在迷宫算法总结篇中我总结了生成迷宫的四种算法,在这一篇文章里面我侧重迷宫游戏的实现以及可视化。
使用python3中的GUI绘图库tkinter实现了一个简陋版的迷宫游戏,地图截图如下图所示。
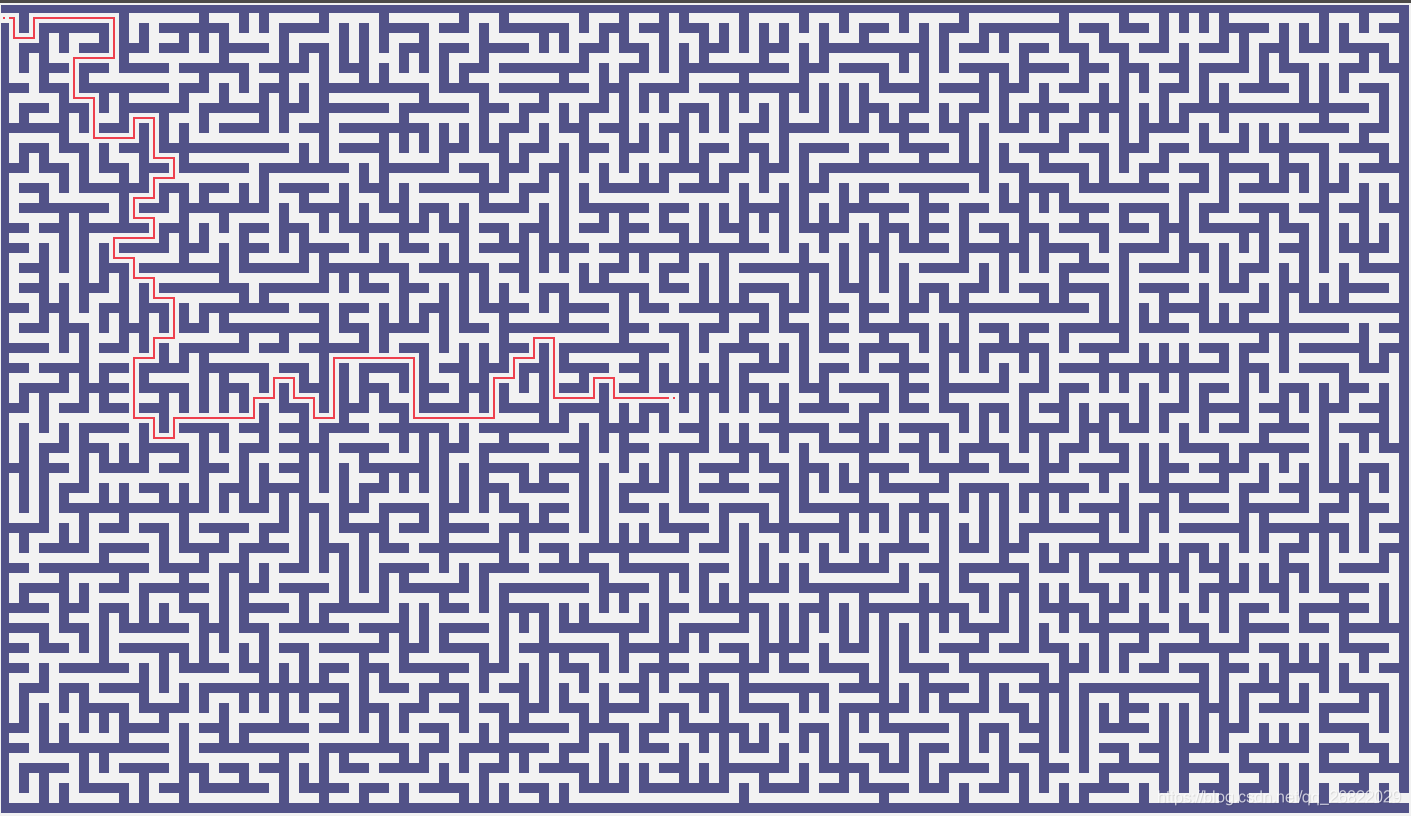
为了降低游戏的难度,在寻找路径的过程中你可以通过点击图中的空白点,生成从起点到你点击位置的路径。迷宫的难度主要由以下几个参数决定:
- 迷宫的长和宽:尺寸越大,生成的地图越难
- 迷宫生成算法:地图难度:kruskal算法 > 随机深度优先算法 > prim算法 > 递归分割算法。
目前已经开发到版本1.0.7,已经实现的功能有:
当前版本代码在Maze-game-v1.0.7.
