BIO,NIO模型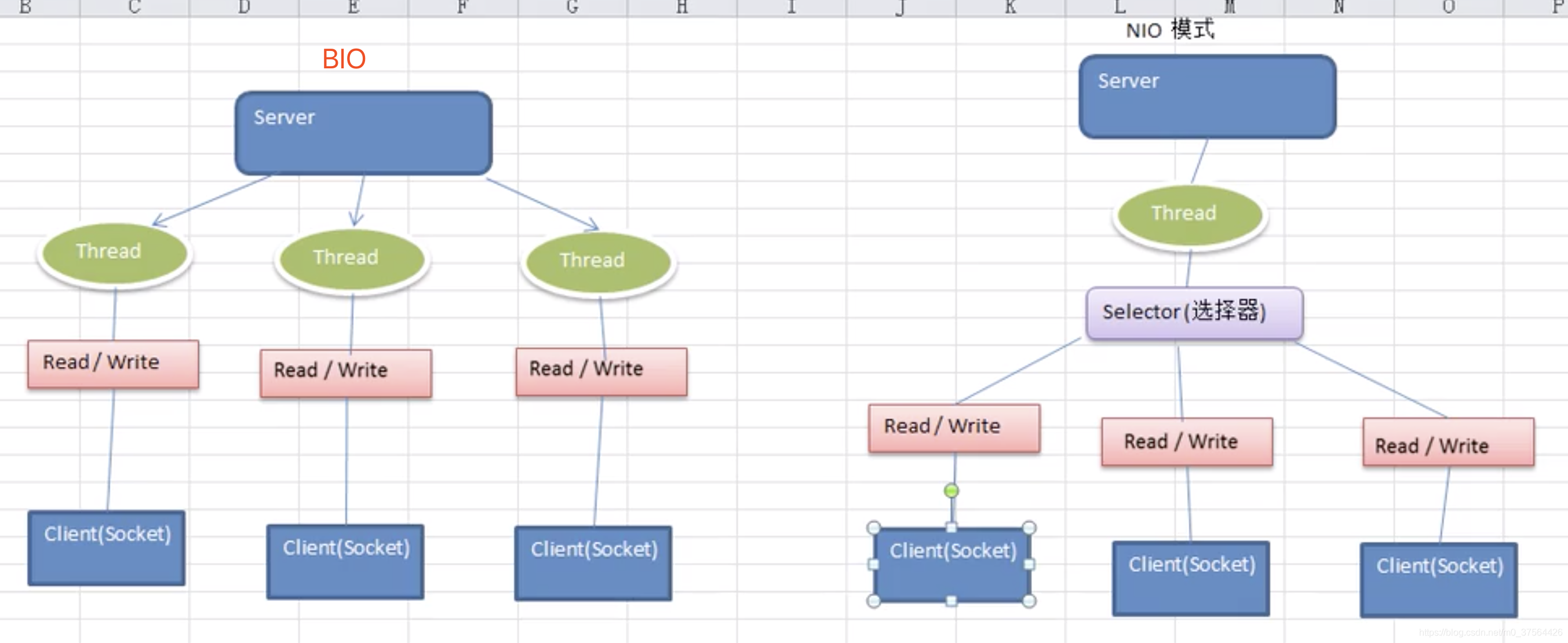
BIO代码实现
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
public class BIOServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(8888);
System.out.println("服务器启动...");
while(true){
// 监听
final Socket socket = serverSocket.accept();
System.out.println("连接一个客户端...");
newCachedThreadPool.execute(new Runnable(){
@Override
public void run() {
handler(socket);
}
});
}
}
public static void handler(Socket socket){
try {
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
InputStream ins = socket.getInputStream();
while(true){
int readLength = ins.read(bytes);
if(-1 != readLength){
System.out.println("线程: " + Thread.currentThread().getName() + " ");
System.out.println(new String(bytes,0,readLength));
}else{
break;
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
try {
socket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
使用telnet连接ServerSocket
telnet 127.0.0.1 8888

