1.刘汝佳紫书区间问题三大情况
1.选择不相交区间
贪心策略:一定要选择第一个区间
2.区间选点问题
贪心策略:取最后一个点
3.区间覆盖问题: n个闭区间,选择尽量少的区间覆盖一条指定线段[s,t]
贪心策略:预处理掉[s,t]之外的区间,闭区间从最左向右开始覆盖
应用
Open Judge 1328
要求建在x轴半径d的雷达覆盖所有已知点

#include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<string> #include<algorithm> #include<queue> #include<deque> #include<set> #include<map> #include<cmath> #include<stack> const double PI = acos(-1.0); #define eps 1e-6 #define INF 0x3f3f3f3f typedef long long ll; using namespace std; struct P { double a; double b; friend bool operator <(const P& x, const P& y) { if (x.b != y.b) return x.b < y.b; else return x.a > y.a; } }; P p[1005]; int main() { double d,xi,yi; int n; int kase = 1; while (scanf("%d%lf", &n, &d), n||d) { memset(p, 0, sizeof p); int t = 1; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { scanf("%lf%lf", &xi, &yi); if (yi > d||yi<0) { t = 0; } p[i].a = xi - sqrt(d * d - yi * yi); p[i].b = xi + sqrt(d * d - yi * yi); } if (!t) printf("Case %d: -1\n", kase++); if (!t) continue; sort(p, p + n); int ans = 1; double f = p[0].b; for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) { if (p[i].a > f) f = p[i].b, ans++; } printf("Case %d: %d\n", kase++, ans); } return 0; }
POJ 1065
描述
C小加有一些木棒,它们的长度和质量都已经知道,需要一个机器处理这些木棒,机器开启的时候需要耗费一个单位的时间,如果第i+1个木棒的重量和长度都大于等于
第i个处理的木棒,那么将不会耗费时间,否则需要消耗一个单位的时间。因为急着去约会,C小加想在最短的时间内把木棒处理完,你能告诉他应该怎样做吗?

#include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<string> #include<algorithm> #include<queue> #include<deque> #include<set> #include<map> #include<cmath> #include<stack> const double PI = acos(-1.0); #define eps 1e-6 #define INF 0x3f3f3f3f typedef long long ll; using namespace std; struct R { int l; int w; friend bool operator <(const R& a, const R& b) { if (a.w != b.w) return a.w < b.w; else return a.l < b.l; } }; int vis[5005]; R a[5005]; int main() { int T,n; scanf("%d", &T); while (T--) { memset(vis, 0, sizeof vis); memset(a, 0, sizeof a); scanf("%d", &n); for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) scanf("%d%d", &a[i].l, &a[i].w); sort(a, a + n); int ans = 0; int cnt = 0; while (cnt!=n) { ans++; int f = -1; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { if (vis[i]) continue; if (a[i].l >=f) f = a[i].l, cnt++, vis[i] = 1; } } printf("%d\n", ans); } return 0; }
有点思维的题

code:

#include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<string> #include<algorithm> #include<queue> #include<deque> #include<set> #include<map> #include<cmath> #include<stack> const double PI = acos(-1.0); #define eps 1e-6 #define INF 0x3f3f3f3f typedef long long ll; using namespace std; int Hash[220]; int main() { int T,n; int x, y; scanf("%d", &T); while (T--) { memset(Hash, 0, sizeof Hash); scanf("%d", &n); for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { scanf("%d%d", &x, &y); if (x > y) swap(x, y); if (x & 1) x >>= 1; else x = x - 1 >> 1; if (y & 1) y >>= 1; else y = y - 1 >> 1; for (int i = x; i <= y; i++) Hash[i]++; } int Max = -1; for (int i = 0; i < 220; i++) { Max = max(Max, Hash[i]); } printf("%d\n", Max*10); } return 0; }
可以对比的两题:
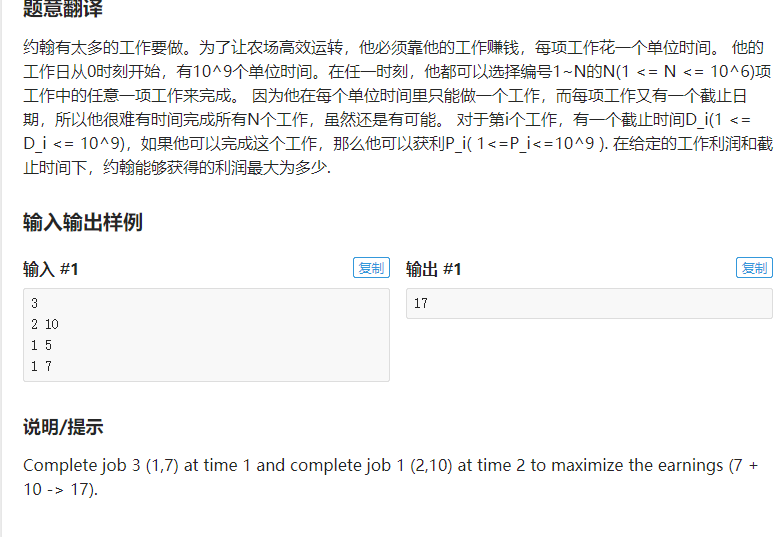
贪心策略:后悔法
#include <algorithm> #include <cmath> #include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include <iostream> #include <queue> using namespace std; struct f { long long d; long long x; } a[100005]; bool cmp(f A, f B) { return A.d < B.d; } priority_queue<long long, vector<long long>, greater<long long> > q; int main() { long long n, i, j; cin >> n; for (i = 1; i <= n; i++) { scanf("%d%d", &a[i].d, &a[i].x); } sort(a + 1, a + n + 1, cmp); long long ans = 0; for (i = 1; i <= n; i++) { if (a[i].d <= q.size()) { if (q.top() < a[i].x) { ans += a[i].x - q.top(); q.pop(); q.push(a[i].x); } } else { ans += a[i].x; q.push(a[i].x); } } cout << ans << endl; return 0; }


#include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<string> #include<algorithm> #include<queue> #include<deque> #include<set> #include<map> #include<cmath> #include<cstring> #include<stack> const double PI = acos(-1.0); #define eps 1e-6 #define INF 0x3f3f3f3f typedef long long ll; using namespace std; struct P { int d; int s; friend bool operator < (const P& a, const P& b) { return a.s >b.s; } }; P p[1005]; int vis[1005]; int main() { int T; int n; int tot; scanf("%d", &T); while (T--) { tot = 0; scanf("%d", &n); memset(p, 0, sizeof p); memset(vis, 0, sizeof vis); for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) scanf("%d", &p[i].d); for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) scanf("%d", &p[i].s); sort(p, p + n); for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { int x = p[i].d; while (x) { if (!vis[x]) { vis[x] = 1; break; } x--; } if (!x) tot += p[i].s; } printf("%d\n", tot); } return 0; }
