package main
import (
"fmt"
"errors"
)
//使用数组来模拟一个栈的使用
type Stack struct {
MaxTop int // 表示我们栈最大可以存放数个数
Top int // 表示栈顶, 因为栈顶固定,因此我们直接使用Top
arr [5]int // 数组模拟栈
}
//入栈
func (this *Stack) Push(val int) (err error) {
//先判断栈是否满了
if this.Top == this.MaxTop-1 {
fmt.Println("stack full")
return errors.New("stack full")
}
this.Top++
//放入数据
this.arr[this.Top] = val
return
}
//出栈
func (this *Stack) Pop() (val int, err error) {
//判断栈是否空
if this.Top == -1 {
fmt.Println("stack empty!")
return 0, errors.New("stack empty")
}
//先取值,再 this.Top--
val = this.arr[this.Top]
this.Top--
return val, nil
}
//遍历栈,注意需要从栈顶开始遍历
func (this *Stack) List() {
//先判断栈是否为空
if this.Top == -1 {
fmt.Println("stack empty")
return
}
fmt.Println("栈的情况如下:")
for i := this.Top; i >= 0; i-- {
fmt.Printf("arr[%d]=%d\n", i, this.arr[i])
}
}
func main() {
stack := &Stack{
MaxTop: 5, // 表示最多存放5个数到栈中
Top: -1, // 当栈顶为-1,表示栈为空
}
//入栈
stack.Push(1)
stack.Push(2)
stack.Push(3)
stack.Push(4)
stack.Push(5)
//显示
stack.List()
val, _ := stack.Pop()
fmt.Println("出栈val=", val) // 5
//显示
stack.List() //
fmt.Println()
val, _ = stack.Pop()
val, _ = stack.Pop()
val, _ = stack.Pop()
val, _ = stack.Pop()
val, _ = stack.Pop() // 出错
fmt.Println("出栈val=", val) // 5
//显示
stack.List() //
}
package main
import (
"fmt"
"errors"
"strconv"
)
//使用数组来模拟一个栈的使用
type Stack struct {
MaxTop int // 表示我们栈最大可以存放数个数
Top int // 表示栈顶, 因为栈顶固定,因此我们直接使用Top
arr [20]int // 数组模拟栈
}
//入栈
func (this *Stack) Push(val int) (err error) {
//先判断栈是否满了
if this.Top == this.MaxTop - 1 {
fmt.Println("stack full")
return errors.New("stack full")
}
this.Top++
//放入数据
this.arr[this.Top] = val
return
}
//出栈
func (this *Stack) Pop() (val int, err error) {
//判断栈是否空
if this.Top == -1 {
fmt.Println("stack empty!")
return 0, errors.New("stack empty")
}
//先取值,再 this.Top--
val = this.arr[this.Top]
this.Top--
return val, nil
}
//遍历栈,注意需要从栈顶开始遍历
func (this *Stack) List() {
//先判断栈是否为空
if this.Top == -1 {
fmt.Println("stack empty")
return
}
fmt.Println("栈的情况如下:")
for i := this.Top; i >= 0; i-- {
fmt.Printf("arr[%d]=%d\n", i, this.arr[i])
}
}
//判断一个字符是不是一个运算符[+, - , * , /]
func (this *Stack) IsOper(val int) bool {
if val == 42 || val == 43 || val == 45 || val == 47 {
return true
} else {
return false
}
}
//运算的方法
func (this *Stack) Cal(num1 int, num2 int, oper int) int{
res := 0
switch oper {
case 42 :
res = num2 * num1
case 43 :
res = num2 + num1
case 45 :
res = num2 - num1
case 47 :
res = num2 / num1
default :
fmt.Println("运算符错误.")