- 游戏背景音乐
- 游戏难度递增
- 增加状态栏显示状态信息
- 作弊(查看提示)增加惩罚分数(当前作弊一次惩罚20分)
- 保存读取地图
- 菜单栏,可用于设置地图生成算法,地图尺寸等
- 增加迷雾模式
- 增加生存模式,参考Roguelike Vision Algorithms丰富可玩性
- 显示等级以及当前移动步数
- 随机生成游戏地图
- 按方向键后自动前进倒退(到分岔路停止)
- 起点到任意位置辅助路径显示(鼠标左键单击空白地方显示路线) 移动次数计数
- 到达终点后通关,按任意键进入下一关(目前没有难度设置,难度相同)
出现过的bug列表:
-
到达终点后上下左右键仍然可用且不会进入到下一关
已解决:修改进入下一关的逻辑 -
画图很慢,不知道是我代码写的垃圾还是这个python的tkinter库本身的问题[狗头]
已解决:刷新也面前调用Canvas.delete(“all”)清除之前绘制的所有内容再画新的页面即可。 -
通关后生成的地图绘制的就更慢了,按一次方向键后要等一年[狗头]
已解决:同上
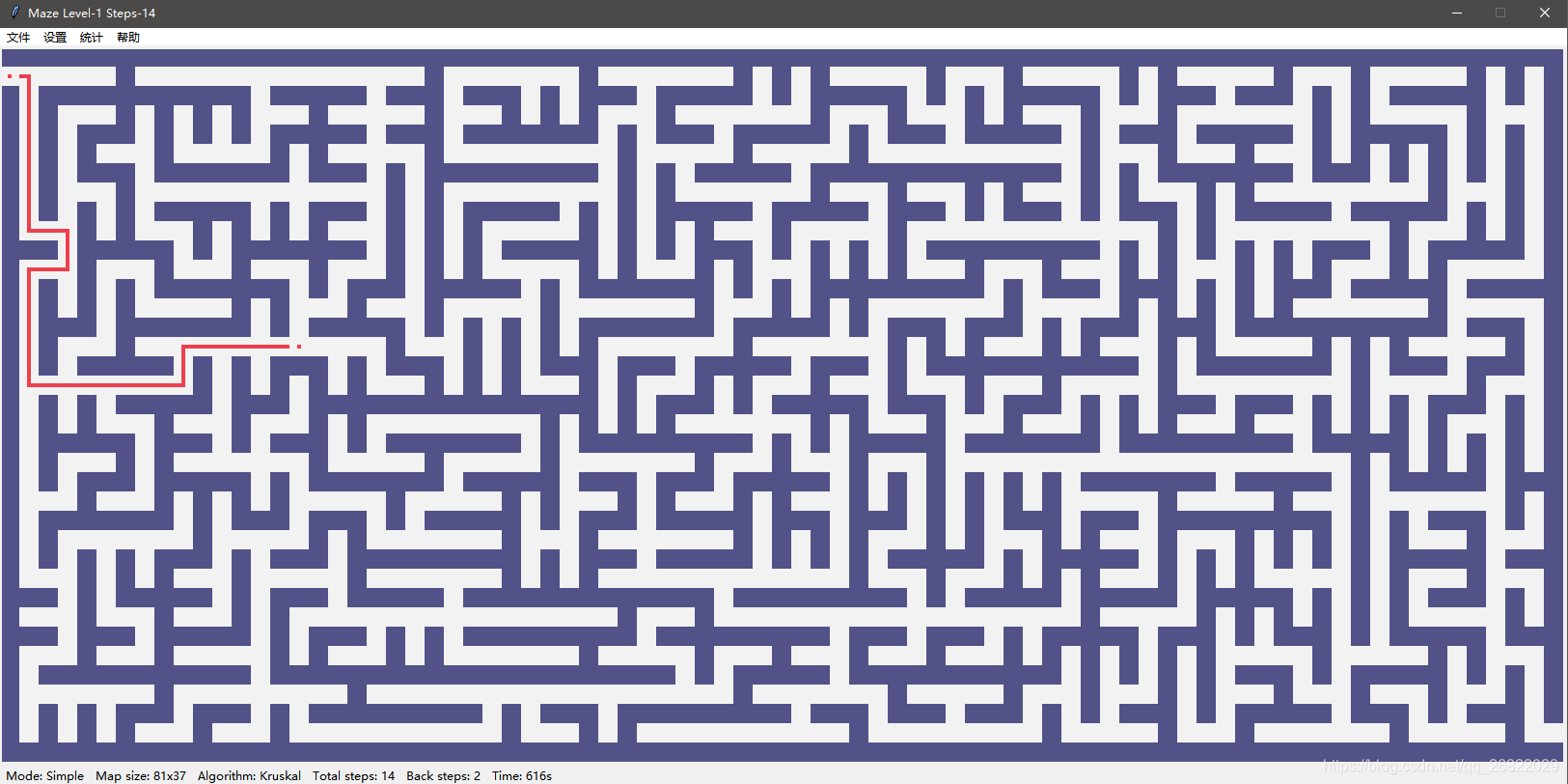
最新版本截图
1 简单模式
2 迷雾模式

详细的介绍以及说明后续补充。现在提供1.0.3版本源码清单如下,为了方便代码管理,后续版本代码将会直接上传到Github,目前已经更新到v1.0.7,最新版本代码Maze-game-v1.0.7.
- 迷宫类 Maze:
├ print_matrix
├ generate_matrix_dfs
├ generate_matrix_prim
├ generate_matrix_kruskal
├ generate_matrix_split
├ find_path_dfs
└ find_path_bfs (TODO) - 并查集类 UnionSet:
├ find
└ union - 可视化:
├ draw_cell
├ draw_path
├ draw_maze
├ check_reach
├ _eventHandler
├ _paint
├ _reset
└ update_maze
迷宫算法源码 mazeGenerator.py:
import numpy as np
import time
import random
import copy
class UnionSet(object):
"""
并查集实现,构造函数中的matrix是一个numpy类型
"""
def __init__(self, arr):
self.parent = {pos: pos for pos in arr}
self.count = len(arr)
def find(self, root):
if root == self.parent[root]:
return root
return self.find(self.parent[root])
def union(self, root1, root2):
self.parent[self.find(root1)] = self.find(root2)
class Maze(object):
"""
迷宫生成类
"""
def __init__(self, width = 11, height = 11):
assert width >= 5 and height >= 5, "Length of width or height must be larger than 5."
self.width = (width // 2) * 2 + 1
self.height = (height // 2) * 2 + 1
self.start = [1, 0]
self.destination = [self.height - 2, self.width - 1]
self.matrix = None
self.path = []
def print_matrix(self):
matrix = copy.deepcopy(self.matrix)
for p in self.path:
matrix[p[0]][p[1]] = 1
for i in range(self.height):
for j in range(self.width):
if matrix[i][j] == -1:
print('□', end = '')
elif matrix[i][j] == 0:
print(' ', end = '')
elif matrix[i][j] == 1:
print('■', end = '')
print('')
def generate_matrix_dfs(self):
# 地图初始化,并将出口和入口处的值设置为0
self.matrix = -np.ones((self.height, self.width))
self.matrix[self.start[0], self.start[1]] = 0
self.matrix[self.destination[0], self.destination[1]] = 0
visit_flag = [[0 for i in range(self.width)] for j in range(self.height)]
def check(row, col, row_, col_):
temp_sum = 0
for d in [[0, 1], [0, -1], [1, 0], [-1, 0]]:
temp_sum += self.matrix[row_ + d[0]][col_ + d[1]]
return temp_sum <= -3
def dfs(row, col):
visit_flag[row][col] = 1
self.matrix[row][col] = 0
