot intersect. However, some logos contain such intersecting shapes. It is necessary to detect them and decide how to change the picture.
Given a set of geometric shapes, you are to determine all of their intersections. Only outlines are considered, if a shape is completely inside another one, it is not counted as an intersection.
Input
Input contains several pictures. Each picture describes at most 26 shapes, each specified on a separate line. The line begins with an uppercase letter that uniquely identifies the shape inside the corresponding picture. Then there is a kind of the shape and two or more points, everything separated by at least one space. Possible shape kinds are:
• square: Followed by two distinct points giving the opposite corners of the square.
• rectangle: Three points are given, there will always be a right angle between the lines connecting the first point with the second and the second with the third.
• line: Specifies a line segment, two distinct end points are given.
• triangle: Three points are given, they are guaranteed not to be co-linear.
• polygon: Followed by an integer number N (3 ≤ N ≤ 20) and N points specifying vertices of the polygon in either clockwise or anti-clockwise order. The polygon will never intersect itself and its sides will have non-zero length.
All points are always given as two integer coordinates X and Y separated with a comma and enclosed in parentheses. You may assume that |X|, |Y | ≤ 10000.
The picture description is terminated by a line containing a single dash (“-”). After the last picture, there is a line with one dot (“.”).
Output
For each picture, output one line for each of the shapes, sorted alphabetically by its identifier (X). The line must be one of the following:
• “X has no intersections”, if X does not intersect with any other shapes.
• “X intersects with A”, if X intersects with exactly 1 other shape.
• “X intersects with A and B”, if X intersects with exactly 2 other shapes.
• “X intersects with A, B, . . ., and Z”, if X intersects with more than 2 other shapes.
Please note that there is an additional comma for more than two intersections. A, B, etc. are all intersecting shapes, sorted alphabetically.
Print one empty line after each picture, including the last one.
Sample Input
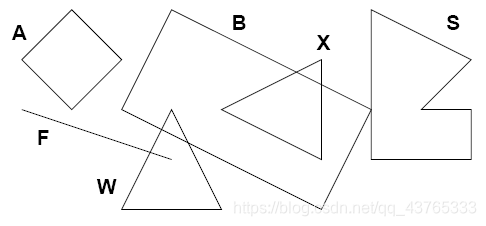
A square (1,2) (3,2)
F line (1,3) (4,4)
W triangle (3,5) (5,5) (4,3)
X triangle (7,2) (7,4) (5,3)
S polygon 6 (9,3) (10,3) (10,4) (8,4) (8,1) (10,2)
B rectangle (3,3) (7,5) (8,3)
-
B square (1,1) (2,2)
A square (3,3) (4,4)
-
.
Sample Output
A has no intersections
B intersects with S, W, and X
F intersects with W
S intersects with B
W intersects with B and F
X intersects with B
A has no intersections
B has no intersections
一道题意不难却奇烦无比的计算几何题,我改了一个下午,主要有这几个坑点:
1.输入必须用scanf,否则会超时
2.注意输出格式!!!我是用set存储答案的,输出时要分三种情况:
(1)size=1时,只需输出字母
(2)size=2时,只需输出and和字母,无逗号!