}
return res
}
//编写一个方法,返回某个运算符的优先级[程序员定义]
//[* / => 1 + - => 0]
func (this *Stack) Priority(oper int) int {
res := 0
if oper == 42 || oper == 47 {
res = 1
} else if oper == 43 || oper == 45 {
res = 0
}
return res
}
func main() {
//数栈
numStack := &Stack{
MaxTop : 20,
Top : -1,
}
//符号栈
operStack := &Stack{
MaxTop : 20,
Top : -1,
}
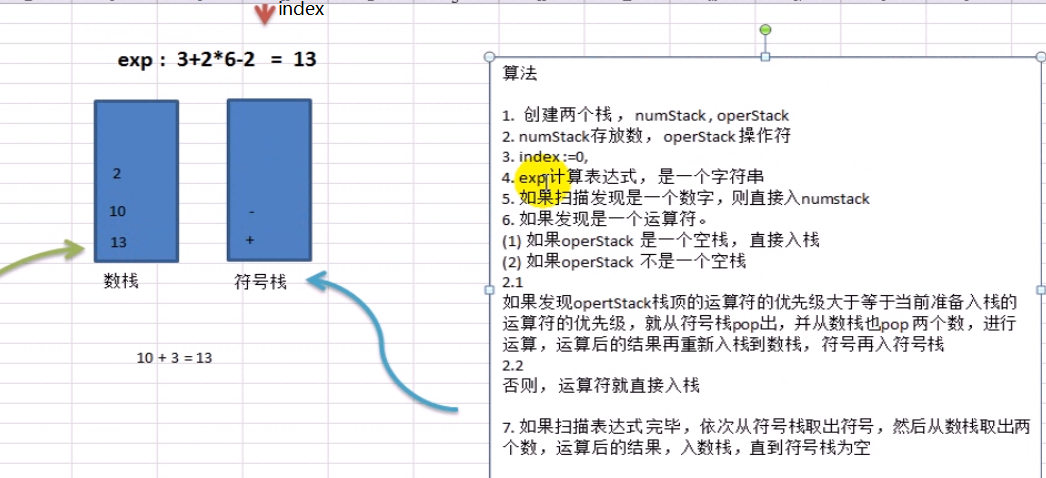
exp := "30+30*6-4-6"
//定义一个index ,帮助扫描exp
index := 0
//为了配合运算,我们定义需要的变量
num1 := 0
num2 := 0
oper := 0
result := 0
keepNum := ""
for {
//这里我们需要增加一个逻辑,
//处理多位数的问题
ch := exp[index:index+1] // 字符串.
//ch ==>"+" ===> 43
temp := int([]byte(ch)[0]) // 就是字符对应的ASCiI码
if operStack.IsOper(temp) { // 说明是符号
//如果operStack 是一个空栈, 直接入栈
if operStack.Top == -1 { //空栈
operStack.Push(temp)
}else {
//如果发现opertStack栈顶的运算符的优先级大于等于当前准备入栈的运算符的优先级
//,就从符号栈pop出,并从数栈也pop 两个数,进行运算,运算后的结果再重新入栈
//到数栈, 当前符号再入符号栈
if operStack.Priority(operStack.arr[operStack.Top]) >=
operStack.Priority(temp) {
num1, _ = numStack.Pop()
num2, _ = numStack.Pop()
oper, _ = operStack.Pop()
result = operStack.Cal(num1,num2, oper)
//将计算结果重新入数栈
numStack.Push(result)
//当前的符号压入符号栈
operStack.Push(temp)
}else {
operStack.Push(temp)
}
}
} else { //说明是数
//处理多位数的思路
//1.定义一个变量 keepNum string, 做拼接
keepNum += ch
//2.每次要向index的后面字符测试一下,看看是不是运算符,然后处理
//如果已经到表达最后,直接将 keepNum
if index == len(exp) - 1 {
val, _ := strconv.ParseInt(keepNum, 10, 64)
numStack.Push(int(val))
} else {
//向index 后面测试看看是不是运算符 [index]
if operStack.IsOper(int([]byte(exp[index+1:index+2])[0])) {
val, _ := strconv.ParseInt(keepNum, 10, 64)
numStack.Push(int(val))
keepNum = ""
}
}
}
//继续扫描
//先判断index是否已经扫描到计算表达式的最后
if index + 1 == len(exp) {
break
}
index++
}
//如果扫描表达式 完毕,依次从符号栈取出符号,然后从数栈取出两个数,
//运算后的结果,入数栈,直到符号栈为空
for {
if operStack.Top == -1 {
break //退出条件
}
num1, _ = numStack.Pop()
num2, _ = numStack.Pop()
oper, _ = operStack.Pop()
result = operStack.Cal(num1,num2, oper)
//将计算结果重新入数栈
numStack.Push(result)
}
//如果我们的算法没有问题,表达式也是正确的,则结果就是numStack最后数
res, _ := numStack.Pop()
fmt.Printf("表达式%s = %v", exp, res)
}