NIO(non-blocking IO)同步非阻塞
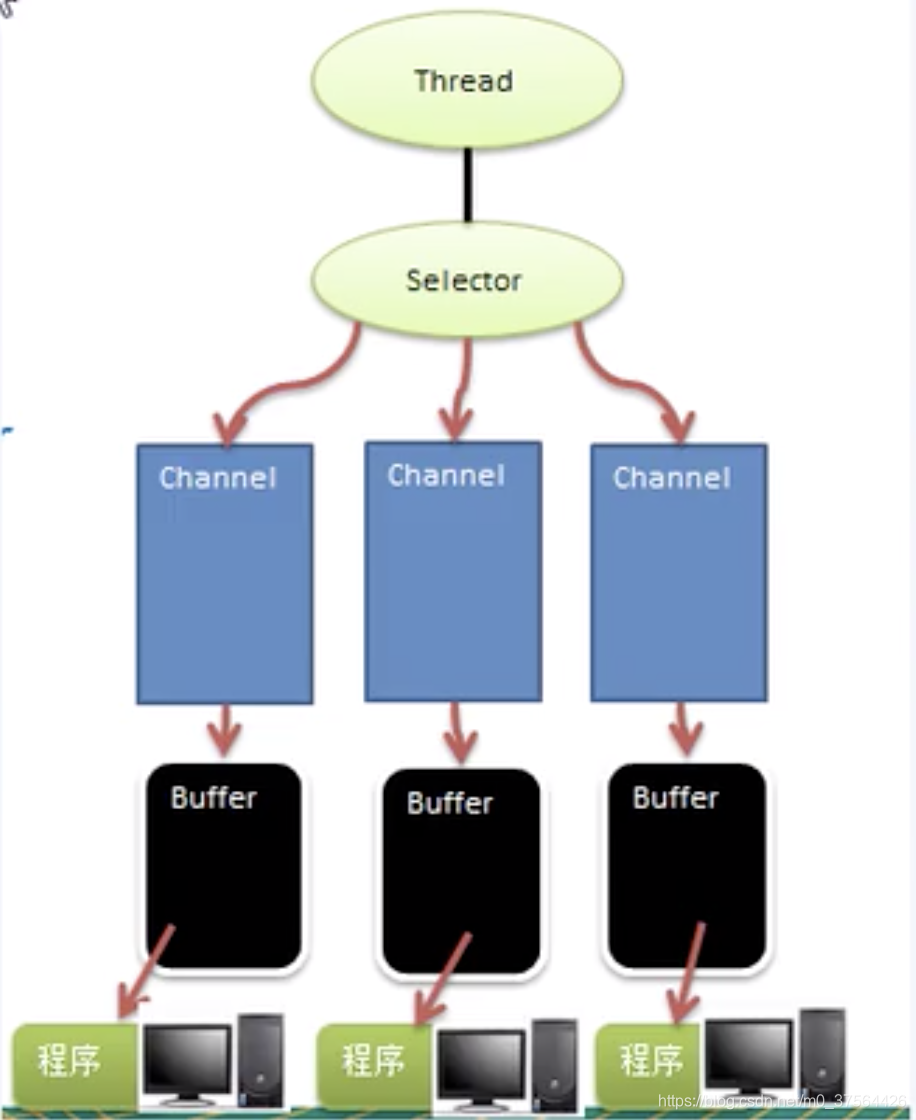
NIO有三大核心部分, Channel(通道), Buffer(缓冲区), Selector(选择器)
1.每个Channel都会对应一个Buffer。
2.Selector对应一个线程,一个线程对应多个channel。
3.程序切换到哪个channel是由事件决定的,Event(事件)就是一个重要的概念。
4.Buffer是一个内存块,底层是有一个数组。
5.数据的读取写入是通过Buffer,这个和BIO不一样, BIO中是通过输入流,输出流两个流进行读取,写入的。而NIO仅仅只通过Buffer就完成读取写入。
6.Channel也是双向的,可以返回底层操作系统的情况,比如linux底层的操作系统通道就是双向的。
buffer

Channel(通道)
- 通道可以同时进行读写,但流只能读或者写
- 通道可以实现异步读写数据
- 通道可以从缓冲(buffer)读数据,也可以写数据到缓冲(buffer)
FileChannel用于文件的数据读写。
DatagramChannel用于UDP的数据读写。
ServerSocketChannel和SocketChannel用于TCP的数据读写。
向本地文件写数据
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel;
public class NIOFileChannel01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
String str = "hello, 风云争霸ddd";
// 创建一个输出流
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("C:\\Users\\haha\\Desktop\\2.txt");
// 通过FileOutputStream 获取对应的 FileChannel
// 这个fileChannel的真是类型是FileChannelImpl
FileChannel fileChannel = fos.getChannel();
// 创建一个缓冲区 ByteBuffer
ByteBuffer bf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
// 将str放入bf中
bf.put(str.getBytes());
bf.flip();
// 将bf数据写入到fileChannel
fileChannel.write(bf);
fos.close();
}
}
从本地文件读数据
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel;
public class NIOFileChannel02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
// 创建一个输出流
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("C:\\Users\\haha\\Desktop\\2.txt");
// 通过FileOutputStream 获取对应的 FileChannel
// 这个fileChannel的真是类型是FileChannelImpl
FileChannel fileChannel = fis.getChannel();
// 创建一个缓冲区 ByteBuffer
ByteBuffer bf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
// 将str放入bf中
fileChannel.read(bf);
System.out.println(new String(bf.array()));
fis.close();
}
}
Buffer类相关方法

ByteBuffer类(最常用的Buffer类)

NIO还支持通过多个Buffer(即Buffer数组)完成读写操作, 即Scattering 和 Gathering
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
/*
* Scattering: 将数据写入到buffer时,可以采用buffer数组,依次写入
* Gathering: 从buffer读取数据时,可以采用buffer数组,依次读
*/
public class ScatteringAndGatheringTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
// 使用ServerSocketChannel,
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
InetSocketAddress inetSocketAddress = new InetSocketAddress(7000);
// 绑定端口到socket,并启动
serverSocketChannel.socket().bind(inetSocketAddress);
// 创建buffer数组
ByteBuffer[] byteBuffers = new ByteBuffer[2];
byteBuffers[0] = ByteBuffer.allocate(5);
byteBuffers[1] = ByteBuffer.allocate(3);
// 等待客户端连接
SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept();
int messageLength = 8;
// 循环的读取
while(true){
int byteRead = 0;
while(byteRead < messageLength){
long l = socketChannel.read(byteBuffers);
byteRead += l; // 累计读取的字节数
System.out.println("byteRead=" + byteRead);
// 看看当前buffer的position,limit
for(int i=0; i<byteBuffers.length; i++){
System.out.println("position="+byteBuffers[i].position()+" "+"limit="+byteBuffers[i].limit());
}
}
// 将所有buffer进行flip
for(int i=0; i<byteBuffers.length; i++){
byteBuffers[i].flip();
}
// 将数据显示到客户端
long byteWrite = 0;
while(byteWrite < messageLength){
long l = socketChannel.write(byteBuffers);
byteWrite += l;
}
// 将所有buffer进行clear
for(int i=0; i<byteBuffers.length; i++){
byteBuffers[i].clear();
}
System.out.println("byteRead="+byteRead+" byteWrite="+byteWrite);
}
}
}