(3)size>2时,前面输出字母和逗号,最后输出and和字母
3.已知正方形两点求另一点和已知矩形三点求另一点都有公式,详见代码吧
AC代码如下:
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<set>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
double eps=1e-8;
int sum=0;
char c;
struct point{
double x,y;
};
struct segment
{
point s,e;
};
struct node{
segment seg[30];
point p[30];
int num;
string s;
char c;
set<char>q;
}G[100];
bool cmp(node a,node b){
return a.c<b.c;
}
double cross(point a,point b,point c){
return (a.x-c.x)*(b.y-c.y)-(a.y-c.y)*(b.x-c.x);
}
bool intersect(segment u,segment v){
return( (max(u.s.x,u.e.x)>=min(v.s.x,v.e.x))&& //排斥实验
(max(v.s.x,v.e.x)>=min(u.s.x,u.e.x))&&
(max(u.s.y,u.e.y)>=min(v.s.y,v.e.y))&&
(max(v.s.y,v.e.y)>=min(u.s.y,u.e.y))&&
(cross(v.s,u.e,u.s)*cross(u.e,v.e,u.s)+eps>=0)&& //跨立实验
(cross(u.s,v.e,v.s)*cross(v.e,u.e,v.s)+eps>=0));
}
void init(int n){//存点
if(G[n].s=="square"){
G[n].num=4;
scanf(" (%lf,%lf)",&G[n].p[0].x,&G[n].p[0].y);
scanf(" (%lf,%lf)",&G[n].p[2].x,&G[n].p[2].y);
G[n].p[1].x=((G[n].p[0].x+G[n].p[2].x)+(G[n].p[2].y-G[n].p[0].y))/2,G[n].p[1].y=((G[n].p[0].y+G[n].p[2].y)+(G[n].p[0].x-G[n].p[2].x))/2;
G[n].p[3].x=((G[n].p[0].x+G[n].p[2].x)-(G[n].p[2].y-G[n].p[0].y))/2,G[n].p[3].y=((G[n].p[0].y+G[n].p[2].y)-(G[n].p[0].x-G[n].p[2].x))/2;
}
if(G[n].s=="rectangle"){
G[n].num=4;
for(int i=0;i<3;i++){
scanf(" (%lf,%lf)",&G[n].p[i].x,&G[n].p[i].y);
}
G[n].p[3].x=G[n].p[2].x+(G[n].p[0].x-G[n].p[1].x);
G[n].p[3].y=G[n].p[2].y+(G[n].p[0].y-G[n].p[1].y);
}
if(G[n].s=="line"){
G[n].num=1;
for(int i=0;i<2;i++){
scanf(" (%lf,%lf)",&G[n].p[i].x,&G[n].p[i].y);
}
}
if(G[n].s=="triangle"){
G[n].num=3;
for(int i=0;i<G[n].num;i++){
scanf(" (%lf,%lf)",&G[n].p[i].x,&G[n].p[i].y);
}
}
if(G[n].s=="polygon"){
for(int i=0;i<G[n].num;i++){
scanf(" (%lf,%lf)",&G[n].p[i].x,&G[n].p[i].y);
}
}
}
void build(){//建边
for(int i=0;i<sum;i++){
if(G[i].num==1) {G[i].seg[0].s=G[i].p[0],G[i].seg[0].e=G[i].p[1];continue;}
for(int j=0;j<G[i].num;j++){
G[i].seg[j].s=G[i].p[j],G[i].seg[j].e=G[i].p[(j+1)%G[i].num];
}
}
}
void print(){//判断+输出
build();
sort(G,G+sum,cmp);
for(int i=0;i<sum;i++){
for(int j=0;j<sum;j++){
if(i==j) continue;
int flag=1;
for(int x=0;x<G[i].num;x++){
for(int y=0;y<G[j].num;y++){
if(intersect(G[i].seg[x],G[j].seg[y])) {flag=0;break;}
}
if(!flag) break;
}
if(!flag) {G[i].q.insert(G[j].c);continue;}
}
}
for(int i=0;i<sum;i++){
if(G[i].q.size()==0) printf("%c has no intersections\n",G[i].c);
else{
printf("%c intersects with ",G[i].c);
int u=0;
if(G[i].q.size()==1){
for(set<char>::iterator j=G[i].q.begin();j!=G[i].q.end();j++){
printf("%c\n",*j);
}
}
else if(G[i].q.size()==2){
for(set<char>::iterator j=G[i].q.begin();j!=G[i].q.end();j++){
u++;
if(u<G[i].q.size()) printf("%c ",*j);
else printf("and %c\n",*j);
}
}
else{
for(set<char>::iterator j=G[i].q.begin();j!=G[i].q.end();j++){
u++;
if(u<G[i].q.size()) printf("%c, ",*j);
else printf("and %c\n",*j);
}
}
}
}
puts("");
}
void Clear(){//清零
for(int i=0;i<sum;i++){
G[i].q.clear();
}
sum=0;
}
int main(){
while(1){
cin>>G[sum].c;
if(G[sum].c=='-') {print();Clear();continue;}
if(G[sum].c=='.') break;
cin>>G[sum].s;
if(G[sum].s=="polygon") cin>>G[sum].num;
init(sum);sum++;
}
return 0;
}