官网code链接:https://www.harrisgeospatial.com/docs/programmingguideclassification_codeexamplesvmapiobjects.html
1.代码中所需要的数据:
链接: https://pan.baidu.com/s/18pCNLr_GVTxUro1Gj8ta3Q 提取码: wm8u
2.需要改绝对路径:
file = ‘D:\F\idl_test\classification\AttributeImage.dat’
ROIfile = ‘D:\F\idl_test\classification\TrainingDataROIs.xml’
‘D:\F\idl_test\classification\TrainedSVMClassifier.epo’
3.如果运行出错,且报错为:

解决办法:请查看你的ENVI版本,ENVI5.3以下不支持
申请使用ENVI5.5的教程网址:http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_764b1e9d0102ycm2.html
激活成功,就可使用。
4.程序有基础的很容易看懂,加油:
PRO SVMClassificationUsingObjects
COMPILE_OPT IDL2
; Start the application
e = ENVI()
; Open an attribute raster to classify
file = 'D:\F\idl_test\classification\AttributeImage.dat'
raster = e.OpenRaster(file)
; Open training data ROIs
ROIfile = 'D:\F\idl_test\classification\TrainingDataROIs.xml'
rois = e.OpenROI(ROIfile)
; Extract examples and class values
outExamples = ENVIExtractExamplesFromRaster(raster,rois)
; Normalize the data
normalizedExamples = ENVIApplyGainOffsetToExamples( $
outExamples, $
OUTPUT_OFFSET=offset, $
OUTPUT_GAIN=gain)
Print, 'Gain: ',gain
Print, 'Offset: ',offset
; Shuffle the examples to create a random distribution
shuffledExamples = ENVIShuffleExamples(normalizedExamples)
; Split the examples into training and evaluation sets
splitExamples = ENVISplitExamples(shuffledExamples, $
SPLIT_FRACTION=0.8)
; Define the SVM classifier inputs
classifier = ENVISVMClassifier( $
NATTRIBUTES=outExamples.NATTRIBUTES, $
NCLASSES=outExamples.NCLASSES, $
CLASS_NAMES=outExamples.CLASS_NAMES)
; Define the trainer inputs
trainer = ENVIIterativeTrainer( $
CONVERGENCE_CRITERION=0.0001, $
MAXIMUM_ITERATIONS=1)
; Train the classifier
ENVITrainClassifier, trainer, classifier, splitExamples[0], $
LOSS_PROFILE=lossProfile
; Save the trained classifier to disk
