夜光序言:
有些痛,说不出来,就只能忍着直到慢慢淡忘。

正文:
以道御术 / 以术识道
下面我将精华梳理一下,主要涉及高并发






package 夜光第一部分;
//实现这个接口,并且重写方法
public class NewThread implements Runnable{
//run方法
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("线程启动了~~~");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//万物皆为对象
//new
// Thread thread = new Thread(); //创建了线程
Thread thread = new Thread(new NewThread()); //创建了线程,并且指定了线程任务
//下面启动线程
thread.start();
}
}

package 夜光第一部分;
public class NewThread01 implements Runnable{
//run方法
@Override
public void run() {
while(true){
System.out.println("自定义的线程执行了~~~");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//万物皆为对象
//new
// Thread thread = new Thread(); //创建了线程
Thread thread = new Thread(new NewThread()); //创建了线程,并且指定了线程任务
//下面启动线程
thread.start();
while (true){
System.out.println("主线程执行了~~");
}
}
}

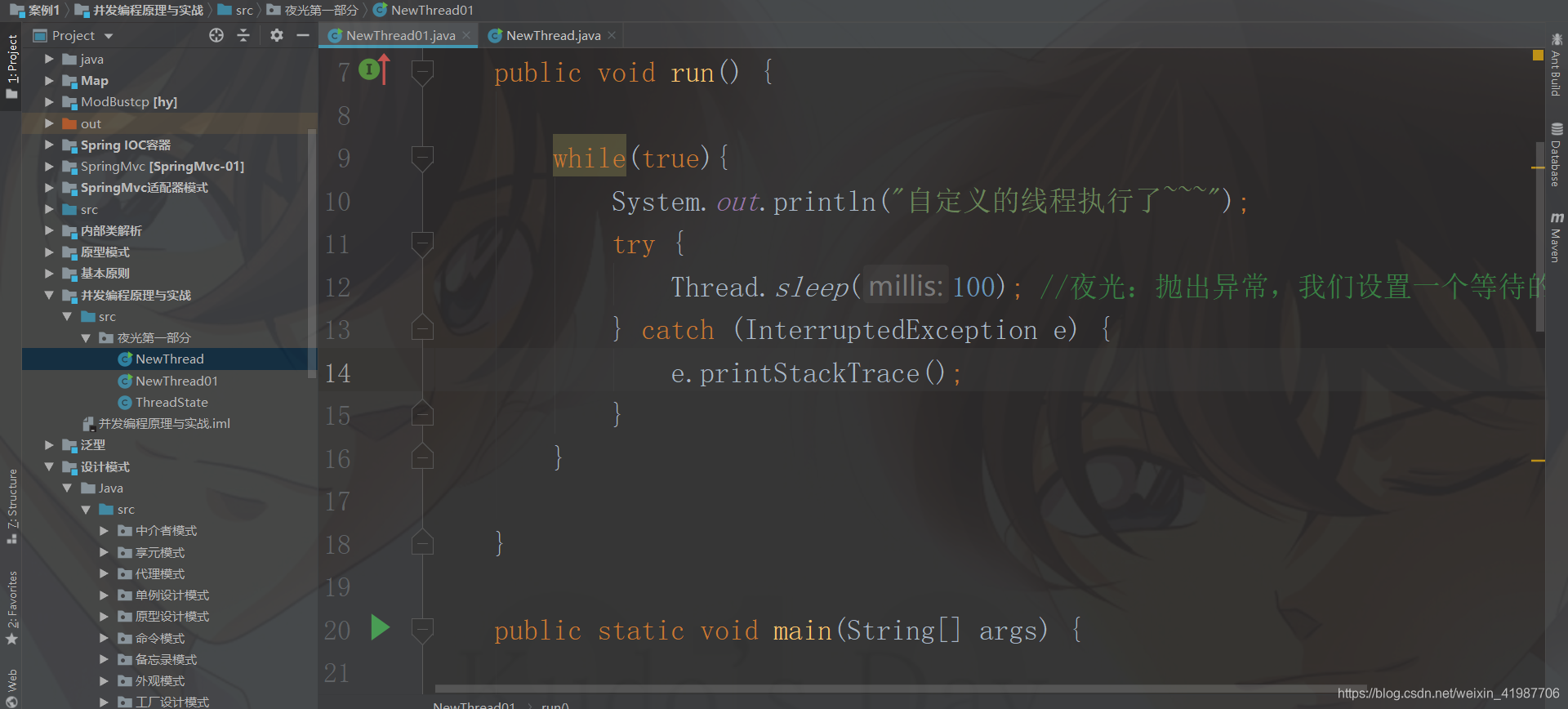
package 夜光第一部分;
public class NewThread01 implements Runnable{
//run方法
@Override
public void run() {
while(true){
System.out.println("自定义的线程执行了~~~");
try {
Thread.sleep(100); //夜光:抛出异常,我们设置一个等待的
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//万物皆为对象
//new
// Thread thread = new Thread(); //创建了线程
//下面这个就是所谓的初始化状态
Thread thread = new Thread(new NewThread()); //创建了线程,并且指定了线程任务
//下面启动线程
thread.start();
while (true){
System.out.println("主线程执行了~~");
try {
Thread.sleep(100); //夜光:抛出异常,我们设置一个等待的
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}

package 夜光第一部分;
public class NewThread02 implements Runnable {
//run方法
@Override
public void run(){
while(true){
try {
wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("自定义的线程执行了~~~");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
NewThread newThread = new NewThread();
//万物皆为对象
//new
// Thread thread = new Thread(); //创建了线程
//下面这个就是所谓的初始化状态
Thread thread = new Thread(newThread); //创建了线程,并且指定了线程任务
//下面启动线程
thread.start();
while (true){
System.out.println("主线程执行了~~");
try {
Thread.sleep(100); //夜光:抛出异常,我们设置一个等待的
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
newThread.notify();
}
}
}
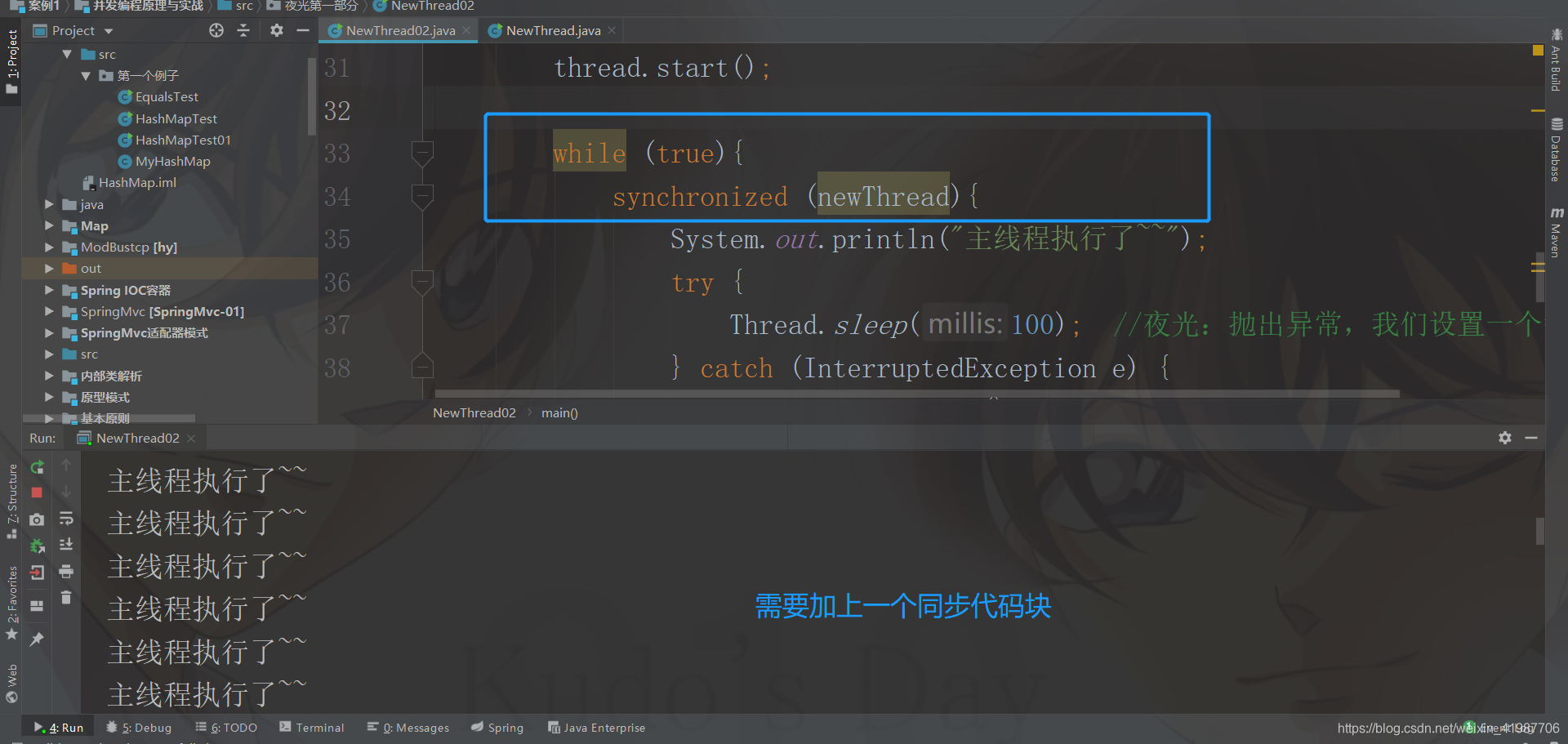
package 夜光第一部分;
public class NewThread02 implements Runnable {
//run方法
@Override
public synchronized void run(){ //这里需要加上一个同步监视器
while(true){
try {
wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("自定义的线程执行了~~~");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
NewThread02 newThread = new NewThread02();
//万物皆为对象
//new
// Thread thread = new Thread(); //创建了线程
//下面这个就是所谓的初始化状态
Thread thread = new Thread(newThread); //创建了线程,并且指定了线程任务
//下面启动线程
thread.start();
while (true){
synchronized (newThread){
System.out.println("主线程执行了~~");
try {
Thread.sleep(100); //夜光:抛出异常,我们设置一个等待的
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
newThread.notifyAll();
}
}
}
}




package 夜光第二部分.案例1;
//首先继承一下
public class Demo1 extends Thread {
public Demo1(String name) {
super(name);
}
//我们来重写一下run方法,夜光
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(getName() + "线程执行了~~");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Demo1 d1 = new Demo1("炎帝");
Demo1 d2 = new Demo1("雷帝");
d1.start();
d2.start();
}
}