if row == self.start[0] and col == self.start[1] + 1:
return
directions = [[0, 2], [0, -2], [2, 0], [-2, 0]]
random.shuffle(directions)
for d in directions:
row_, col_ = row + d[0], col + d[1]
if row_ > 0 and row_ < self.height - 1 and col_ > 0 and col_ < self.width - 1 and visit_flag[row_][col_] == 0 and check(row, col, row_, col_):
if row == row_:
visit_flag[row][min(col, col_) + 1] = 1
self.matrix[row][min(col, col_) + 1] = 0
else:
visit_flag[min(row, row_) + 1][col] = 1
self.matrix[min(row, row_) + 1][col] = 0
dfs(row_, col_)
dfs(self.destination[0], self.destination[1] - 1)
self.matrix[self.start[0], self.start[1] + 1] = 0
# 虽然说是prim算法,但是我感觉更像随机广度优先算法
def generate_matrix_prim(self):
# 地图初始化,并将出口和入口处的值设置为0
self.matrix = -np.ones((self.height, self.width))
def check(row, col):
temp_sum = 0
for d in [[0, 1], [0, -1], [1, 0], [-1, 0]]:
temp_sum += self.matrix[row + d[0]][col + d[1]]
return temp_sum < -3
queue = []
row, col = (np.random.randint(1, self.height - 1) // 2) * 2 + 1, (np.random.randint(1, self.width - 1) // 2) * 2 + 1
queue.append((row, col, -1, -1))
while len(queue) != 0:
row, col, r_, c_ = queue.pop(np.random.randint(0, len(queue)))
if check(row, col):
self.matrix[row, col] = 0
if r_ != -1 and row == r_:
self.matrix[row][min(col, c_) + 1] = 0
elif r_ != -1 and col == c_:
self.matrix[min(row, r_) + 1][col] = 0
for d in [[0, 2], [0, -2], [2, 0], [-2, 0]]:
row_, col_ = row + d[0], col + d[1]
if row_ > 0 and row_ < self.height - 1 and col_ > 0 and col_ < self.width - 1 and self.matrix[row_][col_] == -1:
queue.append((row_, col_, row, col))
self.matrix[self.start[0], self.start[1]] = 0
self.matrix[self.destination[0], self.destination[1]] = 0
# 递归切分算法,还有问题,现在不可用
def generate_matrix_split(self):
# 地图初始化,并将出口和入口处的值设置为0
self.matrix = -np.zeros((self.height, self.width))
self.matrix[0, :] = -1
self.matrix[self.height - 1, :] = -1
self.matrix[:, 0] = -1
self.matrix[:, self.width - 1] = -1
# 随机生成位于(start, end)之间的偶数
def get_random(start, end):
rand = np.random.randint(start, end)
if rand & 0x1 == 0:
return rand
return get_random(start, end)
# split函数的四个参数分别是左上角的行数、列数,右下角的行数、列数,墙壁只能在偶数行,偶数列
def split(lr, lc, rr, rc):
if rr - lr < 2 or rc - lc < 2:
return
# 生成墙壁,墙壁只能是偶数点
cur_row, cur_col = get_random(lr, rr), get_random(lc, rc)
for i in range(lc, rc + 1):
self.matrix[cur_row][i] = -1
for i in range(lr, rr + 1):
self.matrix[i][cur_col] = -1
# 挖穿三面墙得到连通图,挖孔的点只能是偶数点
wall_list = [
("left", cur_row, [lc + 1, cur_col - 1]),
("right", cur_row, [cur_col + 1, rc - 1]),
("top", cur_col, [lr + 1, cur_row - 1]),
("down", cur_col, [cur_row + 1, rr - 1])
]
random.shuffle(wall_list)
for wall in wall_list[:-1]:
if wall[2][1] - wall[2][0] < 1:
continue
if wall[0] in ["left", "right"]:
self.matrix[wall[1], get_random(wall[2][0], wall[2][1] + 1) + 1] = 0
else:
self.matrix[get_random(wall[2][0], wall[2][1] + 1), wall[1] + 1] = 0
# self.print_matrix()
# time.sleep(1)
# 递归
split(lr + 2, lc + 2, cur_row - 2, cur_col - 2)
split(lr + 2, cur_col + 2, cur_row - 2, rc - 2)
split(cur_row + 2, lc + 2, rr - 2, cur_col - 2)
split(cur_row + 2, cur_col + 2, rr - 2, rc - 2)
self.matrix[self.start[0], self.start[1]] = 0
self.matrix[self.destination[0], self.destination[1]] = 0
split(0, 0, self.height - 1, self.width - 1)
# 最小生成树算法-kruskal(选边法)思想生成迷宫地图,这种实现方法最复杂。
def generate_matrix_kruskal(self):
# 地图初始化,并将出口和入口处的值设置为0
self.matrix = -np.ones((self.height, self.width))
def check(row, col):
ans, counter = [], 0
for d in [[0, 1], [0, -1], [1, 0], [-1, 0]]:
row_, col_ = row + d[0], col + d[1]
if row_ > 0 and row_ < self.height - 1 and col_ > 0 and col_ < self.width - 1 and self.matrix[row_, col_] == -1:
ans.append([d[0] * 2, d[1] * 2])
counter += 1
if counter <= 1:
return []
return ans
nodes = set()
row = 1
while row < self.height:
col = 1
while col < self.width:
self.matrix[row, col] = 0
nodes.add((row, col))
col += 2
row += 2
unionset = UnionSet(nodes)
while unionset.count > 1:
row, col = nodes.pop()
directions = check(row, col)
if len(directions):
random.shuffle(directions)
for d in directions:
row_, col_ = row + d[0], col + d[1]
if unionset.find((row, col)) == unionset.find((row_, col_)):
continue
nodes.add((row, col))
unionset.count -= 1
unionset.union((row, col), (row_, col_))
if row == row_:
self.matrix[row][min(col, col_) + 1] = 0
else:
self.matrix[min(row, row_) + 1][col] = 0
break
self.matrix[self.start[0], self.start[1]] = 0
self.matrix[self.destination[0], self.destination[1]] = 0
# 迷宫寻路算法dfs
def find_path_dfs(self, destination):
visited = [[0 for i in range(self.width)] for j in range(self.height)]
def dfs(path):
visited[path[-1][0]][path[-1][1]] = 1
if path[-1][0] == destination[0] and path[-1][1] == destination[1]:
self.path = path[:]
return
for d in [[0, 1], [0, -1], [1, 0], [-1, 0]]:
row_, col_ = path[-1][0] + d[0], path[-1][1] + d[1]
if row_ > 0 and row_ < self.height - 1 and col_ > 0 and col_ < self.width and visited[row_][col_] == 0 and self.matrix[row_][col_] == 0:
dfs(path + [[row_, col_]])
dfs([[self.start[0], self.start[1]]])
if __name__ == '__main__':
maze = Maze(51, 51)
maze.generate_matrix_kruskal()
maze.print_matrix()
maze.find_path_dfs(maze.destination)
print("answer", maze.path)
maze.print_matrix()
迷宫可视化源码 maze.py:
import tkinter as tk
from mazeGenerator import Maze
import time
import copy
import numpy as np
import math
import threading
def draw_cell(canvas, row, col, color="#F2F2F2"):
x0, y0 = col * cell_width, row * cell_width
x1, y1 = x0 + cell_width, y0 + cell_width
canvas.create_rectangle(x0, y0, x1, y1, fill = color, outline =color, width = 0)
def draw_path(canvas, matrix, row, col, color, line_color):
# 列
if row + 1 < rows and matrix[row - 1][col] >= 1 and matrix[row + 1][col] >= 1:
x0, y0 = col * cell_width + 2 * cell_width / 5, row * cell_width
x1, y1 = x0 + cell_width / 5, y0 + cell_width
# 行
elif col + 1 < cols and matrix[row][col - 1] >= 1 and matrix[row][col + 1] >= 1:
x0, y0 = col * cell_width, row * cell_width + 2 * cell_width / 5
x1, y1 = x0 + cell_width, y0 + cell_width / 5
# 左上角
elif col + 1 < cols and row + 1 < rows and matrix[row][col + 1] >= 1 and matrix[row + 1][col] >= 1:
x0, y0 = col * cell_width + 2 * cell_width / 5, row * cell_width + 2 * cell_width / 5
x1, y1 = x0 + 3 * cell_width / 5, y0 + cell_width / 5
canvas.create_rectangle(x0, y0, x1, y1, fill = color, outline = line_color, width = 0)
x0, y0 = col * cell_width + 2 * cell_width / 5, row * cell_width + 2 * cell_width / 5
x1, y1 = x0 + cell_width / 5, y0 + 3 * cell_width / 5
# 右上角
elif row + 1 < rows and matrix[row][col - 1] >= 1 and matrix[row + 1][col] >= 1:
x0, y0 = col * cell_width, row * cell_width + 2 * cell_width / 5
x1, y1 = x0 + 3 * cell_width / 5, y0 + cell_width / 5
canvas.create_rectangle(x0, y0, x1, y1, fill = color, outline = line_color, width = 0)
x0, y0 = col * cell_width + 2 * cell_width / 5, row * cell_width + 2 * cell_width / 5
x1, y1 = x0 + cell_width / 5, y0 + 3 * cell_width / 5
# 左下角
elif col + 1 < cols and matrix[row - 1][col] >= 1 and matrix[row][col + 1] >= 1:
x0, y0 = col * cell_width + 2 * cell_width / 5, row * cell_width
x1, y1 = x0 + cell_width / 5, y0 + 3 * cell_width / 5
canvas.create_rectangle(x0, y0, x1, y1, fill = color, outline = line_color, width = 0)
x0, y0 = col * cell_width + 2 * cell_width / 5, row * cell_width + 2 * cell_width / 5
x1, y1 = x0 + 3 * cell_width / 5, y0 + cell_width / 5
# 右下角
elif matrix[row - 1][col] >= 1 and matrix[row][col - 1] >= 1:
x0, y0 = col * cell_width, row * cell_width + 2 * cell_width / 5
x1, y1 = x0 + 3 * cell_width / 5, y0 + cell_width / 5
canvas.create_rectangle(x0, y0, x1, y1, fill = color, outline = line_color, width = 0)
x0, y0 = col * cell_width + 2 * cell_width / 5, row * cell_width
x1, y1 = x0 + cell_width / 5, y0 + 3 * cell_width / 5
else:
x0, y0 = col * cell_width + 2 * cell_width / 5, row * cell_width + 2 * cell_width / 5
x1, y1 = x0 + cell_width / 5, y0 + cell_width / 5
canvas.create_rectangle(x0, y0, x1, y1, fill = color, outline = line_color, width = 0)
def draw_maze(canvas, matrix, path, moves):
"""
根据matrix中每个位置的值绘图:
-1: 墙壁
0: 空白
1: 参考路径
2: 移动过的位置
"""
for r in range(rows):
for c in range(cols):
if matrix[r][c] == 0:
draw_cell(canvas, r, c)
elif matrix[r][c] == -1:
draw_cell(canvas, r, c, '#525288')
elif matrix[r][c] == 1:
draw_cell(canvas, r, c)
draw_path(canvas, matrix, r, c, '#bc84a8', '#bc84a8')
elif matrix[r][c] == 2:
draw_cell(canvas, r, c)
draw_path(canvas, matrix, r, c, '#ee3f4d', '#ee3f4d')
for p in path:
matrix[p[0]][p[1]] = 1
for move in moves:
matrix[move[0]][move[1]] = 2
def update_maze(canvas, matrix, path, moves):
canvas.delete("all")
matrix = copy.copy(matrix)
for p in path:
matrix[p[0]][p[1]] = 1
for move in moves:
matrix[move[0]][move[1]] = 2
row, col = movement_list[-1]
colors = ['#525288', '#F2F2F2', '#525288', '#F2F2F2', '#525288', '#F2F2F2', '#525288', '#F2F2F2']
if level > 2:
colors = ['#232323', '#252525', '#2a2a32', '#424242', '#434368', '#b4b4b4', '#525288', '#F2F2F2']
for r in range(rows):
for c in range(cols):
distance = (row - r) * (row - r) + (col - c) * (col - c)
if distance >= 100:
color = colors[0:2]
elif distance >= 60:
color = colors[2:4]
elif distance >= 30:
color = colors[4:6]
else:
color = colors[6:8]
if matrix[r][c] == 0:
draw_cell(canvas, r, c, color[1])
elif matrix[r][c] == -1:
draw_cell(canvas, r, c, color[0])
elif matrix[r][c] == 1:
draw_cell(canvas, r, c, color[1])
draw_path(canvas, matrix, r, c, '#bc84a8', '#bc84a8')
elif matrix[r][c] == 2:
draw_cell(canvas, r, c, color[1])
draw_path(canvas, matrix, r, c, '#ee3f4d', '#ee3f4d')
def check_reach():
global next_maze_flag
if movement_list[-1] == maze.destination:
print("Congratulations! You reach the goal! The step used: {}".format(click_counter))
x0, y0 = width / 2 - 200, 30
x1, y1 = x0 + 400, y0 + 40
canvas.create_rectangle(x0, y0, x1, y1, fill = '#F2F2F2', outline ='#525288', width = 3)
canvas.create_text(width / 2, y0 + 20, text = "Congratulations! You reach the goal! Steps used: {}".format(click_counter), fill = "#525288")
next_maze_flag = True
def _eventHandler(event):
global movement_list
global click_counter
global next_maze_flag
global level
if not next_maze_flag and event.keysym in ['Left', 'Right', 'Up', 'Down']:
click_counter += 1
windows.title("Maze Level-{} Steps-{}".format(level, click_counter))
cur_pos = movement_list[-1]
ops = {'Left': [0, -1], 'Right': [0, 1], 'Up': [-1, 0], 'Down': [1, 0]}
r_, c_ = cur_pos[0] + ops[event.keysym][0], cur_pos[1] + ops[event.keysym][1]
if len(movement_list) > 1 and [r_, c_] == movement_list[-2]:
movement_list.pop()
while True:
cur_pos = movement_list[-1]
counter = 0
for d in [[0, 1], [0, -1], [1, 0], [-1, 0]]:
r_, c_ = cur_pos[0] + d[0], cur_pos[1] + d[1]
if c_ >= 0 and maze.matrix[r_][c_] == 0:
counter += 1
if counter != 2:
break
movement_list.pop()
elif r_ < maze.height and c_ < maze.width and maze.matrix[r_][c_] == 0:
while True:
movement_list.append([r_, c_])
temp_list = []
for d in [[0, 1], [0, -1], [1, 0], [-1, 0]]:
r__, c__ = r_ + d[0], c_ + d[1]
if c__ < maze.width and maze.matrix[r__][c__] == 0 and [r__, c__] != cur_pos:
temp_list.append([r__, c__])
if len(temp_list) != 1:
break
cur_pos = [r_, c_]
r_, c_ = temp_list[0]
update_maze(canvas, maze.matrix, maze.path, movement_list)
check_reach()
elif next_maze_flag:
next_maze_flag = False
movement_list = [maze.start]
click_counter = 0
maze.generate_matrix_kruskal()
maze.path = []
draw_maze(canvas, maze.matrix, maze.path, movement_list)
level += 1
def _paint(event):
x, y = math.floor((event.y - 1) / cell_width), math.floor((event.x - 1) / cell_width)
if maze.matrix[x][y] == 0:
maze.find_path_dfs([x, y])
update_maze(canvas, maze.matrix, maze.path, movement_list)
def _reset(event):
maze.path = []
update_maze(canvas, maze.matrix, maze.path, movement_list)
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 基础参数
cell_width = 20
rows = 37
cols = 51
height = cell_width * rows
width = cell_width * cols
level = 1
click_counter = 0
next_maze_flag = False
windows = tk.Tk()
windows.title("Maze")
canvas = tk.Canvas(windows, background="#F2F2F2", width = width, height = height)
canvas.pack()
maze = Maze(cols, rows)
movement_list = [maze.start]
maze.generate_matrix_kruskal()
draw_maze(canvas, maze.matrix, maze.path, movement_list)
canvas.bind("<Button-1>", _paint)
canvas.bind("<Button-3>", _reset)
canvas.bind_all("<KeyPress>", _eventHandler)
windows.mainloop()
将以上两个代码分别保存到mazeGenerator.py 和maze.py,确保两个py文件在同一文件夹下,运行maze.py即可。
(暂时 完)