classifierURI = 'D:\F\idl_test\classification\TrainedSVMClassifier.epo'
classifier.Save, URI=classifierURI
; Evaluate the result
confusionMatrix = ENVIEvaluateClassifier(splitExamples[1], classifier)
; Print the confusion matrix
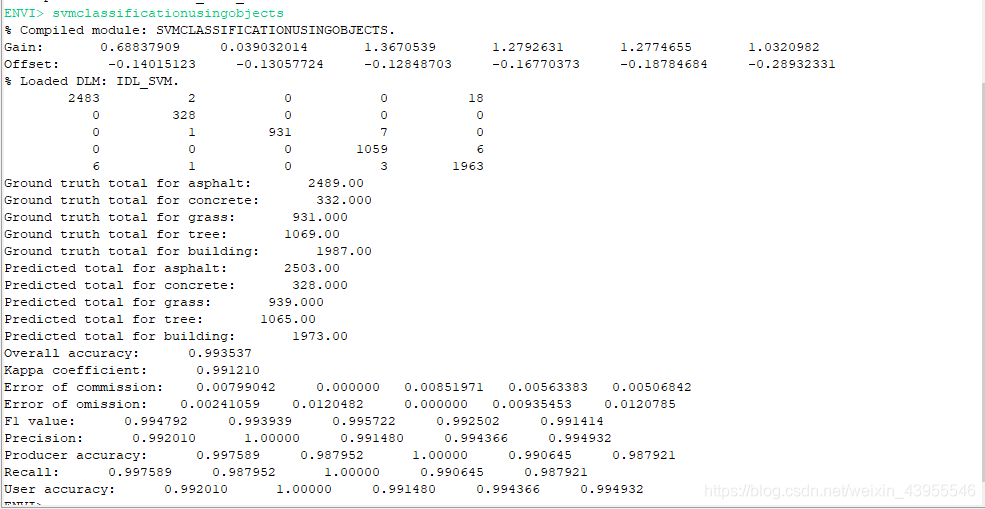
Print, confusionMatrix.Confusion_Matrix
; Print the column totals
columnTotals = confusionMatrix.ColumnTotals()
FOR i=0, (outExamples.NCLASSES)-1 DO $
Print, 'Ground truth total for ', $
outExamples.CLASS_NAMES[i],': ', $
columnTotals[i]
; Print the row totals
rowTotals = confusionMatrix.RowTotals()
FOR i=0, (outExamples.NCLASSES)-1 DO $
Print, 'Predicted total for ', $
outExamples.CLASS_NAMES[i],': ', $
rowTotals[i]
; Print the accuracy metrics
accuracy = confusionMatrix.Accuracy()
Print, 'Overall accuracy: ', accuracy
kappa = confusionMatrix.KappaCoefficient()
Print, 'Kappa coefficient: ', kappa
commissionError = confusionMatrix.CommissionError()
Print, 'Error of commission: ', commissionError
omissionError = confusionMatrix.OmissionError()
Print, 'Error of omission: ', omissionError
F1 = confusionMatrix.F1()
Print, 'F1 value: ', F1
precision = confusionMatrix.Precision()
Print, 'Precision: ', precision
producerAccuracy = confusionMatrix.ProducerAccuracy()
Print, 'Producer accuracy: ', producerAccuracy
recall = confusionMatrix.Recall()
Print, 'Recall: ', recall
userAccuracy = confusionMatrix.UserAccuracy()
Print, 'User accuracy: ', userAccuracy
; Normalize the data
normalizedRaster = ENVIGainOffsetRaster(raster, gain, offset)
; Classify the normalized attribute image
classRaster = ENVIClassifyRaster(normalizedRaster, classifier)
; Display the result
view = e.GetView()
layer = view.CreateLayer(raster)
layer2 = view.CreateLayer(classRaster)
view.Zoom, /FULL_EXTENT
END
5.程序运行结果:
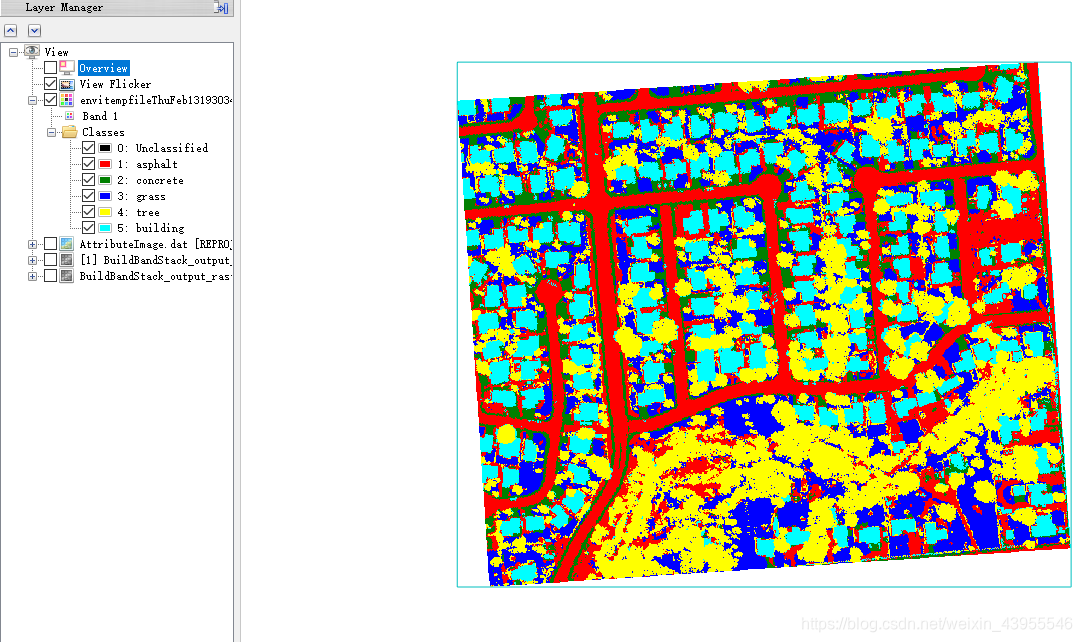
运行后在ENVI里面的显示: